Methods and compositions for mitigating pain
a technology of nitrate and esters, which is applied in the direction of drug compositions, phosphorous compound active ingredients, nitro compound active ingredients, etc., can solve the problem that no attempt has been made to develop organic nitrates themselves as analgesic agents, and achieve the effect of raising cgmp levels
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Characterization of Guanylyl Cyclase Activation
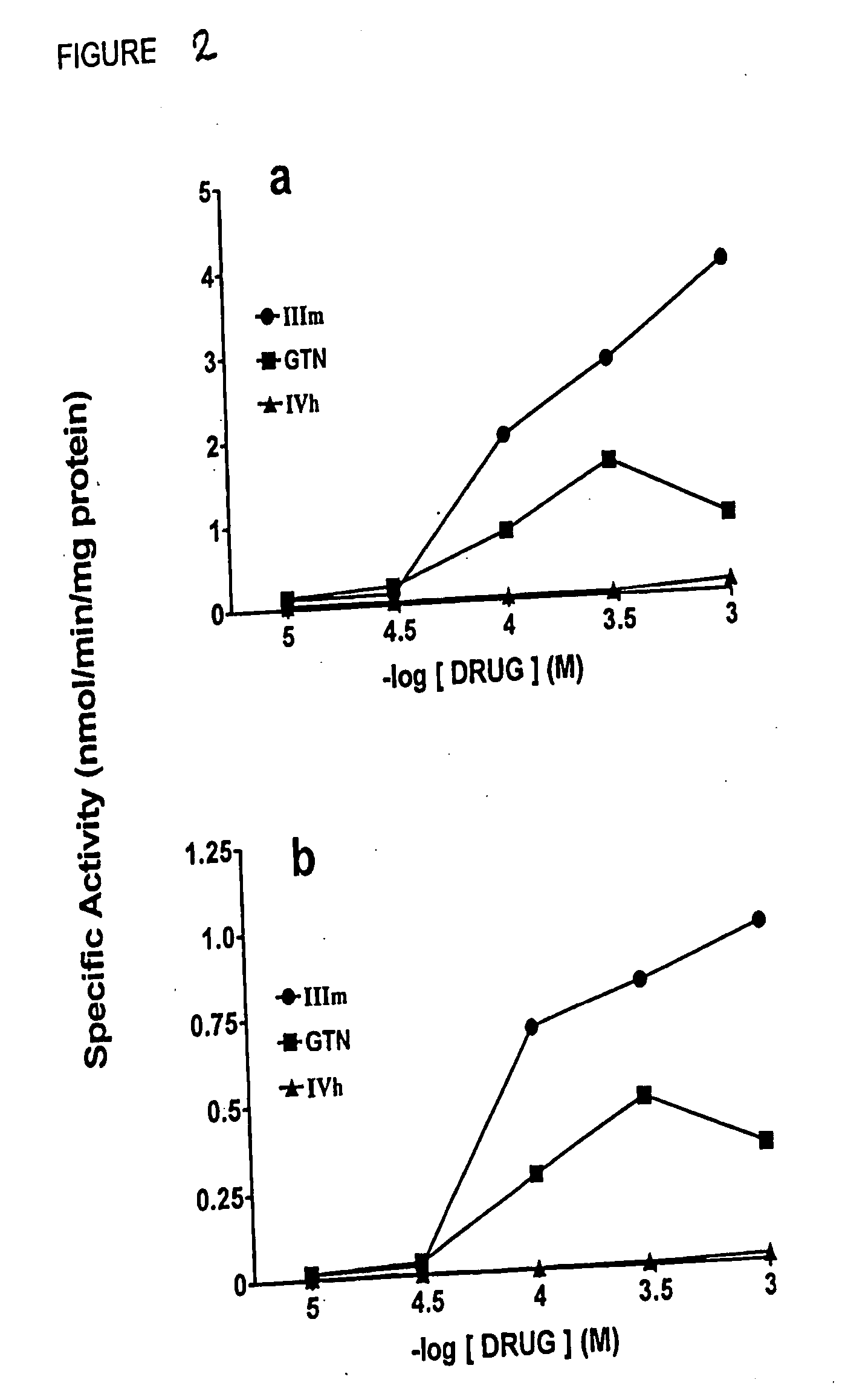
[0136] Activation of soluble guanylyl cyclase (GCase) by nitrates IIIm, IVa, IVb, WVd, IVe, WVf, Ig, WVj, Va, Vb, and GTN was assayed employing partially purified enzyme freshly prepared from the 105,000 g supernatant fraction of rat aorta homogenates, using the radioimmunoassay method described by Bennett et al. (1992). Dose-response curves were obtained for GCase activation by nitrates IVa, IVb, IVd, IVe, IVf, IVg, IVj, and GTN in the presence and absence of cysteine and dithiothreitol (DTT; both 2mM). In all cases, data were normalized to the maximal GTN response carried out in identical GCase preparations. Experimental incubations were performed at 37° C for 10 min. The data for WVd is summarized in FIG. 1. The GCase assay data show that WVd activates GCase, with a submiulimolar EC-50 (effective concentration for 50% of the subjects) in the absence of any added thiol, in contrast to GTN, which requires added cysteine. Compounds WV...
example 2
Characterization of Cyclic GMP Accumulation
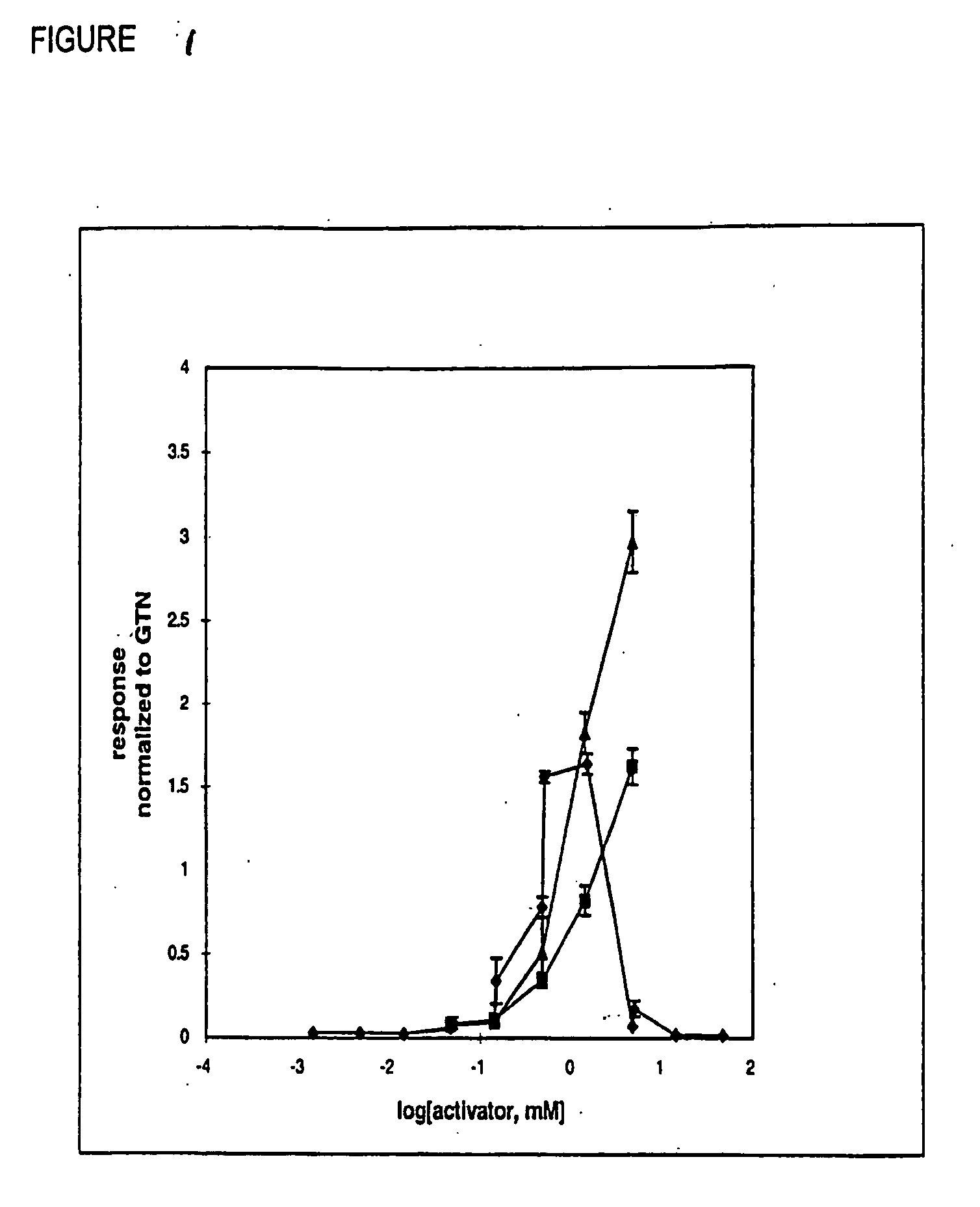
[0140] In order to extend the GCase data further, the effects of nitrates Va, IlIm, Vb, Vc, and WVk on cyclic GMP accumulation in intact isolated rat aorta were examined (FIGS. 4, 5). Thoracic aortic strips were prepared from male Sprague-Dawley rats (Charles-River, Canada) as described in McGuire et al. (1994) and Stewart et al. (1989). Tissues were contracted submaximally with phenylephrine (0.1CtM) and exposed to various concentrations of drug for 1 min. Cyclic GMP accumulation was determined using the radioitnmunoassay method described by Bennett et al. (1992). At concentrations of 1 liM and 10 AM, GTN and WVk significantly increased cGMP accumulation (FIGS. 5). At a concentration of 1 AM, Va, IIlm, Vb, and Vc did not significantly increase cyclic GMP accumulation (FIGS. 4a, 5a). At a concentration of 10 [tM, Va, Vb, and WVk significantly increased cyclic GMP accumulation whereas IIIm and Vc did not (FIGS. 4b, 5b).
