Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
a semiconductor and liquid crystal display technology, applied in the direction of optics, instruments, electrical equipment, etc., can solve the problems of disturbing the display picture, affecting the efficiency of light utility, and affecting the effect of brightness, etc., and achieve excellent effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
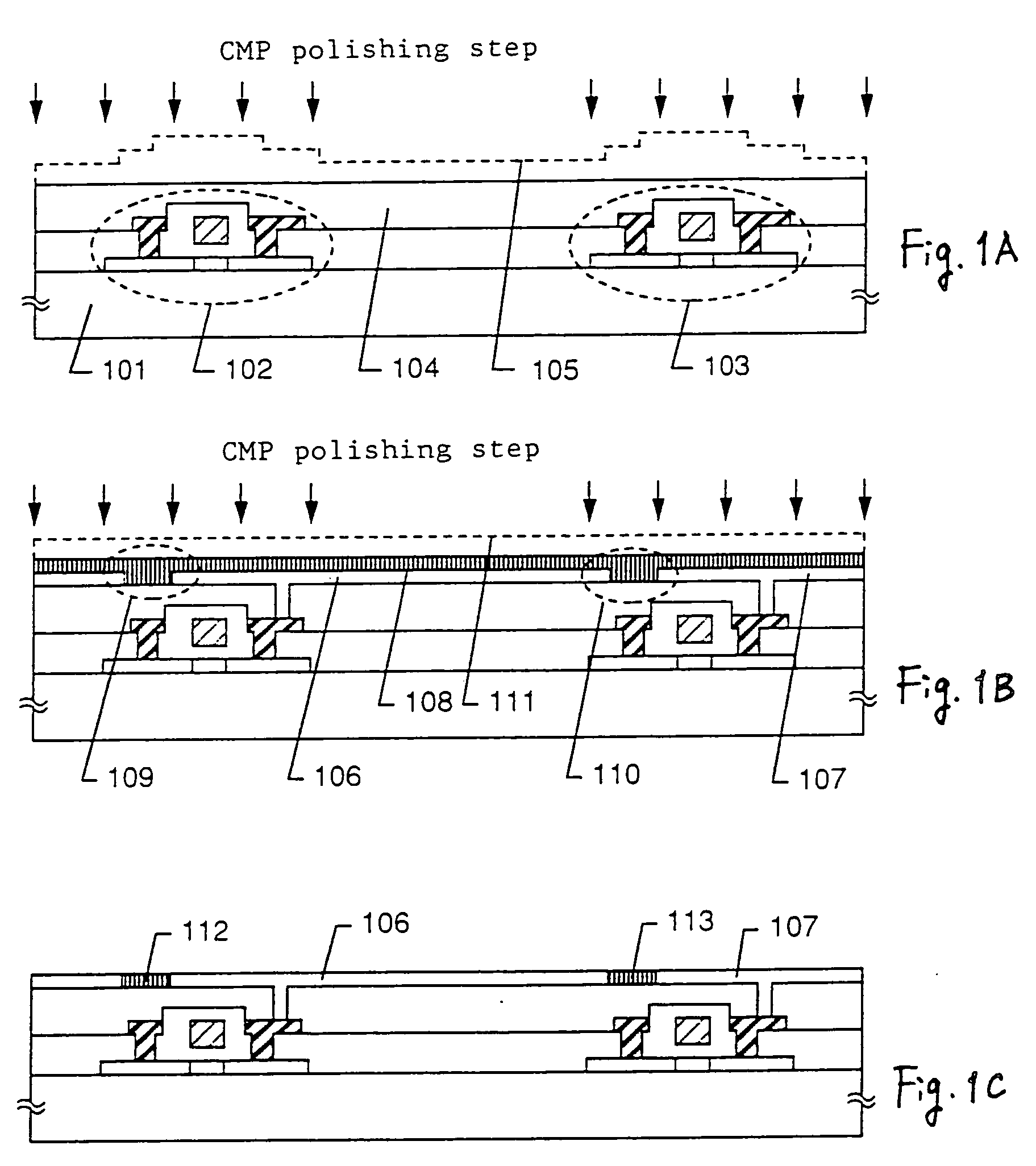
[0060] In this embodiment, an example of steps of manufacturing a pixel matrix circuit of a reflection type LCD using the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS. 3 and 4. Since the present invention relates to a technique for flattening a pixel, a TFT structure itself is not limited to this embodiment.
[0061] First, a substrate 301 having an insulating surface is prepared. In this embodiment, a silicon oxide film as an under layer is formed on the glass substrate. Active layers 302 to 304 made of crystalline silicon films are formed on the substrate 301. In this embodiment, although only three TFTs are shown, actually a million TFTs or more are formed in a pixel matrix circuit.
