Device for melting down metal-containing material
a technology of metal-containing materials and devices, which is applied in the direction of lighting and heating apparatus, charge manipulation, furniture, etc., can solve the problems of not being able to efficiently process large amounts, and achieve the effects of reducing production costs, high investment and operational costs, and efficient processing large amounts
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
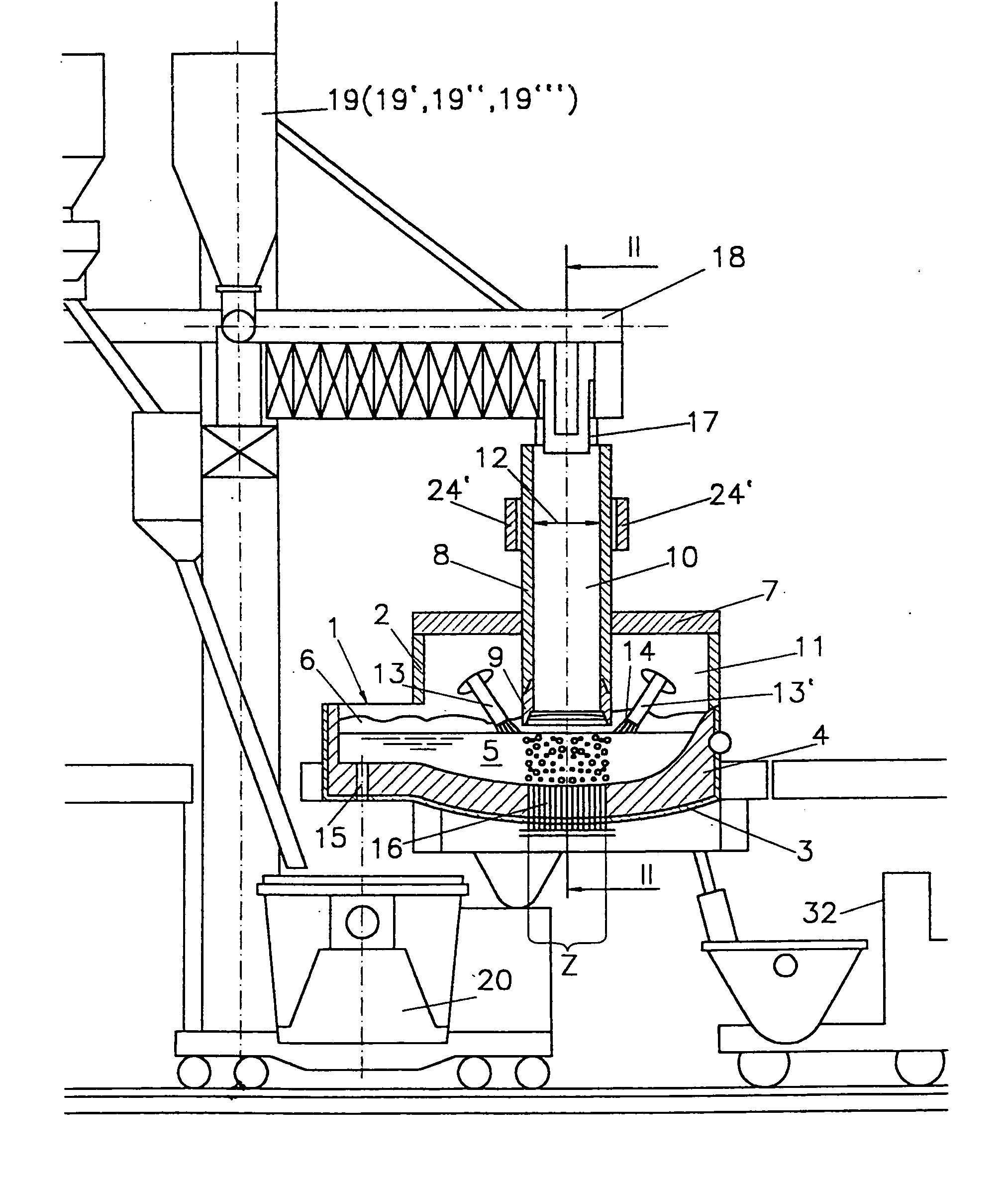
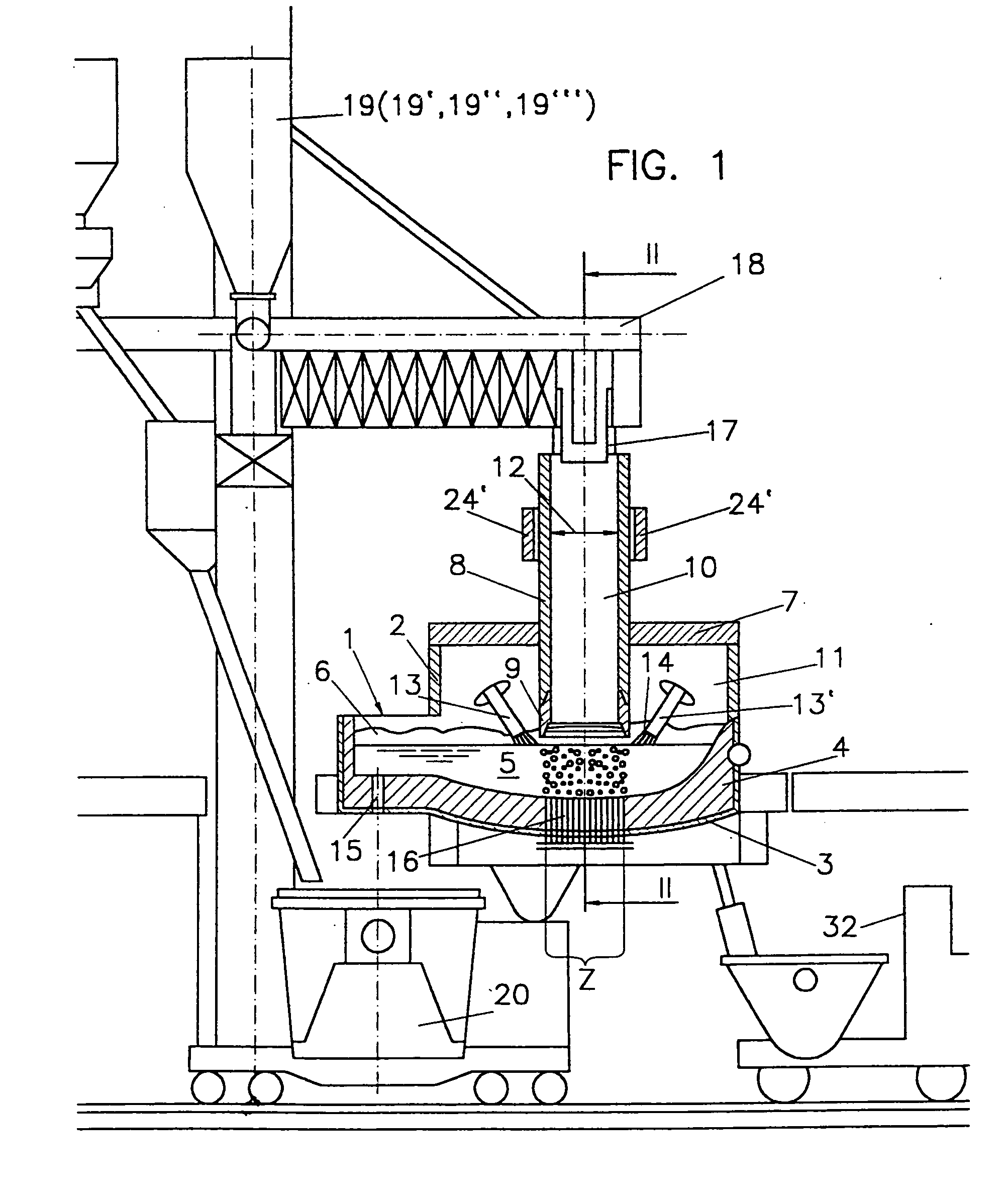
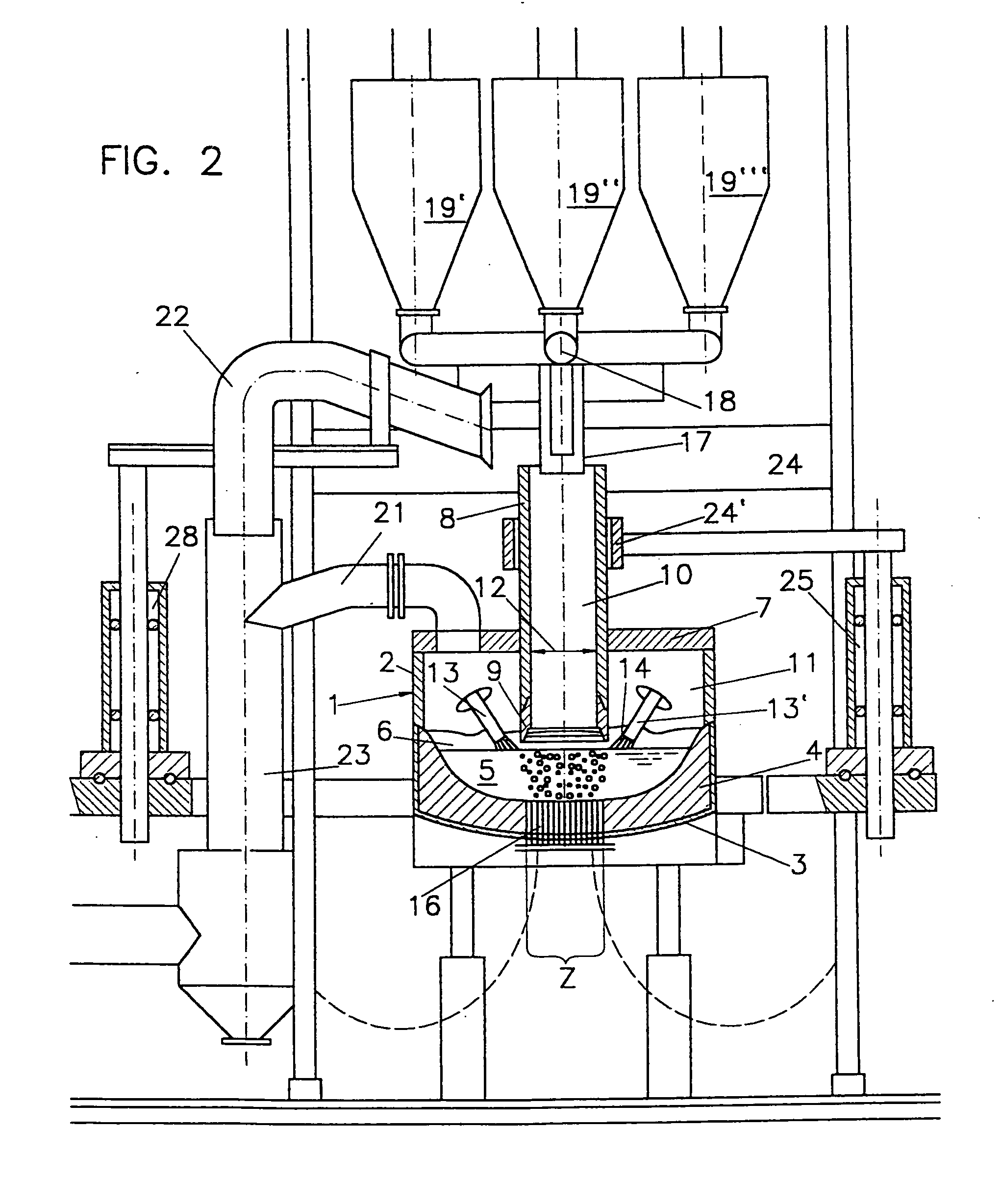
[0041] According to a preferred embodiment of the method of the invention, the metal-containing material is charged into the melting furnace through the charging tube in the hot and / or cold state, preferably at a temperature of between 500° C. and 1000° C., most preferably of between 600° C. and 700° C., which roughly corresponds to the temperature sponge iron has after being directly reduced. In that manner, energy costs can be saved, if, prior to being melted down, the charging material was subjected to a process which led to an increase in temperature of the particles, since the energy immanent to the charged material may be used for lowering the necessary melting energy consumption without any particular plant-related technical expenditures. That is rendered feasible by the particularly simple charging according to the invention, which does not necessitate any mechanical elements in the high temperature region of the melting furnace.
[0042] A preferred application of the method ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com