Temperature compensated RF circuitry
a technology of rf circuitry and rf, which is applied in the direction of transmission, transmission monitoring, electrical equipment, etc., can solve the problems of excessive loss of the typical, inexpensive coaxial transmission line between the radio and the antenna at these frequencies, waste of power, and further expense and power wastage, so as to improve the mounting arrangement and permit reliable operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
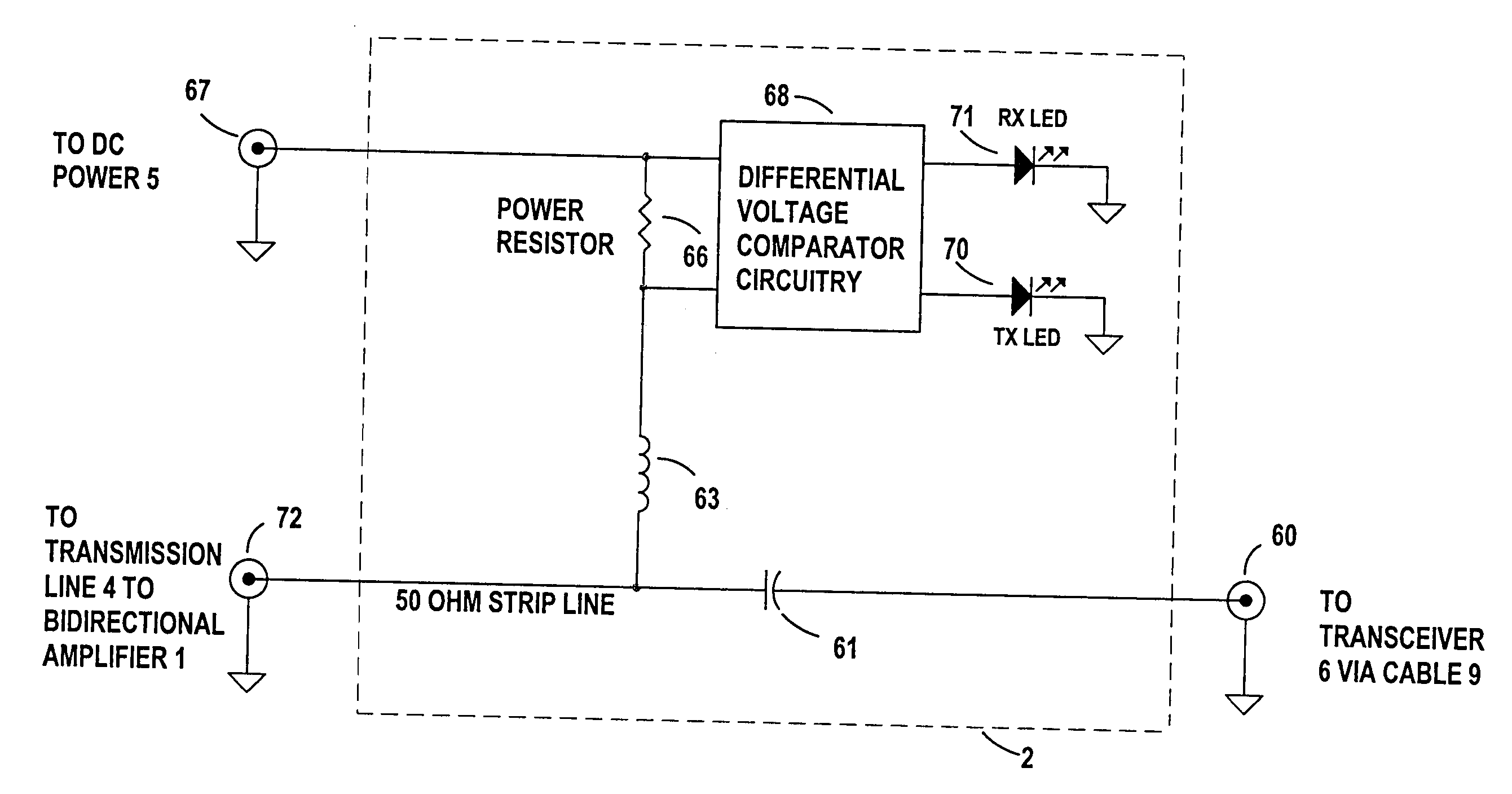
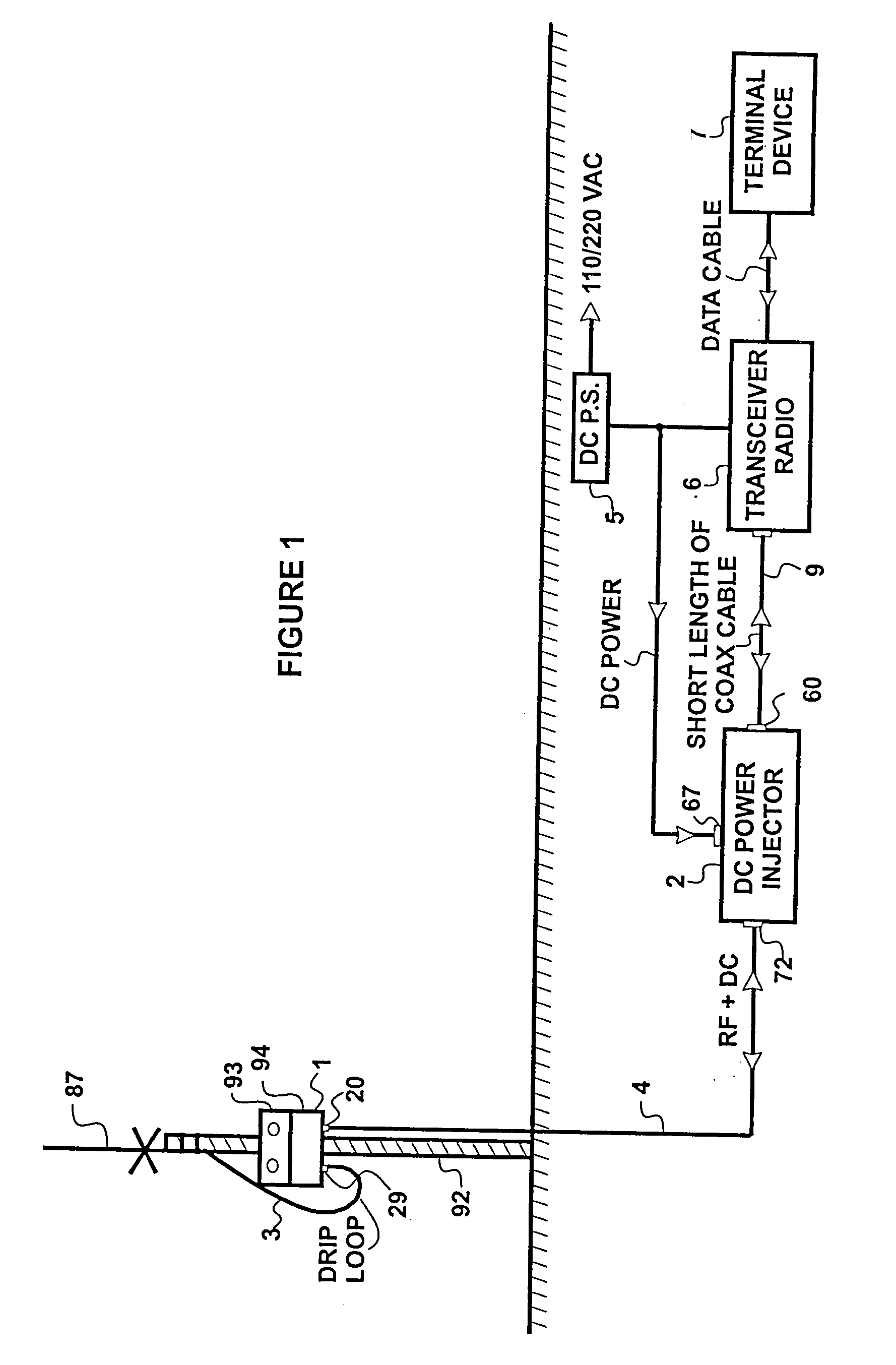
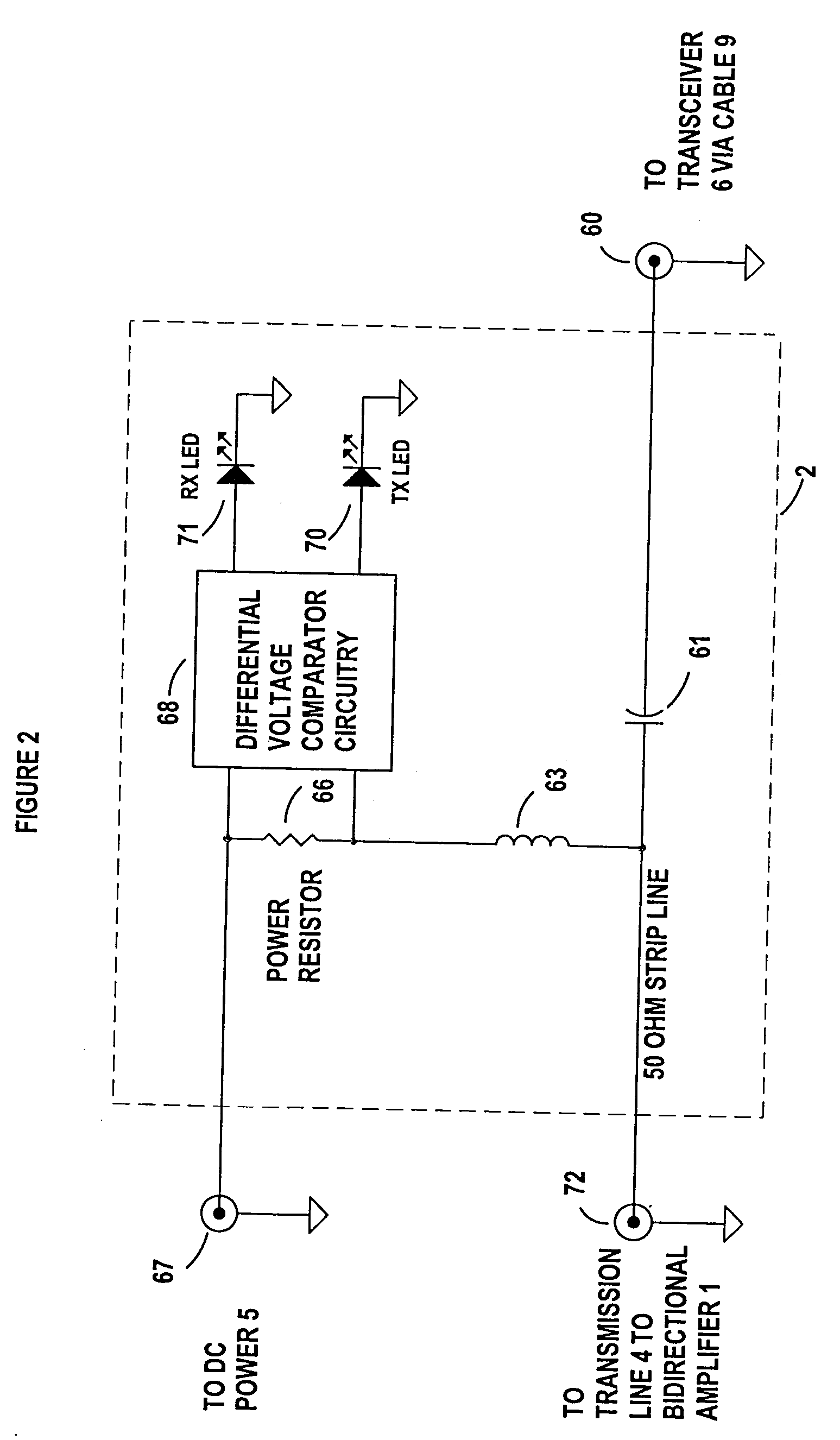
[0026]FIG. 1 show the remote bi-directional switching amplifier telecommunications system in a preferred typical installation. The bi-directional amplifier 1, inside the housing enclosure 94; the DC power input to the housing enclosure 94 from the DC power injector 2 supplied through connection 20, connection between the bi-directional switching amplifier I at 29 to the antenna 87 is made through a short length of inexpensive connecting cable 3 and the L-bracket 93 in conjunction with the mast 92 are the primary preferred components of the remote part of the system. The secondary components include a transmission line 4 connected to the housing enclosure 94 at 20, a DC Power Injector 2 preferably located remote from the bi-directional switching amplifier I housing 94, a DC Power Supply 5 which can be either DC or AC line operated, a radio transceiver 6, an appropriate computer, router or terminal device 7, and connecting cables between the various elements, such as 9 between the DC ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com