Receptor on the surface of activated T-cells: ACT-4
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
A Monoclonal Antibody Against ACT-4-h-1
[0140] Mice were immunized with PHA-transformed T-lymphoblasts. Splenocytes from immunized mice were fused with SP2 / O myeloma cells and hybridomas secreting antibodies specific for the T-cell clone were selected. The hybridomas were cloned by limiting dilution. A monoclonal antibody, designated L106, produced by one of the resulting hybridoma, was selected for further characterization. The L106 antibody was found to have an IgG1 isotype. A hybridoma producing the antibody, designated HBL106 has been deposited at the American Type Culture Collection at______, on______, and assigned ATCC Accession No.______.
example 2
Cellular Distribution of Polypeptide Recognized by L106 Antibody
[0141] Samples containing the antibody L106 were made available to certain participants at the Fourth International Workshop and Conference on Human Leucocyte Differentiation Antigens (Vienna 1989) for the purpose of identifying tissue and cell types which bind to the L106 antibody. The data from the workshop are presented in Leukocyte Typing IV (ed. W, Knapp, Oxford U. Press, 1989) (incorporated by reference for all purposes) and an accompanying computer data base available from Walter R. Gilks, MRC Biostatistics Unit, Cambridge University, England. This reference reports the L106 antibody binds a polypeptide of about 50 kDa. This polypeptide was reported to be present on