Attack signature generation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
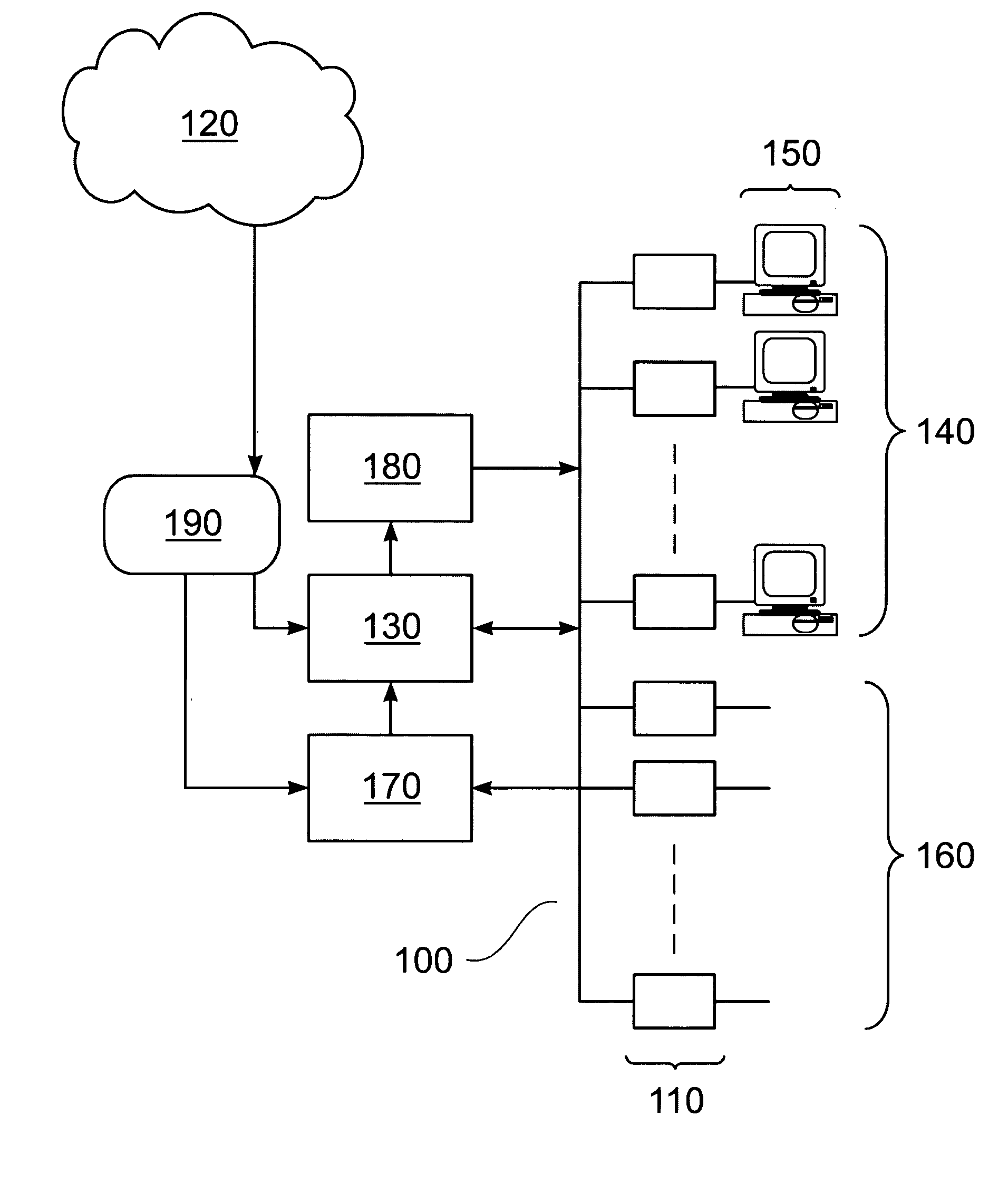
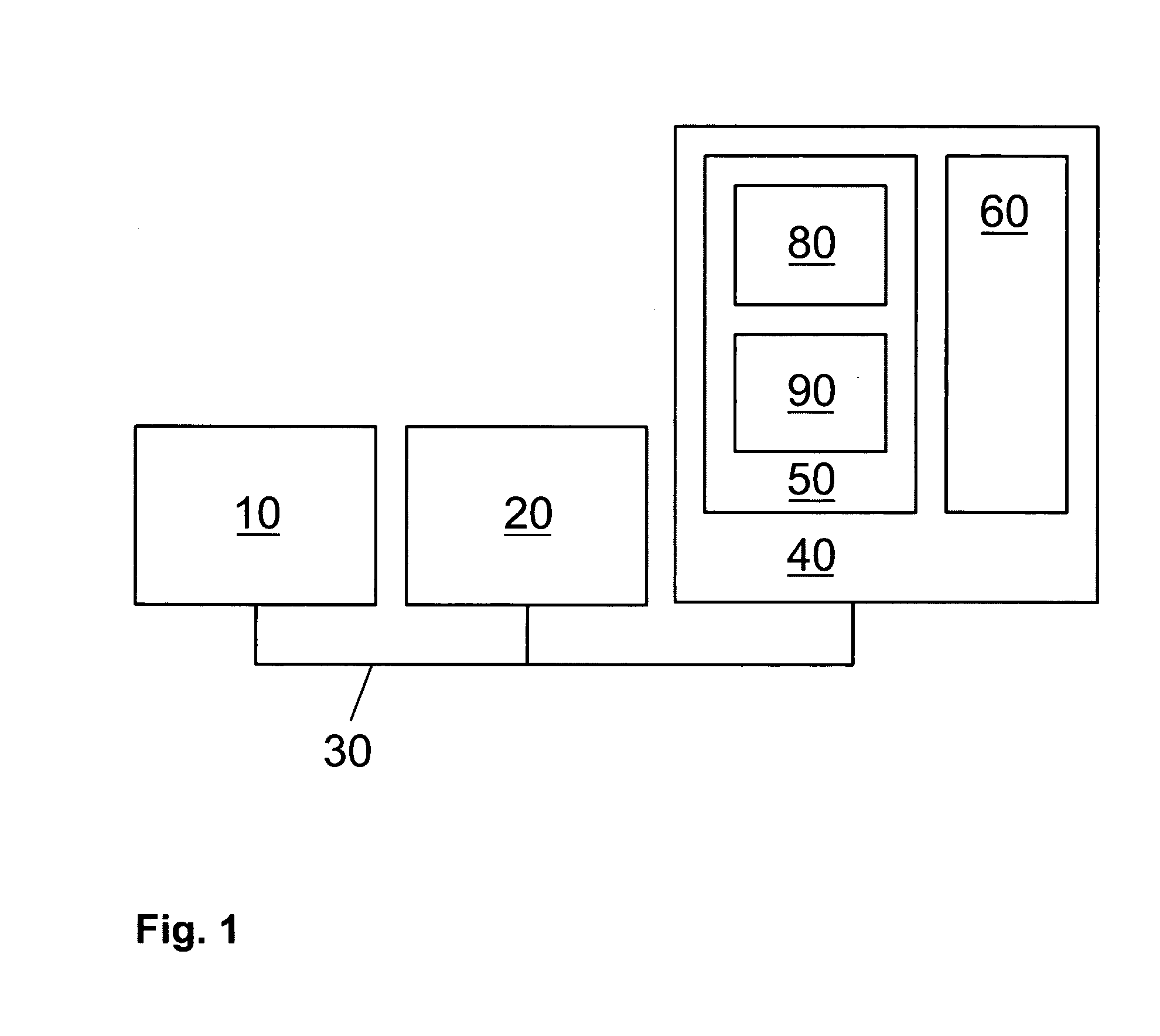
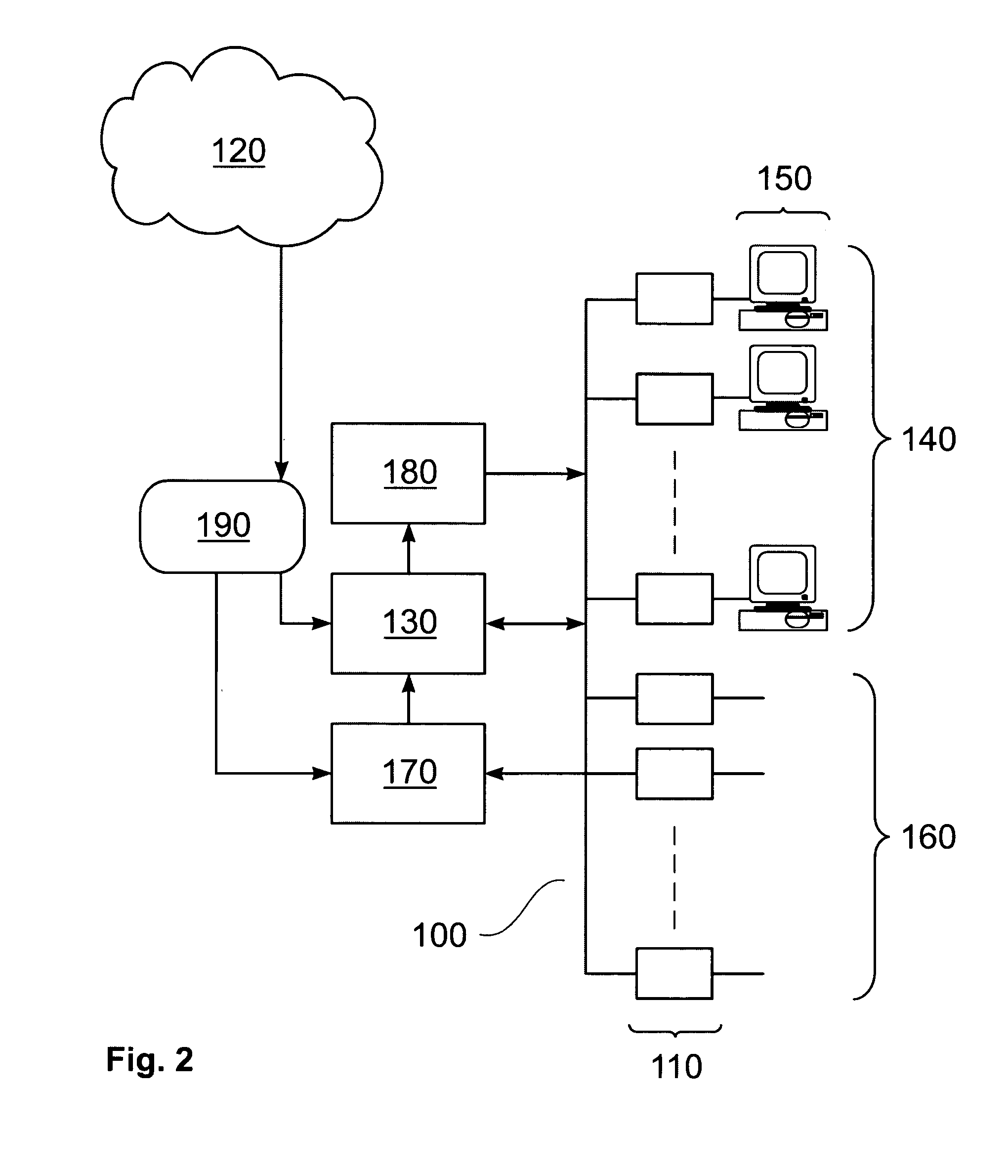
[0041] Referring first to FIG. 1, a data processing system comprises a CPU 10, an I / O subsystem 20, and a memory subsystem 40, all interconnected by a bus subsystem 30. The memory subsystem 40 may comprise random access memory (RAM), read only memory (ROM), and one or more data storage devices such as hard disk drives, optical disk drives, and the like. The I / O subsystem 20 may comprise: a display; a printer; a keyboard; a pointing device such as a mouse, tracker ball, or the like; and one or more network connections permitting communication between the data processing system and one or more similar systems and / or peripheral devices via a data network. The combination of such systems and devices interconnected by such a network may itself form a distributed data processing system. Such distributed systems may be themselves interconnected by additional data networks.
[0042] In the memory subsystem 40 is stored data 60 and computer program code 50 executable by the CPU 10. The program...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com