Flexible wiring substrate, semiconductor device and electronic device using flexible wiring substrate, and fabricating method of flexible wiring substrate
a technology of flexible wiring and wiring substrate, which is applied in the direction of printed circuit aspects, sustainable manufacturing/processing, final product manufacturing, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to realize in the actual tcp such a fine pitch of wiring pattern, difficult to form a wiring pattern having a pitch of less than 45 m, etc., to achieve good shape, improve mechanical strength of wiring pattern, reduce variation in thickness of wiring pattern (inner lead).
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
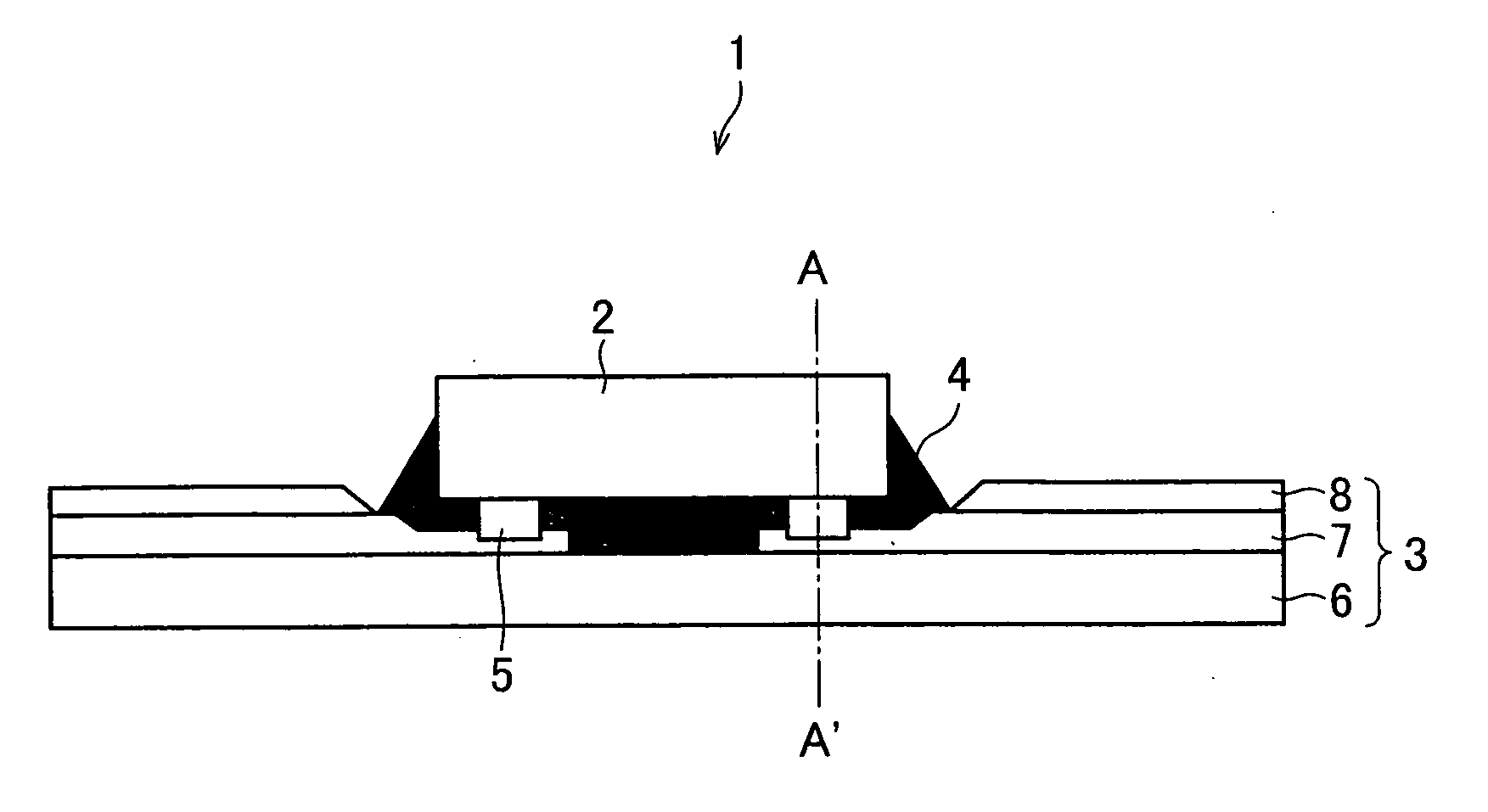
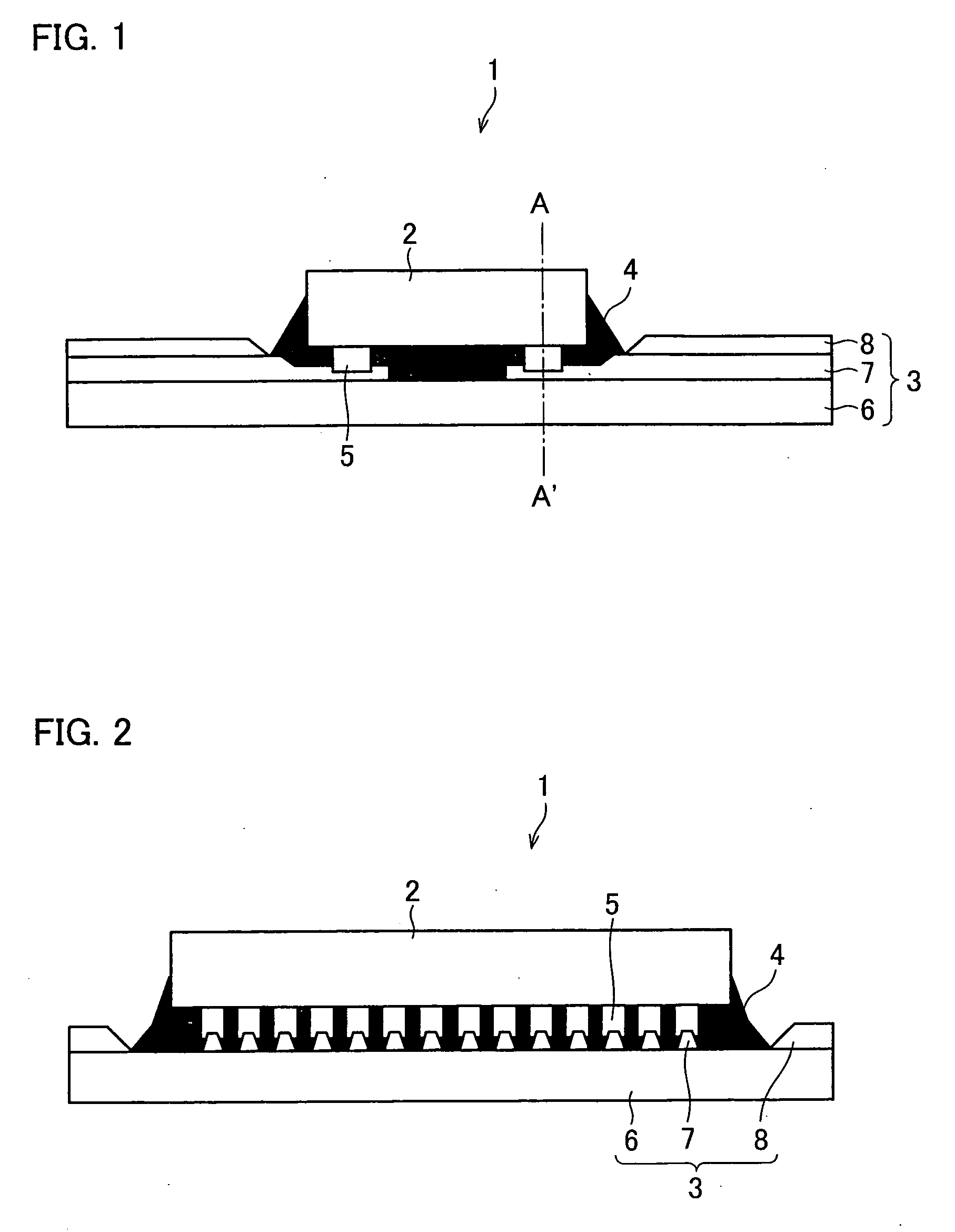
[0065] With reference to FIGS. 1 through 4(d), a first embodiment of the present invention is described below. FIG. 1 is a cross-sectional view schematically illustrating a structure of a semiconductor device of the present embodiment. Further, FIG. 2 is a cross-sectional view schematically illustrating the structure of the semiconductor device taken along line A-A′ of FIG. 1.
[0066] As illustrated in FIGS. 1 and 2, the semiconductor device 1 includes a semiconductor element (electronic component) 2 and a tape carrier (flexible wiring substrate) 3. The semiconductor element 2 is connected to the tape carrier 3. That is, the semiconductor element 2 is mounted on the tape carrier 3. Further, a gap between the tape carrier 3 and the semiconductor element 2 is sealed with an insulation resin 4. The present embodiment discusses, as an example, a COF-type semiconductor device having the above structure, in which the semiconductor element 2 is mounted on the tape carrier 3.
[0067] An examp...
second embodiment
[0093] With reference to FIGS. 1 through 3 and 5(d), a second embodiment of the present invention is described below. FIG. 1 is a cross-sectional view schematically illustrating a structure of a semiconductor device of the present embodiment. Further, FIG. 2 is a cross-sectional view schematically illustrating a structure of the semiconductor device taken along line A-A′ of FIG. 1.