HUT-102 cells (a transformed T-cell line), PHA-activated peripheral blood lymphocytes, an EBV-transformed B-lymphoid cell line, and HTLV-II transformed T-cell line, PMA-activated tonsil cells, ConA- or PHA-activated PBLs, and PMA-activated monocytes...
example 3
Time Course of ACT-4-h-1 Expression Responsive to CD4+ T-cell Activation
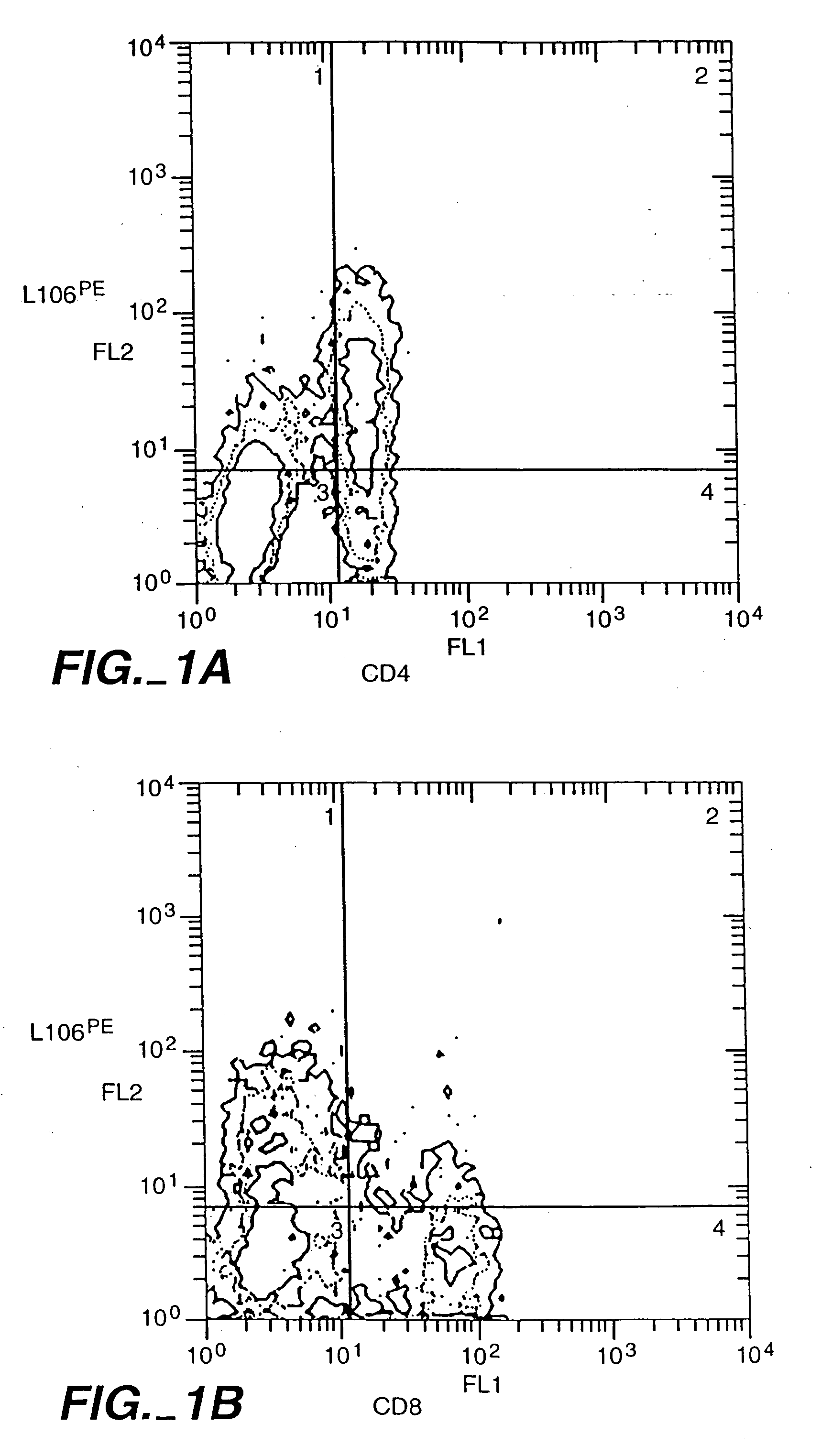
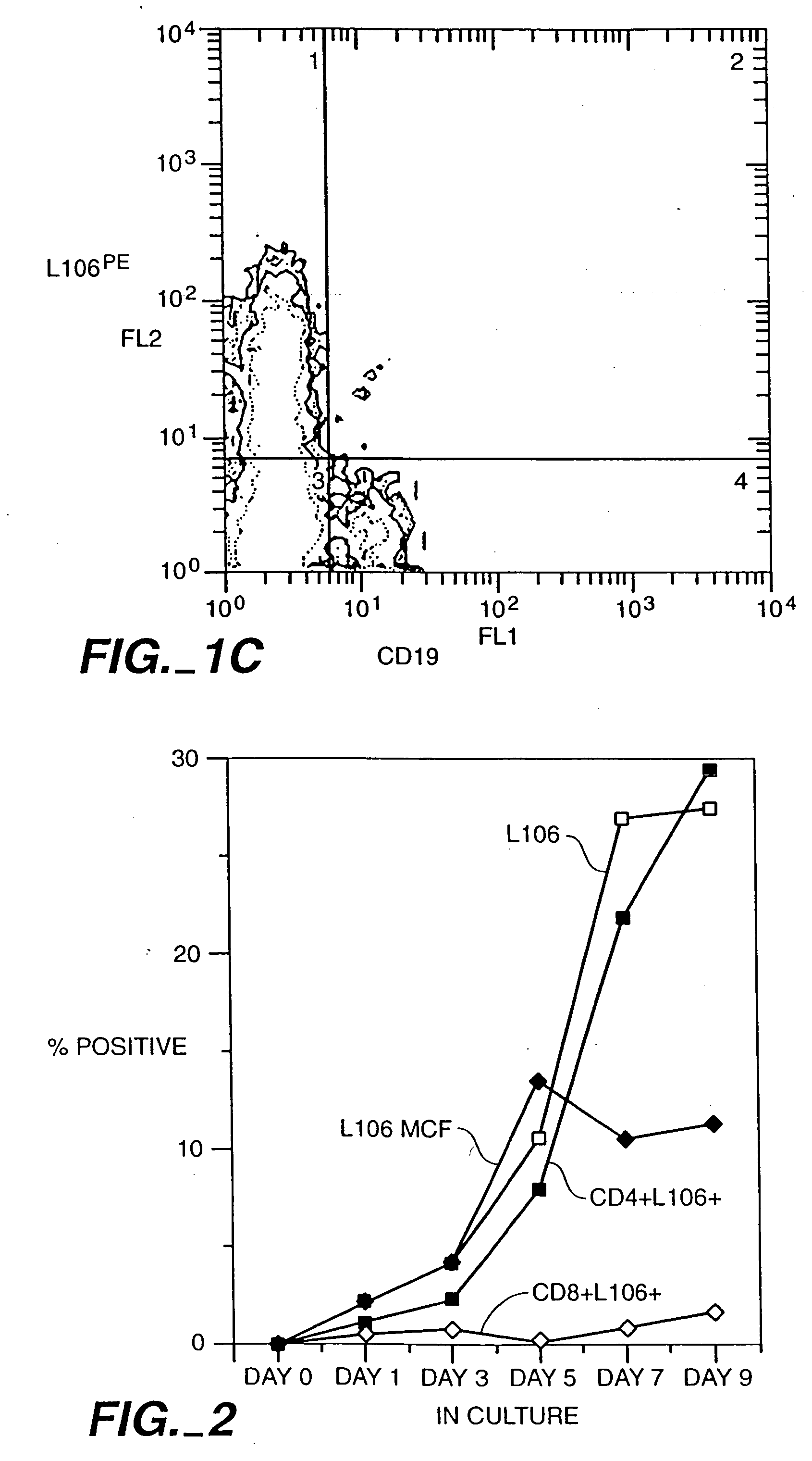
[0145] CD4+ T-cells were tested for expression of ACT-4-h-1 receptors in response to various activating stimuli. CD4+ T-cells were purified from peripheral blood mononuclear cells by solid-phase immunoadsorption (“panning”). 5×104 CD4+ T-cells were cultured with an activating agent in microtiter wells containing RPMI medium supplemented with 10% human serum. Three different activating agents were used: (1) 5×104 irradiated (3000 rads) monocytes, (2) PHA (1 μg / ml) and (3) tetanus toxoid (5 μg / ml). 3H-thymidine was added to the cultures 12-16 h before harvest. After harvest, cells were tested for the expression of cell surface antigens by incubation with various labelled antibodies (L106, anti-CD4 and anti-CD8), as described by Engleman et al., J. Immunol. 127:2124-2129 (1981).
[0146]FIG. 2 shows the appearance of ACT-4-h-1 in response to alloantigen activation. Before activation, no expression was observed. The...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Atomic weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Atomic weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap