Method and apparatus for distributing multimedia to remote clients
a multimedia and remote client technology, applied in electrical apparatus, multi-digital computer combinations, transmission, etc., can solve the problems of limited utility of data and image files generated within any individual personal computer, high complexity of functions to be performed within the device, and limited information display and display quality to levels, so as to achieve the effect of image control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
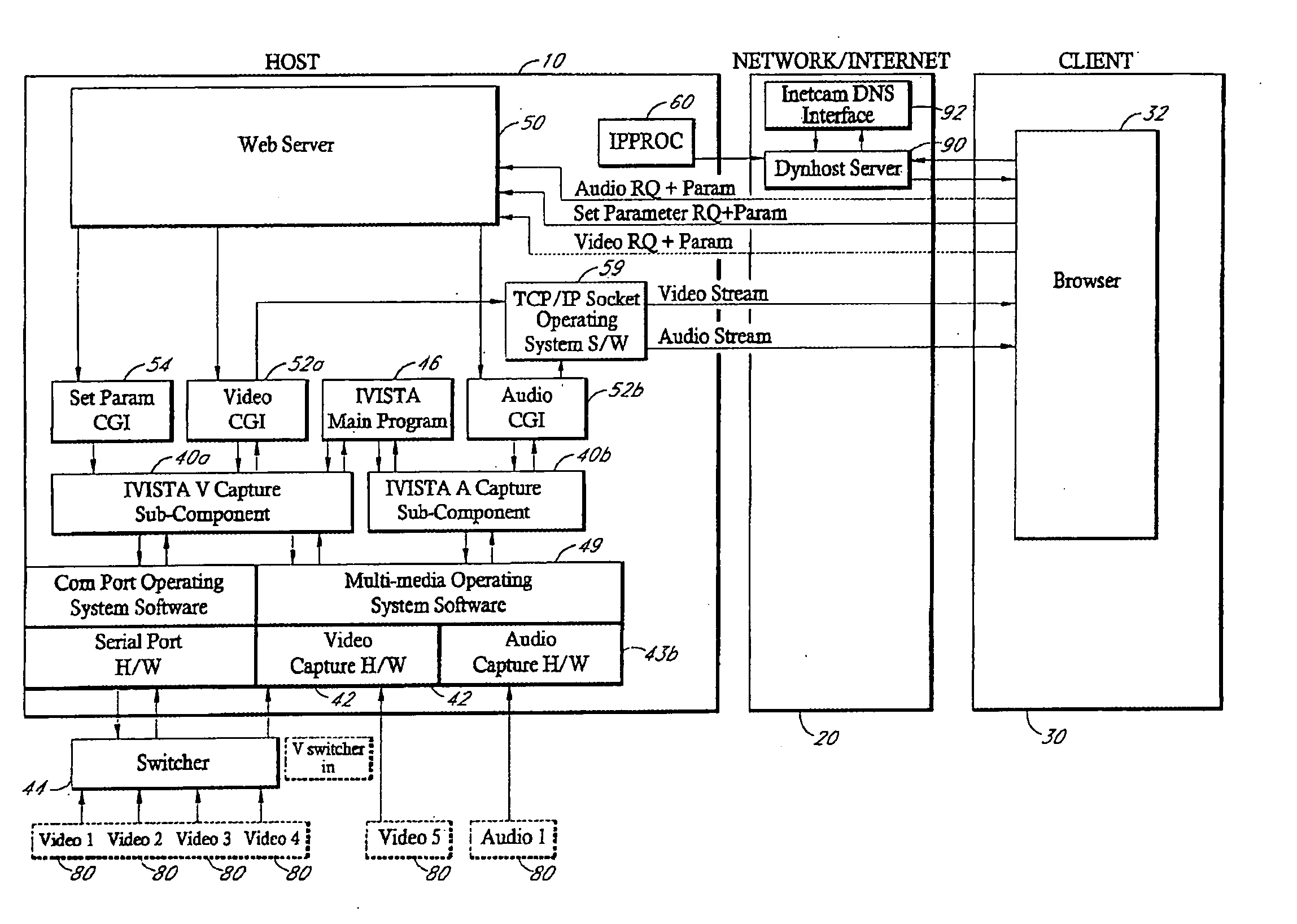
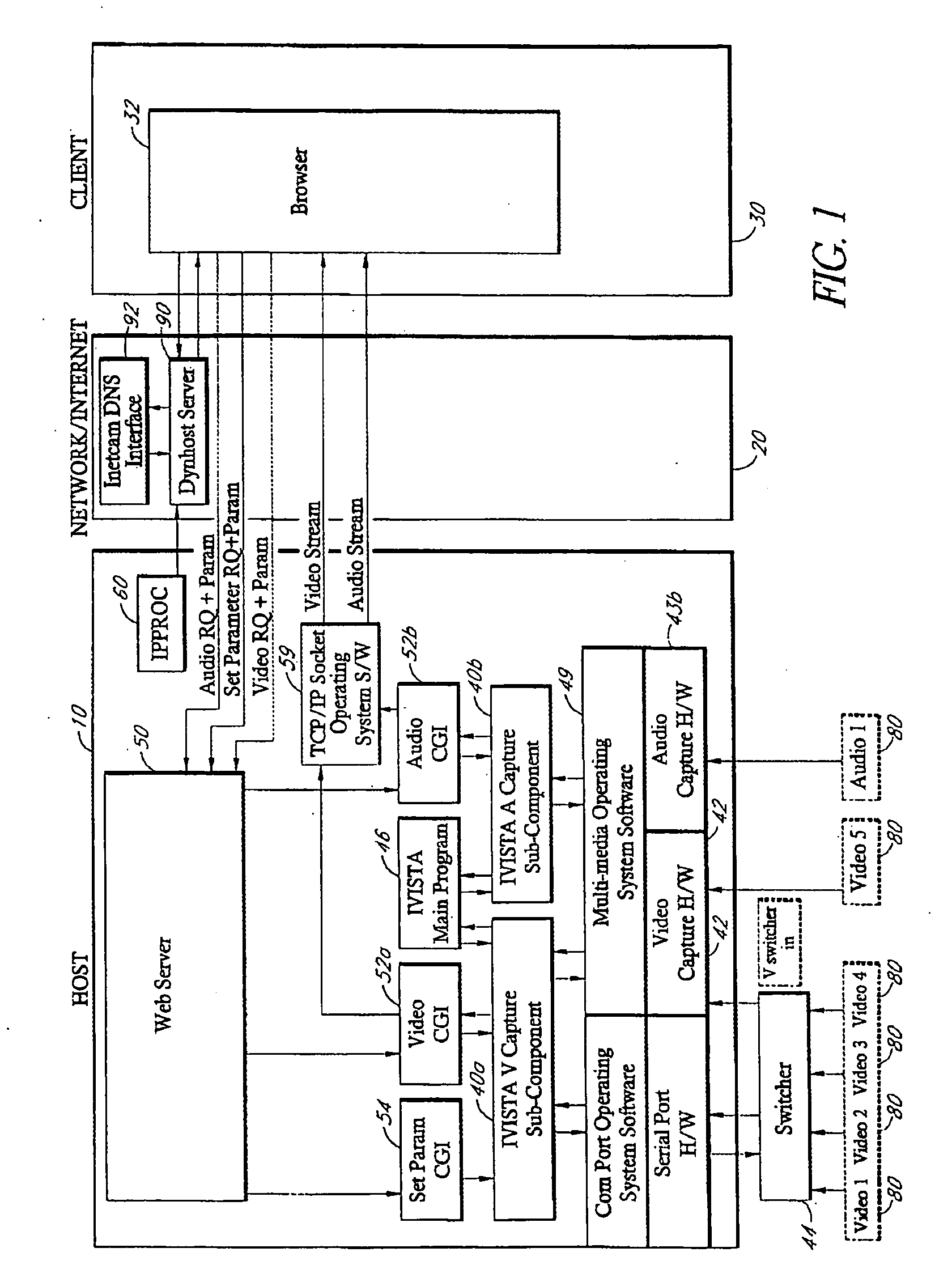
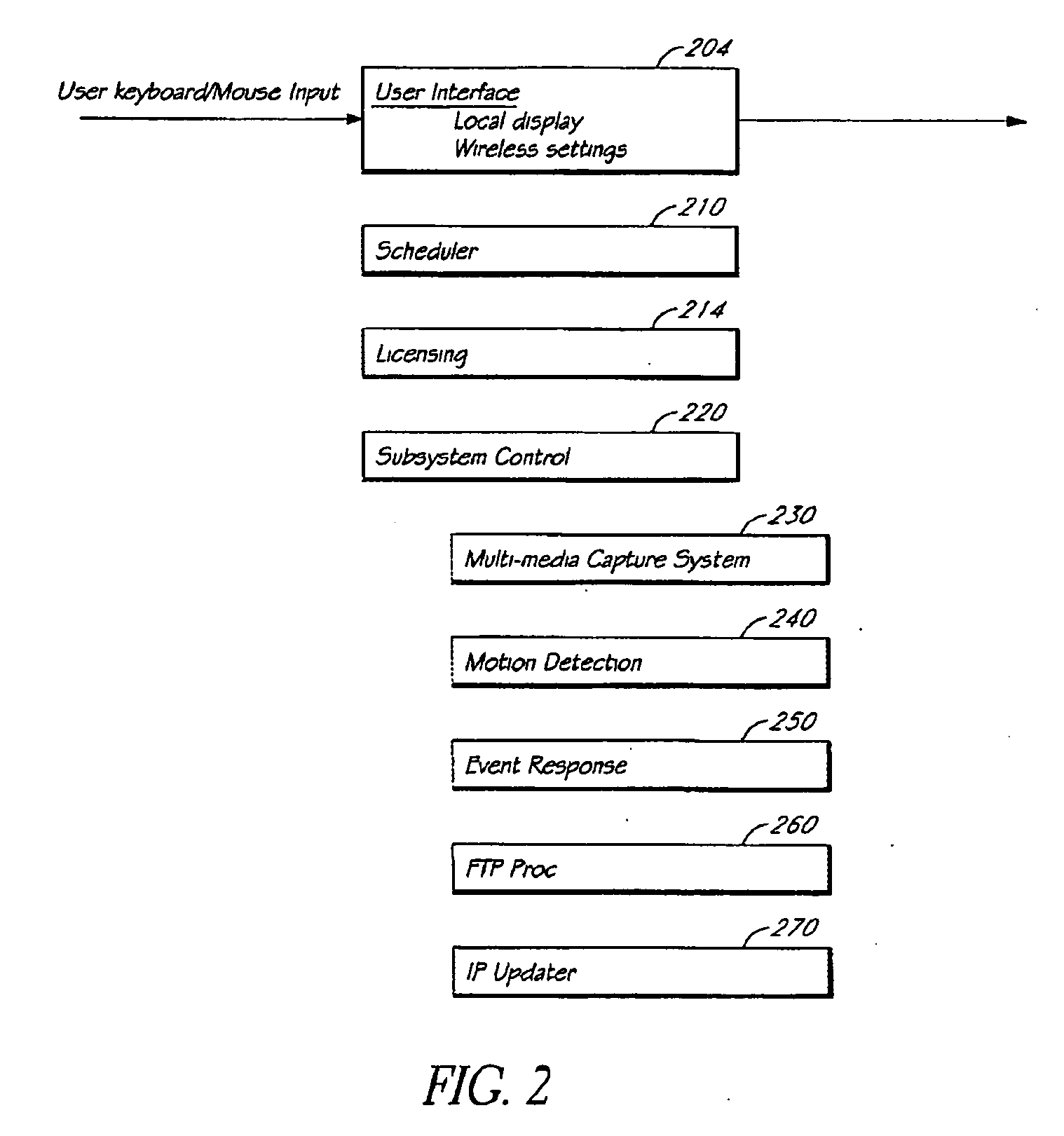
[0042] As used herein, a computer, including one or more computers comprising a web server, may be any microprocessor- or processor-controlled device or system that permits access to a network, including terminal devices, such as personal computers, workstations, servers, clients, mini computers, main-frame computers, laptop computers, a network of individual computers, mobile computers, palm-top computers, hand-held computers, set top boxes for a television, interactive televisions, interactive kiosks, personal digital assistants, interactive wireless communications devices, mobile browsers, or a combination thereof. The computers may further possess input devices such as a keyboard, mouse, touchpad, joystick, pen-input-pad, and output devices such as a computer screen and a speaker.
[0043] These computers may be uni-processor or multi-processor machines. Additionally, these computers include an addressable storage medium or computer accessible medium, such as random access memory ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com