Electronic camera video signal correcting device
a technology of video signal and electronic camera, which is applied in the direction of color television details, television system details, television systems, etc., can solve the problems of large number of dark-time white spots, inability to correctly shoot subjects, and inability to accurately shoot subjects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
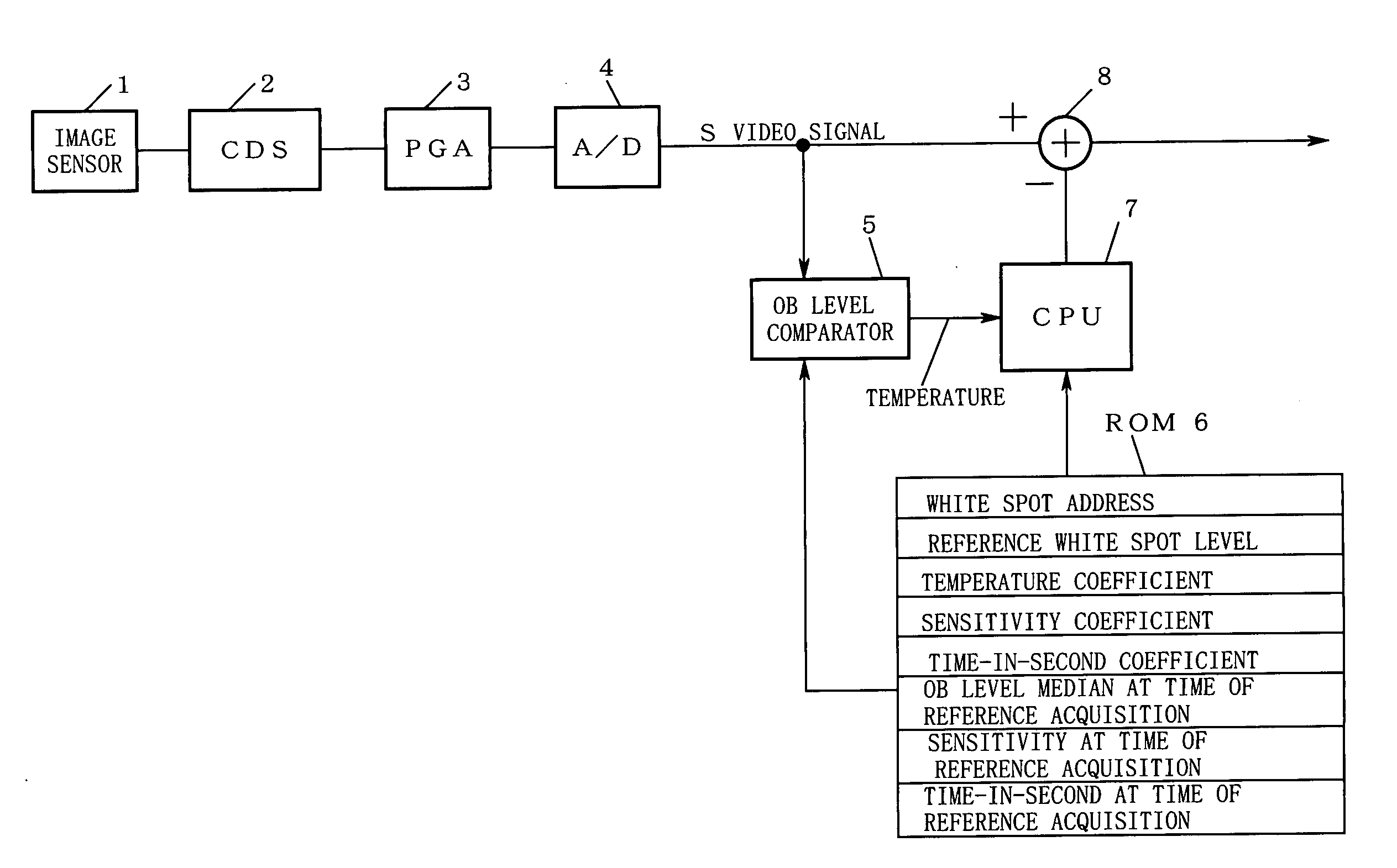
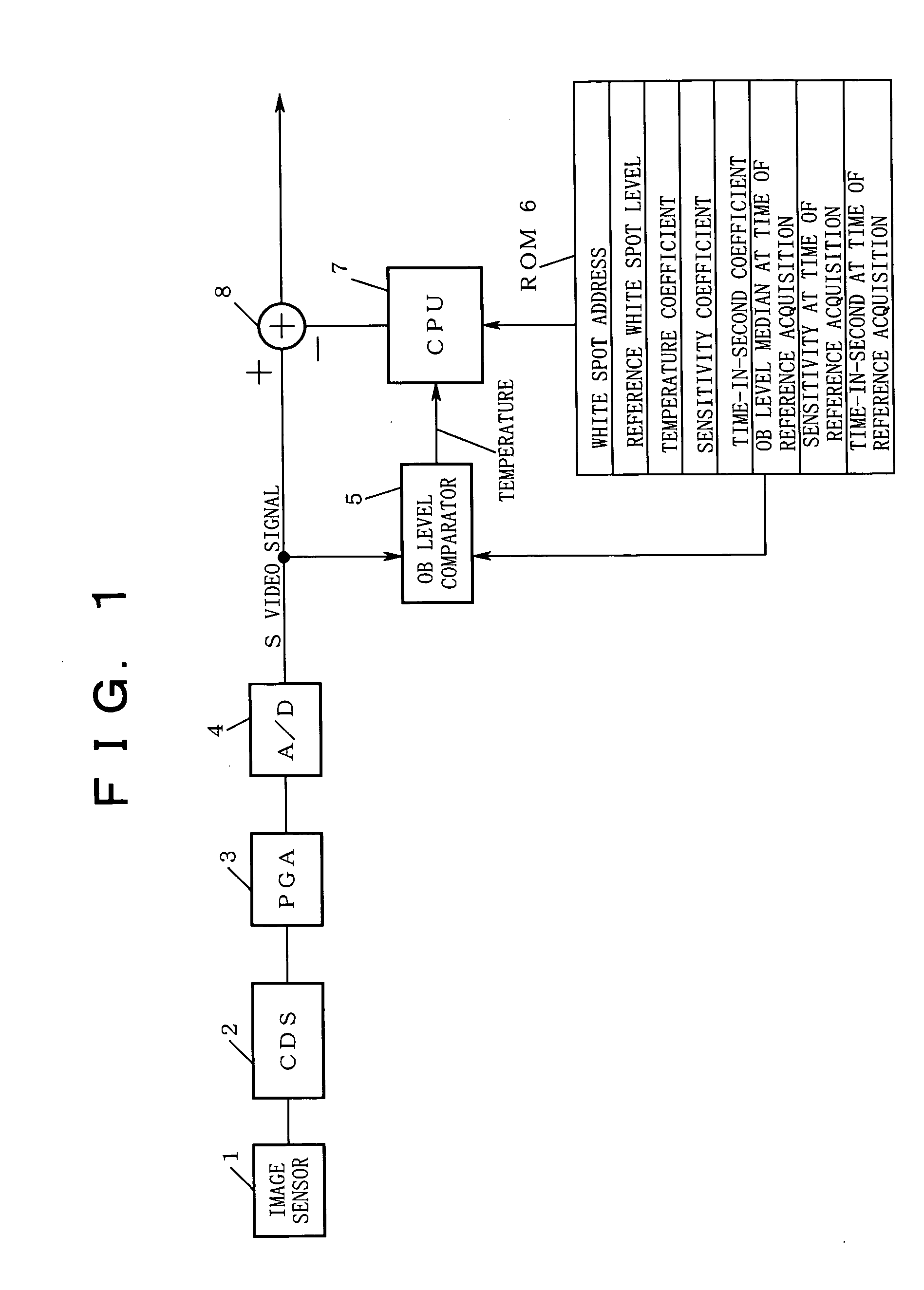
[0030]FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a first embodiment of the present invention.
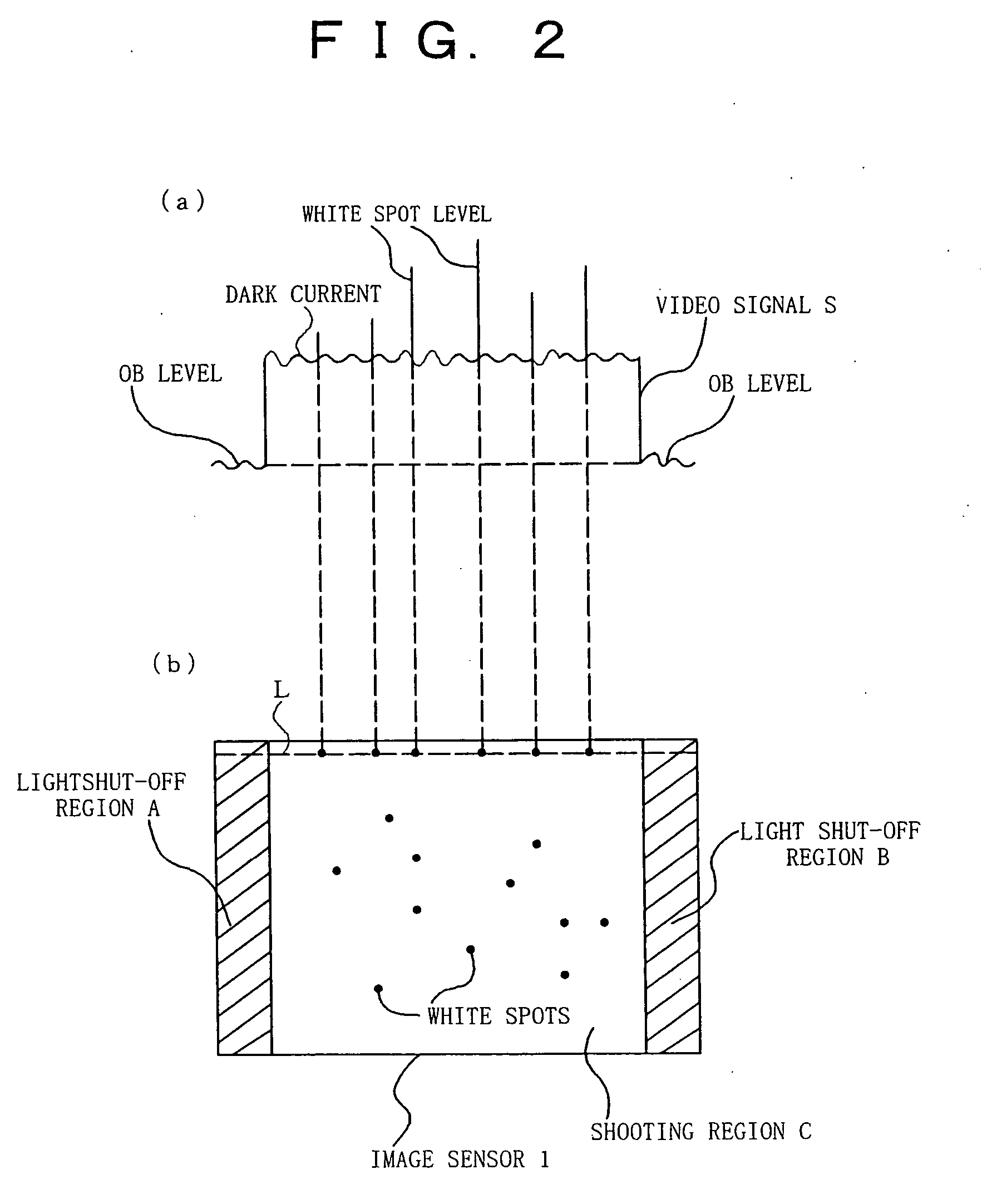
[0031] In FIG. 1, reference numeral 1 denotes an image sensor composed of, although not shown in the drawing, plural photodiodes, and CCDs in plural lines for transferring charges generated in each photodiode, etc. Reference numeral 2; a correlated double sampling (referred to as CDS in the figure) circuit, reference numeral 3; a programmable gain amplifier (referred to as PGA in the figure), reference numeral 4; an analog-to-digital converter (referred to as A / D in the figure), reference numeral 5; an optical black level comparator (referred to as OB level comparator in the figure), reference numeral 6; a ROM for storing various data, reference numeral 7; a CPU, and reference numeral 8; an adder.
[0032] Here, the image sensor 1 shoots a subject and outputs a shooting result as an electric signal. As well known, the correlated double sampling circuit 2 has a role to reduce low frequency noise from t...
second embodiment
[0067]FIG. 4 is a block diagram showing a second embodiment of the present invention. In the second embodiment shown in FIG. 4, the same parts as those in the first embodiment shown in FIG. 1 are assigned with the same symbols and the explanation thereof will be omitted.
[0068] The second embodiment differs from the first embodiment in that a temperature sensor 9 is provided instead of the OB level comparator 5 in the first embodiment, the reference dark current level median and the temperature at the time of acquisition of the reference are stored in the ROM 6, and the OB level median at the time of acquisition of the reference is not stored in the ROM 6.
[0069] Additionally, instead of the reference dark current level median, the reference dark current level average may be stored.
[0070] The operation in the second embodiment shown in FIG. 4 will be explained below.
[0071] (1) First, the electronic camera performs dark shooting and stores various data shown in the drawing in the R...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com