RNA silencing in animals as an antiviral defense
a technology of rna silencing and animal body, applied in animal repellents, peptide sources, biocide, etc., can solve the problems of ineffective co-transfection with dsrnas targeting mrnas of the two i>drosophila /i>dicer genes, and achieve the effect of inhibiting the expression of a candidate gene, enhancing the antiviral rna silencing pathway, and treating or preventing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
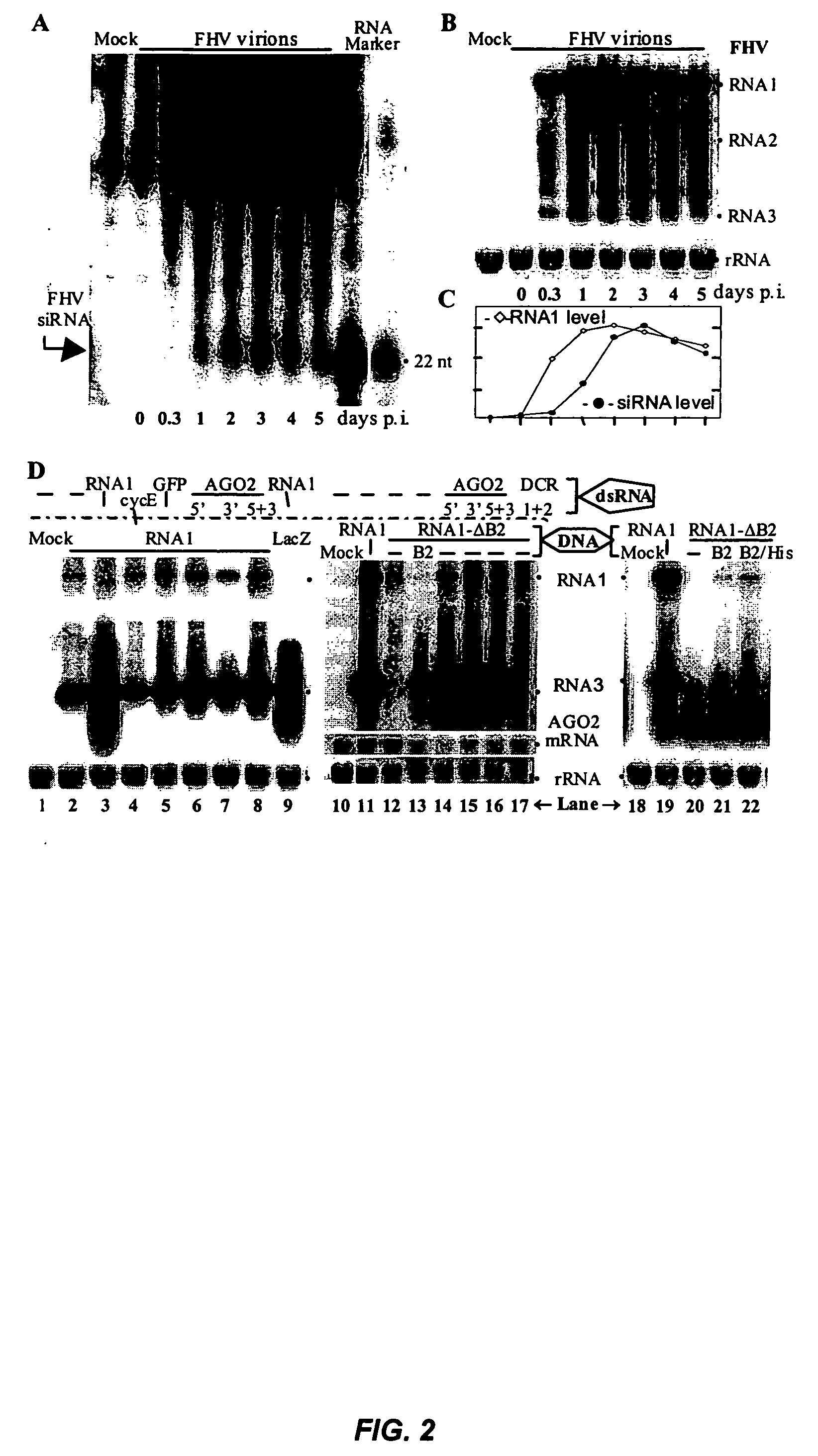
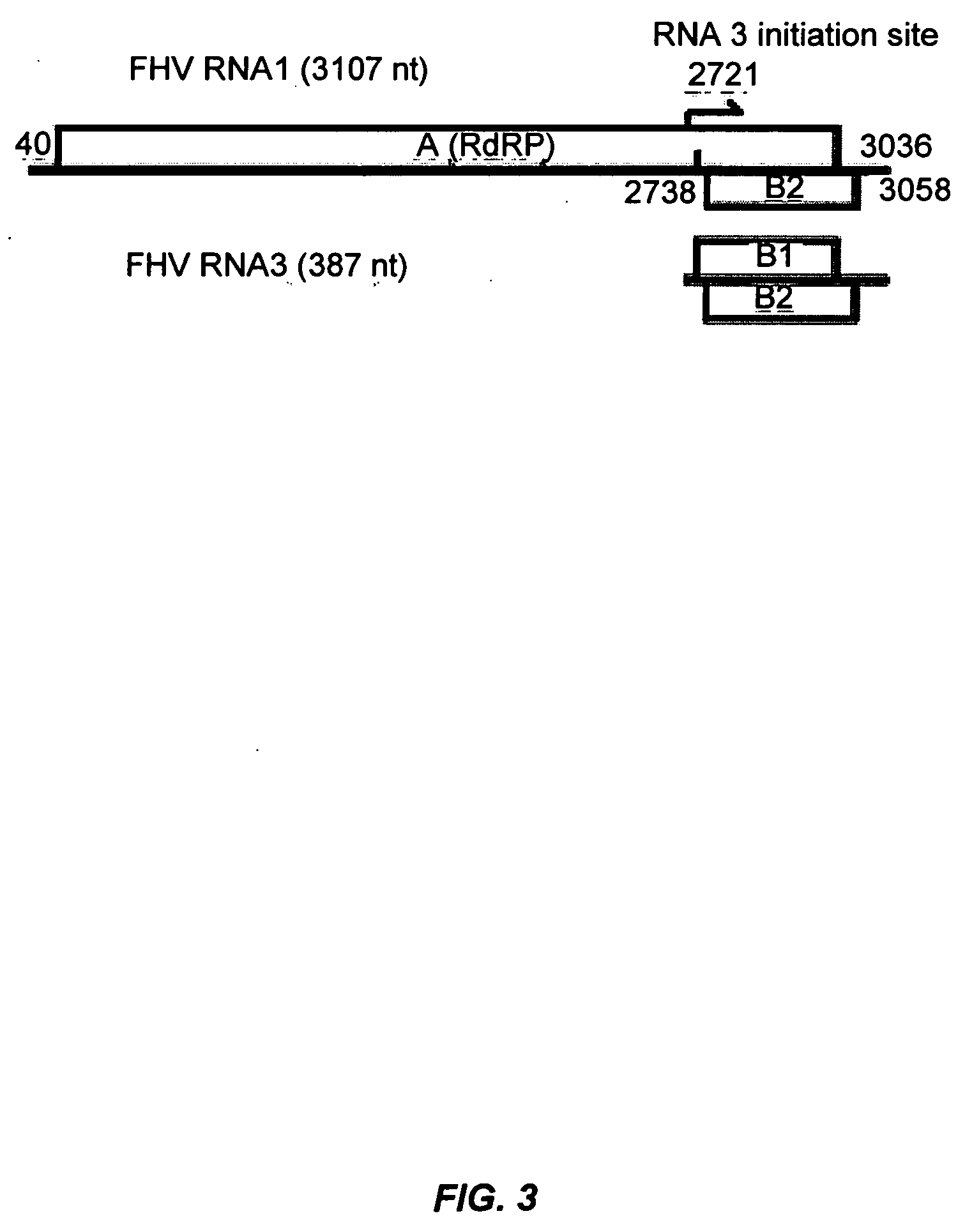
[0117] This example illustrates that RNA silencing is a natural antiviral defense mechanism in animals and that certain animal viruses encode RNA silencing suppressors to counter this defense mechanism.
Summary
[0118] RNA silencing is a sequence-specific RNA degradation mechanism that is operational in plants and animals. Here we show that flock house virus (FHV) is both an initiator and a target of RNA silencing in Drosophila host cells and that FHV infection requires suppression of RNA silencing by a FHV-encoded protein, B2. These findings establish RNA silencing as a novel adaptive antiviral defense in animal cells. B2 also inhibits RNA silencing in transgenic plants, providing evidence for a conserved RNA silencing pathway in the plant and animal kingdoms.
Background
[0119] Posttranscriptional gene silencing, quelling and RNA interference (RNAi) are mechanistically related RNA silencing processes that destroy RNA in a sequence-specific manner (D. Baulcombe, Curr. Biol., 12:R83...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com