[0062] In this embodiment, an amorphous silicon film is thermally crystallized to obtain a crystalline silicon film. The crystalline silicon film is patterned by a normal photolithography step to obtain the active layers 302 to 304. In this embodiment, a catalytic element (nickel) for prom...
embodiment 2
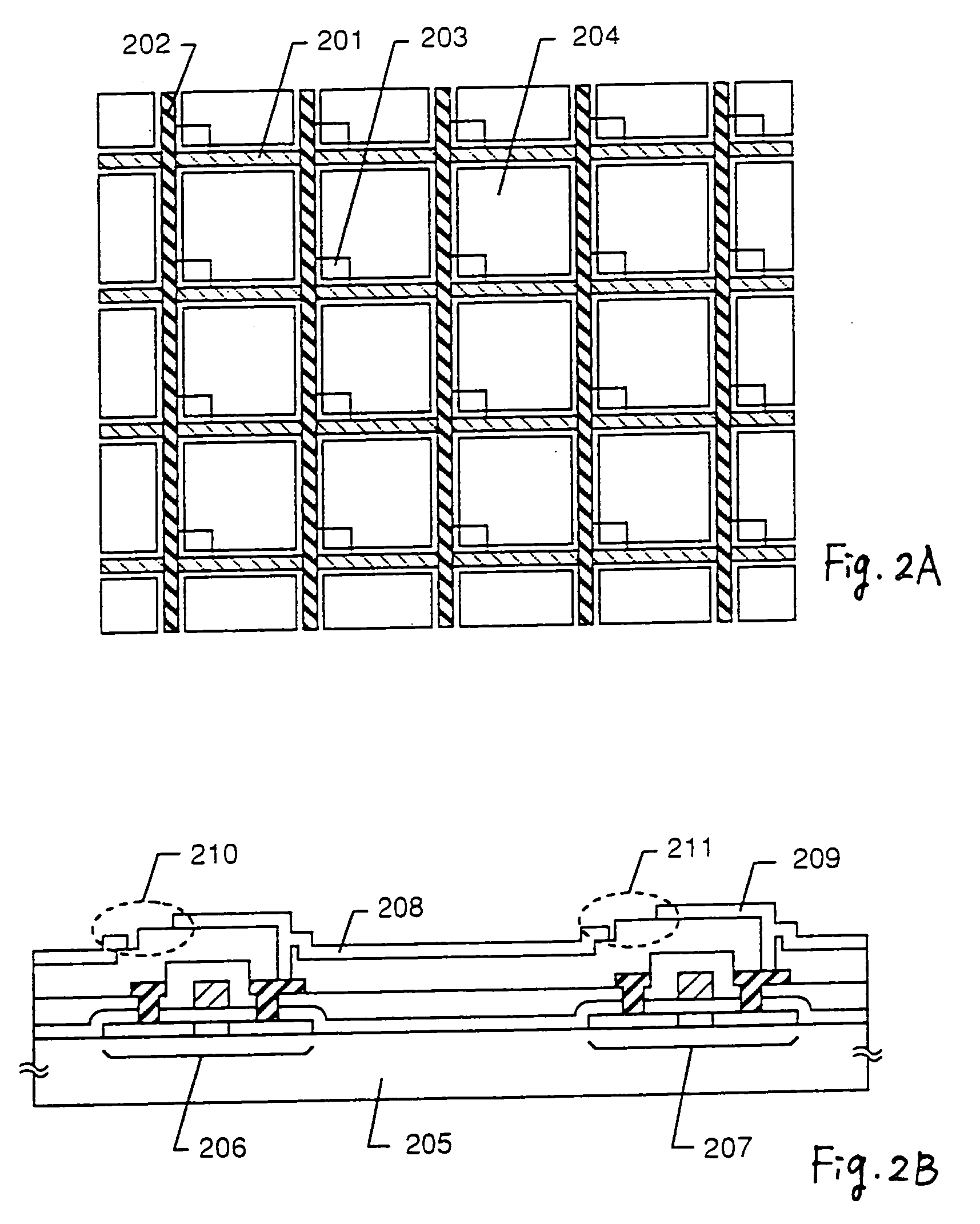
[0088] In this embodiment, an example of steps of manufacturing a pixel matrix circuit of a transmission type LCD by using the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS. 5A to 5C. Since the steps are the same as those of the reflection type LCD shown in the Embodiment 1 partway, only different points will be described here.
[0089] After the first CMP polishing step as shown in FIG. 3D is ended, pixel electrodes 501 and 502 shown in FIG. 5A are formed. In this embodiment, as the material for the pixel electrodes 501 and 502, transparent conductive films (ITO, SnO2, etc.) are used. At this time, the pixel electrodes 501 and 502 are formed so that they do not overlap with the TFTs.
