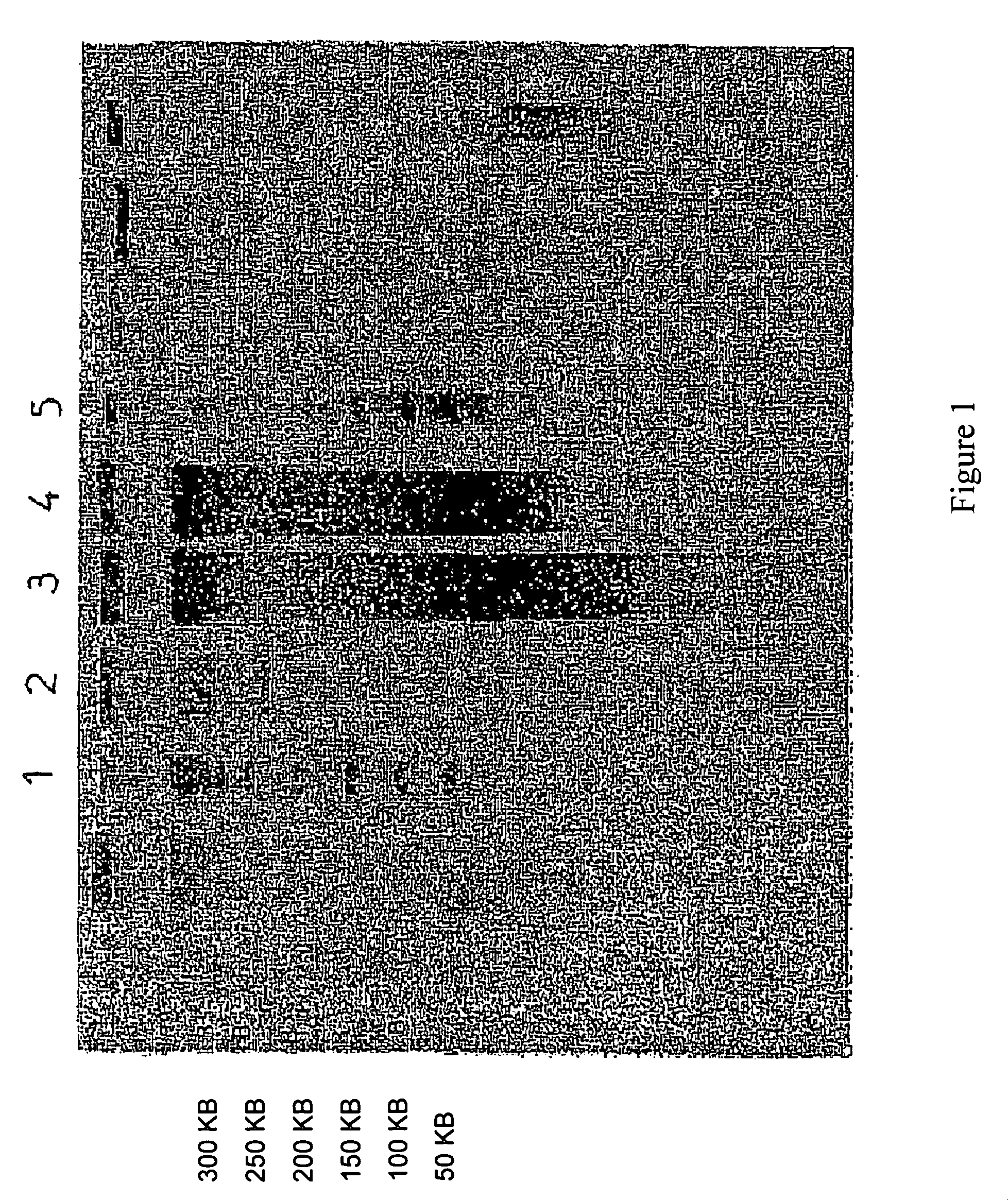
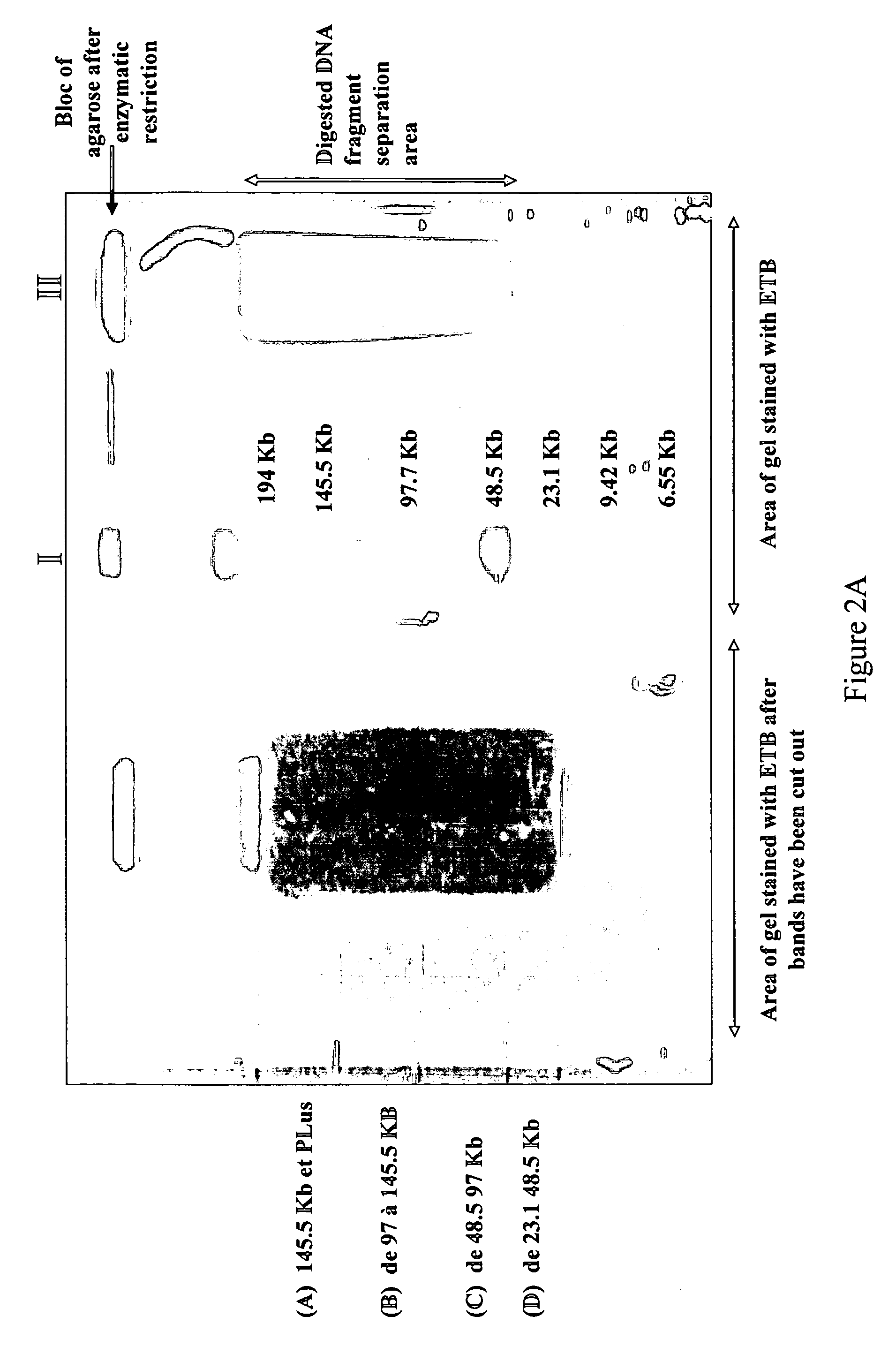
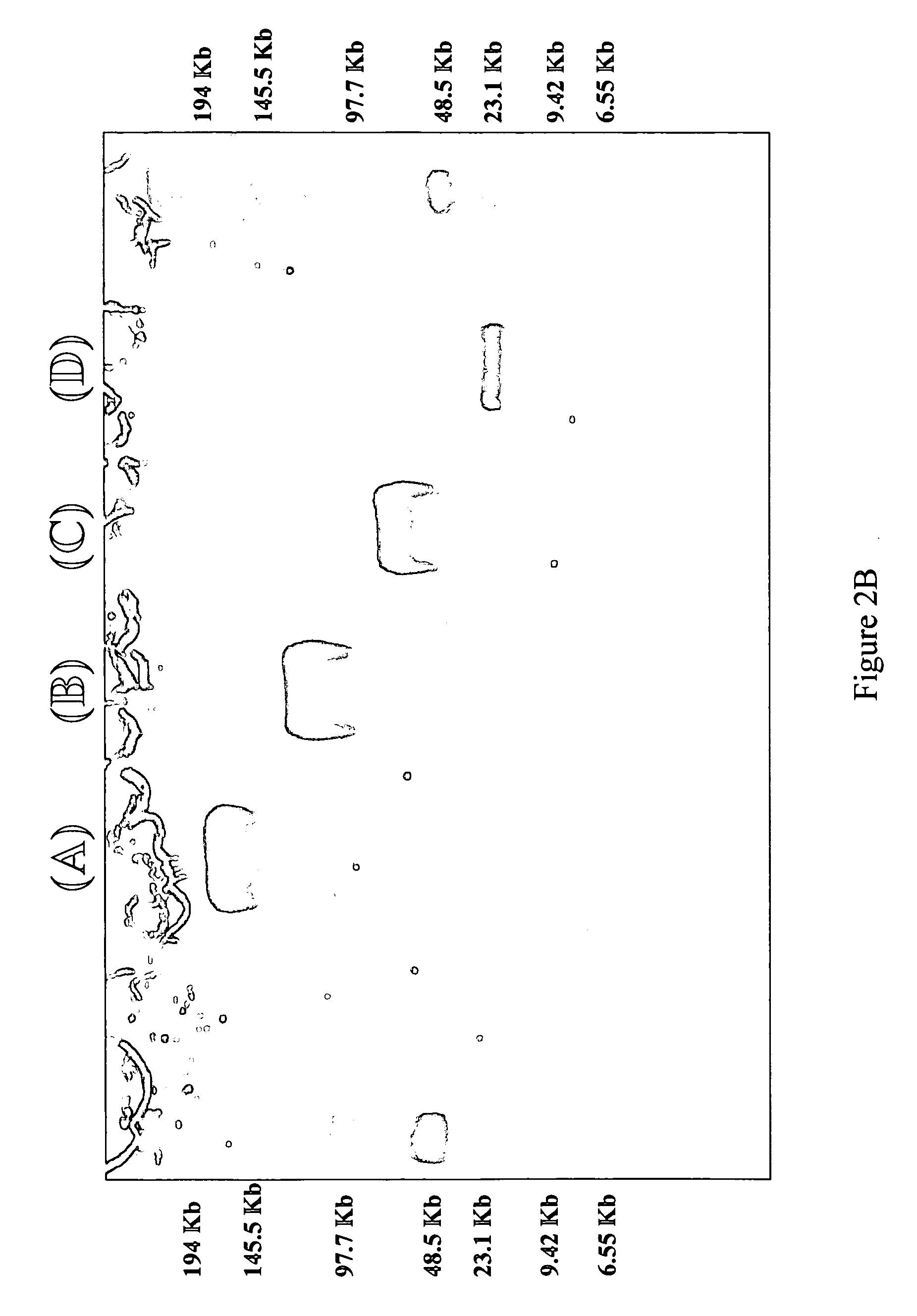
Method for extracting DNA from organisms
a technology of organisms and extracting dna, which is applied in the field of extracting dna from organisms, can solve the problems of not being exploited industrially, not being accessible, and the vast diversity of soil bacteria is still unknown, and the technique has the drawback of being relatively slow and tedious
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 2
EXTRACTION OF THE BACTERIAL FLORA FROM SOIL
[0137] I—Starting Material
[0138] 7.5 g of soil are taken up in 50 ml of a buffer solution comprising 30 mM sucrose, 25 mM EDTA and 50 mM TES.
[0139] II—Grinding of Material
[0140] a) the material is ground in a grinding bowl using a WaringBlender for 1 minute at maximum power;
[0141] b) the ground material is taken up in a 50 ml Falcon tube and centrifuged at 6 000 rpm at 10° C. for 10 minutes;
[0142] c) the supernatant is removed and the pellet is taken up with 50 ml of 0.8% NaCl;
[0143] d) 2 rounds of grinding for 1 minute with a WaringBlender at maximum power are carried out, with a 5 minute pause between the two in ice (cooling of the ground soil material);
[0144] e) the ground material is taken up in a 50 ml Falcon tube and kept in ice.
[0145] III—Carrying Out the Density Cushion Sedimentation
[0146] A 60% weight / volume solution of NYCODENZ is prepared (30 g in the final volume of 50 ml of ultrapure water), corresponding to a density...
example 1
is repeated
EXAMPLE 3
EXTRACTION OF INTESTINAL BACTERIAL FLORA
[0166] I—Starting Material
[0167] 3 g of stools are taken up in 50 ml of 0.8% NaCl.
[0168] II—Grinding of Material
[0169] The grinding is carried out using a sterile Teflon Potter homogenizer in a borosilicate glass cylinder;
[0170] a) grinding for 2-5 minutes in ice;
[0171] b) should the grinding with the Potter homogenizer not be sufficient, the material is subjected to very rapid grinding in a WaringBlender (5-10 seconds);
[0172] c) the ground material is filtered through sterile gauze.
[0173] III—Carrying Out the Density Cushion Sedimentation
[0174] A 30% weight / volume NYCODENZ solution is prepared (15 grams in a final volume of 50 ml of ultrapure water), corresponding to a density of 1.16. A 10 ml cushion of NYCODENZ is then put in place in the ultraclear tube, using a pipette, under the suspension derived from the grinding. The sedimentation is then accelerated for 30 minutes at a temperature of 4° C. by ultracentri...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com