[0141] Sections of ...
example 3
Characterization of Relaxation of Isolated Blood Vessels
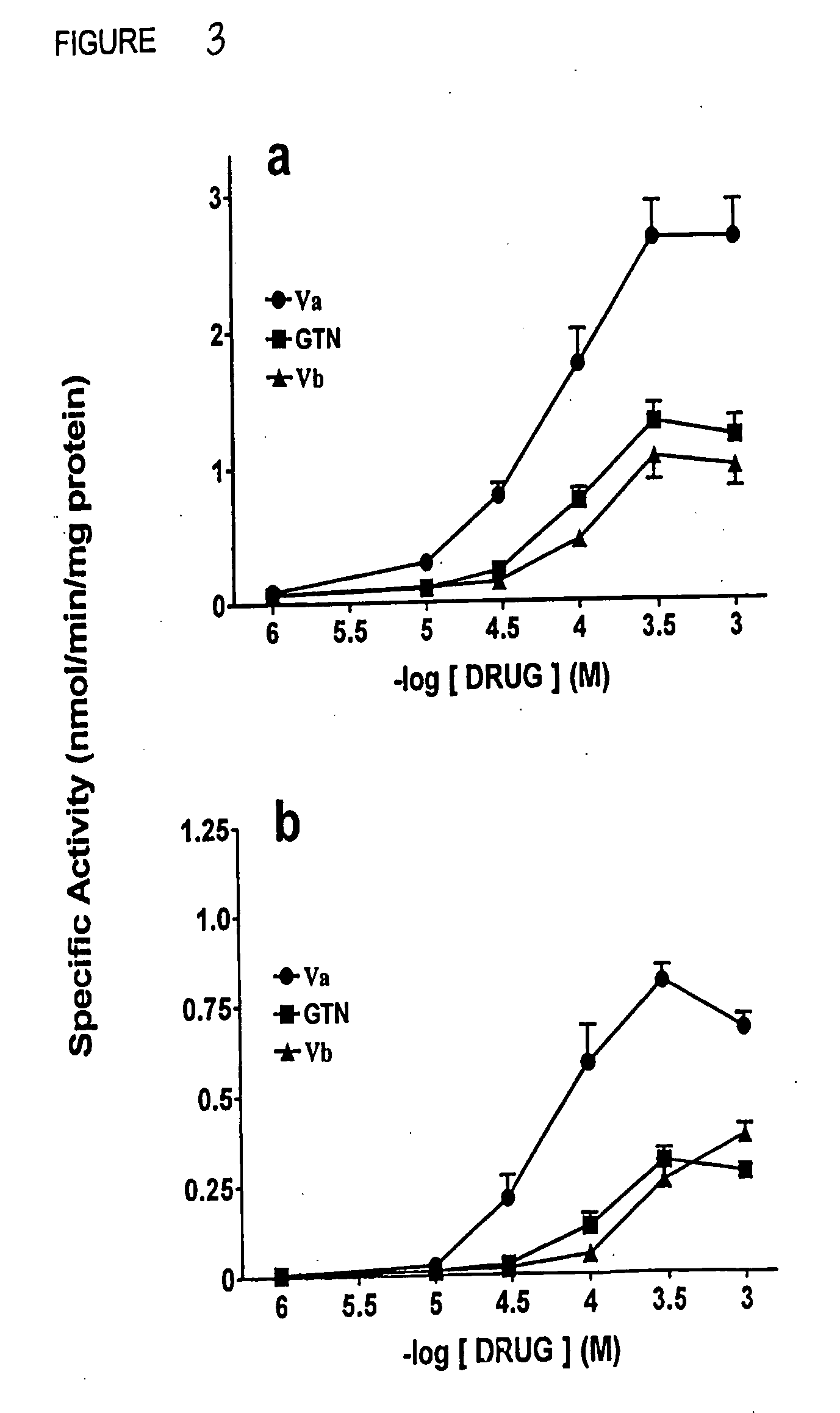
[0142] In order to extend the GCase data, the relaxing effects of nitrates Illm, WVc, WVd, WVf, WVg, WVh, Wk, Va, Vb, and Vc on rat aortic tissue were examined. Thoracic aortic strips were prepared from male Sprague-Dawley rats (Charles-River, Canada) as described in McGuire et al. (1994), and Stewart et al. (1989). Tissues were contracted submaximally with phenylephrine (0.1 pM) and exposed to various concentrations of nitrovasodilator to obtain concentration-response curves. In this intact tissue assay, all of the nitrates were observed to cause relaxation of the tissue with a maximal relaxant response equal to that obtained with GTN. However, the compounds differed in potency, with EC-50 values of 7.87 nM, 94.3 nM, 6.59 ,M, 25.2 tM, 11.0 μM, and 0.203 μM, for GTN and compounds Va, IVd, IVg, WVf, and IVc, respectively (FIG. 7,8). In another series of experiments, the EC-50 values for relaxation were 0.61 nM, 3.19 nM, 8.40 n...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| RI | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com