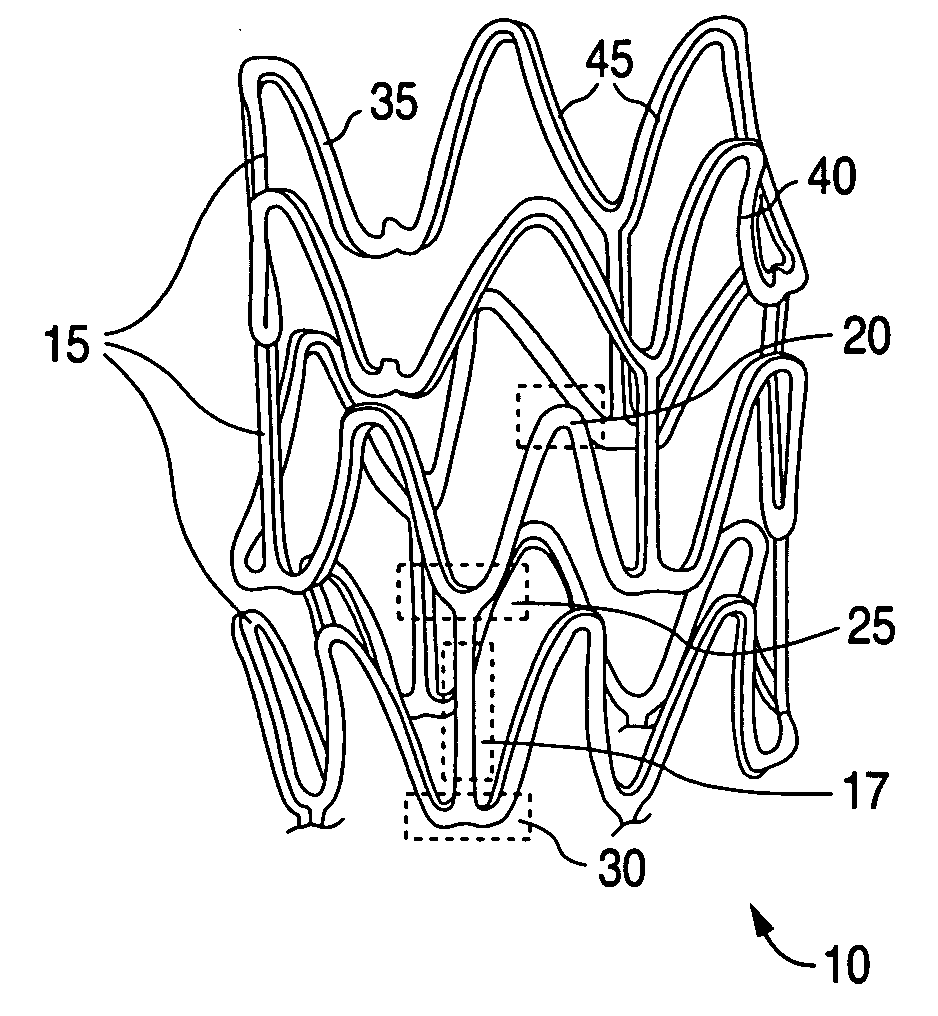
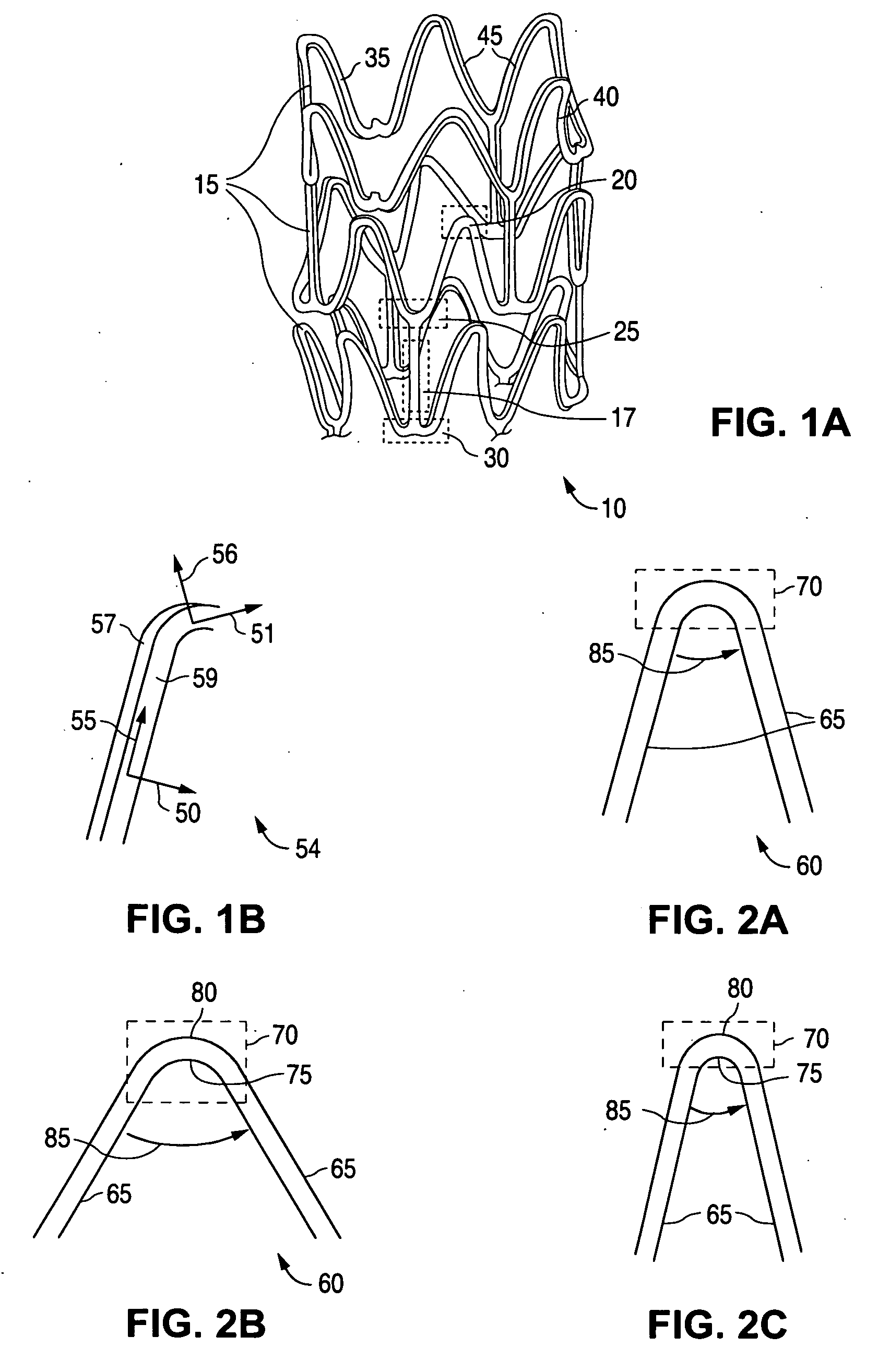
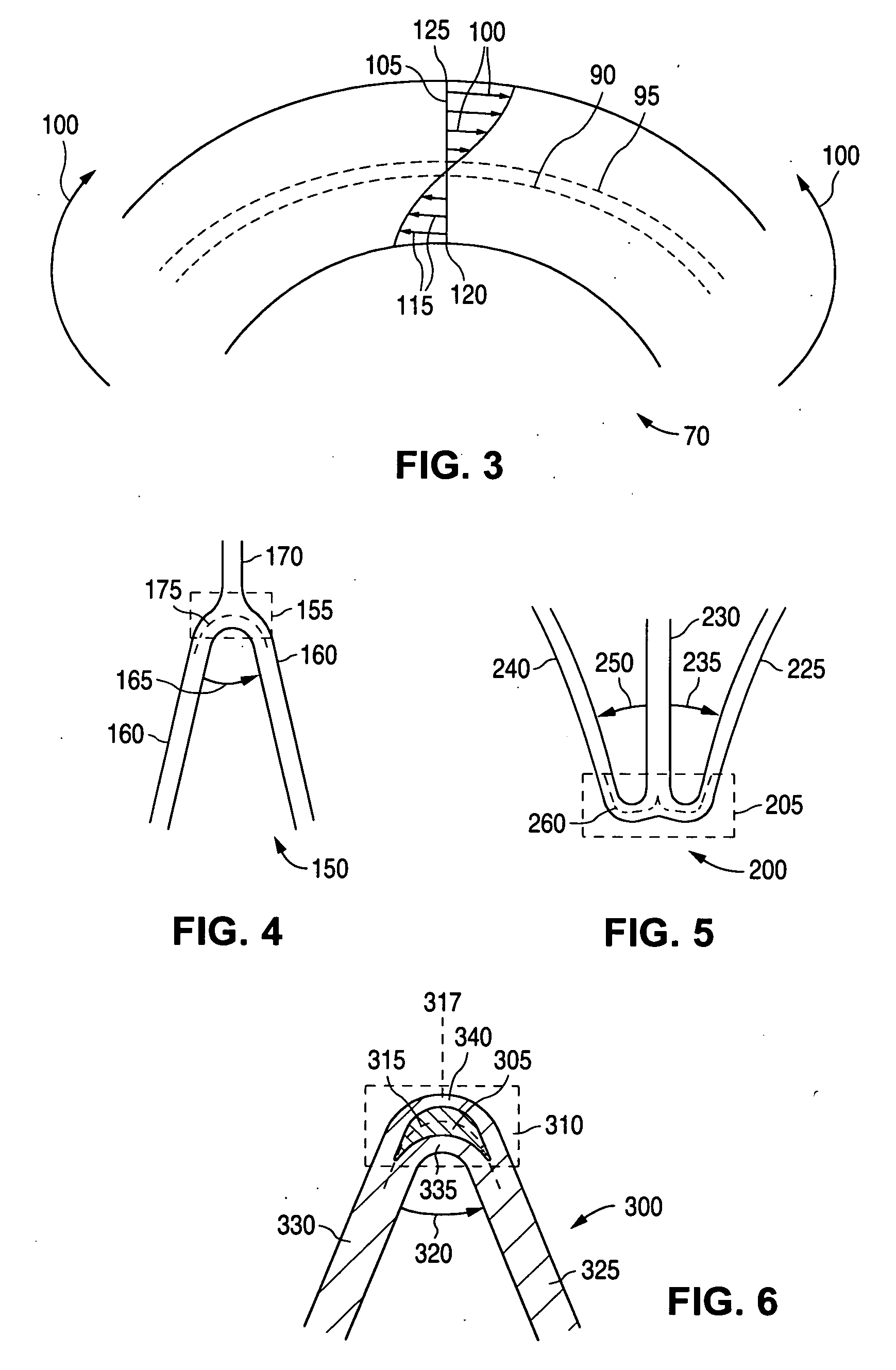
Stent with flexible sections in high strain regions
a flexible section and stent technology, applied in the field of stents, can solve the problems of stent struts that are susceptible to cracking, localized portions of the stent pattern subject to substantial deformation are the most susceptible to failure, and the stent pattern is subject to substantial deformation. , to achieve the effect of increasing the resistance to strain, reducing the risk of fracture, and increasing the flexibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
[0088] Some embodiments of the present invention are illustrated by the following examples. The examples are being given by way of illustration only and not by way of limitation. The parameters are not to be construed to unduly limit the scope of the embodiments of the invention.
[0089] A structural element may be composed of a high modulus polymer such as poly(L-lactide), poly(D,L-lactide), or poly(ε-caprolactone), mixtures thereof, or copolymers thereof. A flexible section may composed of flexible polymers such as poly(D,L-lactide)-polyethylene glycol-poly(D,L-lactide) triblock copolymer, 70 / 30 poly(L-lactide-co-trimethylene carbonate), or polyanhydrides.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com