System and method for minimizing guard time in a time division duplex communication system
a communication system and time division technology, applied in the field of broadband radio frequency communication systems and methods, can solve the problems of large physical distances between information communication systems of processor-based systems, such as local area networks (lans) and other general purpose computers, and the inability to integrate such systems, and the choice available to bridge the physical gap between such systems has not only been limited, and the trade-offs between cost, performance and reliability are numerous, so as to achieve the effect of optimizing the use of the available spectrum
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
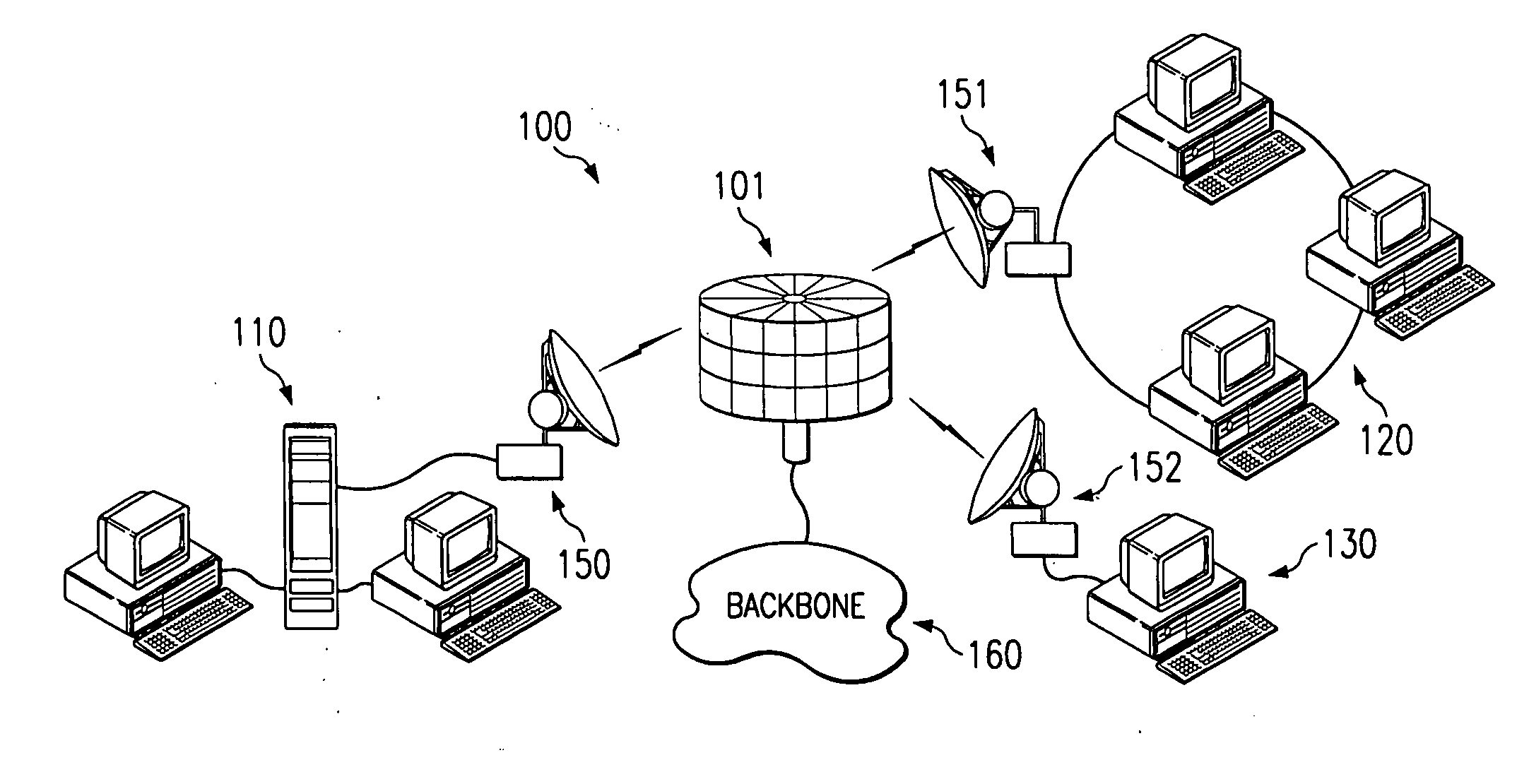
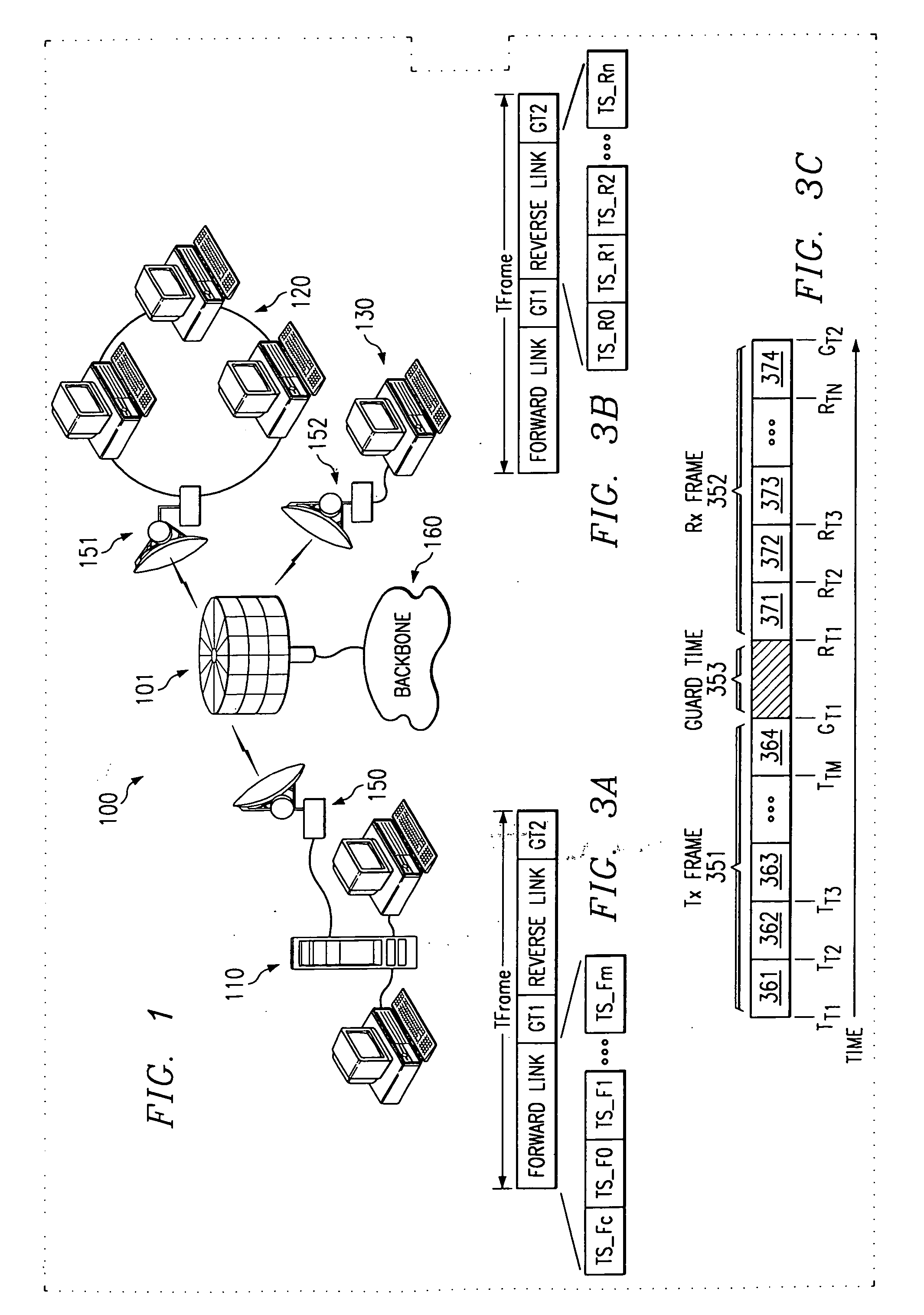
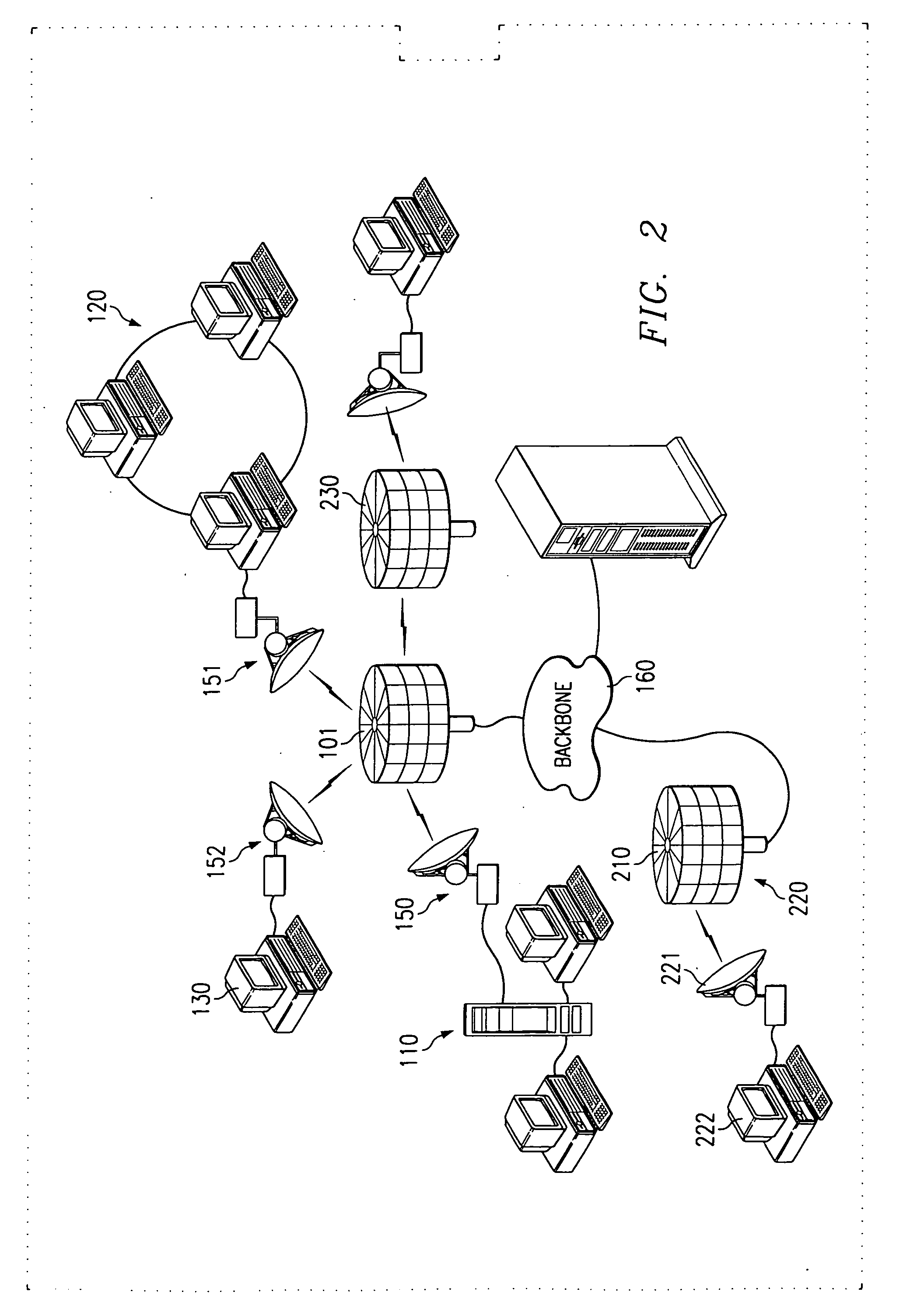
[0035] The present invention provides high speed data communication via an air interface allowing data access to and from subscriber's remotely located systems. Referring to FIG. 1, it can be seen that such wireless communication may be utilized, for example, to provide high speed bridging of a physical gap between a plurality of processor-based systems, as illustrated by system 100. The processor-based systems may include local area networks (LAN), such as LANs 110 and 120, or individual computer systems, such as PC 130. It shall be appreciated that the processor-based systems utilizing the present invention may be general purpose computers, both standing alone and interconnected such as by a LAN. Furthermore, the system can connect other communication systems such as voice or video in combination with, or in place of, communication sourced by the above mentioned processor-based systems.
[0036] Systems bridged by the present invention may utilize a communication device, hereinafter...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com