[0090] Next, an insulating layer 503 covering the pixel electrodes 501 and 502 is formed. In this embodiment, for the insulating layer 503, polyimide with a dispersed black pigment or the like is used. In the case of the transmission type, since the active layer of the TFT is also required t...
embodiment 3
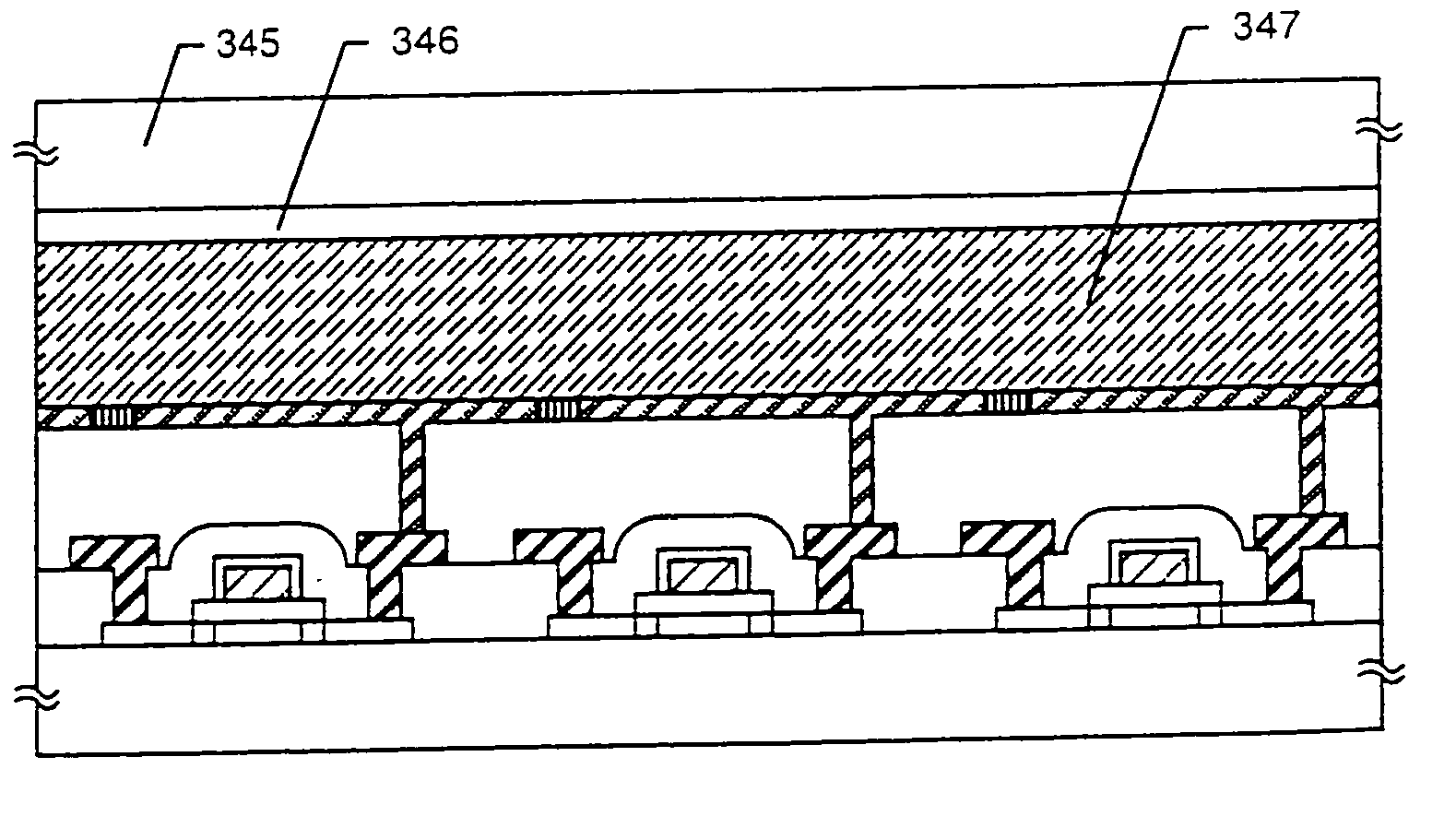
[0096] In the manufacturing steps of the embodiment 1, only the second interlayer insulating film 337 and the embedded insulating layer 341 are flattened. However, in the present invention, it is also possible to make a flattening step to the first interlayer insulating layer 330.
[0097] In the case where an interlayer insulating film is formed of a lamination structure, it is also possible to make a flattening step for every formation of the respective layers.
[0098] In the present invention, before pixel electrodes are formed, sufficient flatness is secured, and further, the gaps between the pixel electrodes are filled with the embedded insulating layers to improve the flatness of the surfaces of the pixel electrodes. Thus, there is no problem even if the number of flattening steps is large, rather it is preferable.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| flatness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com