[0094] As illustrated in FIG. 1, the semiconductor device 1 includes a semiconductor element 2 and a tape carrier 3. Compared to the first embodiment, the present embodiment describes a different fabricating method of the semiconductor device 1, though the structure of the semiconductor device 1 is the same. Thus, constituting elements having the same functions as those described in the first embodiment are indicated by the same reference numerals, and their explanations are omitted. In the present embodiment, the fabricating method of the semiconductor device 1 is mainly described. Further, the terms use...
third embodiment
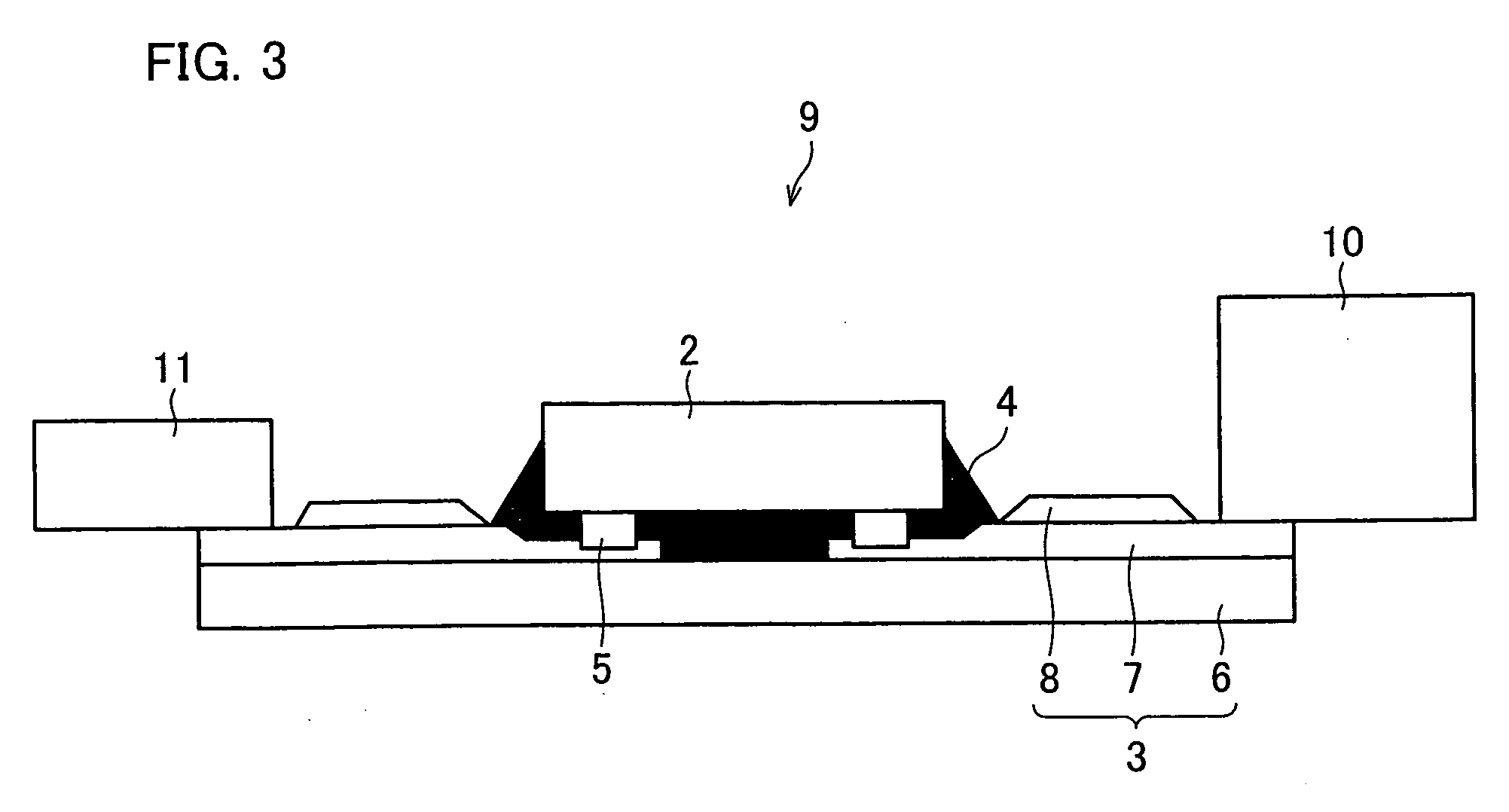
[0105] With reference to FIGS. 6 through 9(d), a third embodiment of the present invention is described below. FIG. 6 is a cross-sectional view schematically illustrating a structure of a semiconductor device of the present embodiment. Further, FIG. 7 is a cross-sectional view schematically illustrating a structure of the semiconductor device taken along line B-B′ of FIG. 6.
[0106] As illustrated in FIGS. 6 and 7, a semiconductor device 21 includes a semiconductor element 2 and a tape carrier (flexible wiring substrate) 23. The semiconductor element 2 is connected to and mounted on the tape carrier 23. Further, an insulation resin 4 is completely filled in a gap between the tape carrier 23 and the semiconductor element 2. The present embodiment discusses, as an example, a COF-type semiconductor apparatus having a structure in which the semiconductor element 2 is mounted on the tape carrier 23. Note that, constituting elements having the same functions as those described in the first...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com