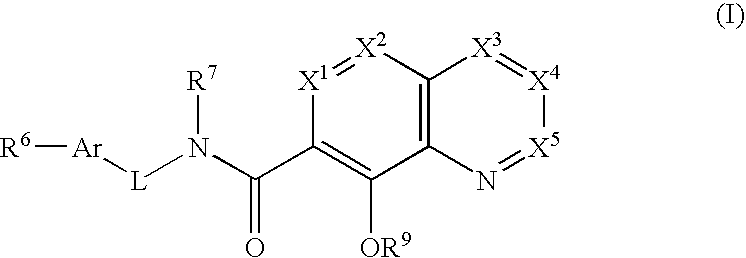
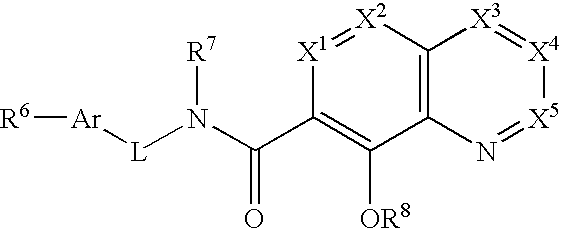
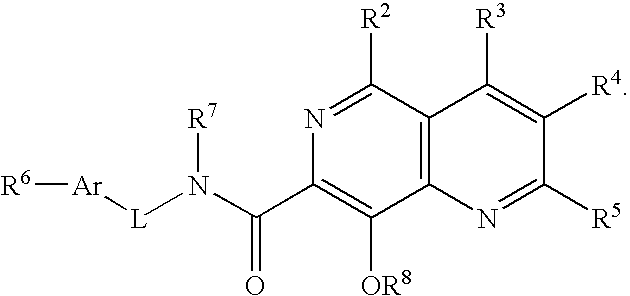
Aza-quinolinol phosphonate integrase inhibitor compounds
a technology of aza-quinolinol and integrase, which is applied in the direction of antiinfective drugs, group 5/15 element organic compounds, drug compositions, etc., can solve the problems of inability to inhibit the hiv infection and related diseases, limited usefulness of resistant strains, and inability to fully integrate inhibitory complexes,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0148] Reference will now be made in detail to certain embodiments of the invention, examples of which are illustrated in the accompanying descriptions, structure and formulas. While the invention will be described in conjunction with the enumerated embodiments, it will be understood that they are not intended to limit the invention to those embodiments. On the contrary, the invention is intended to cover all alternatives, modifications, and equivalents, which may be included within the scope of the present invention as defined by the claims.
Difinitions
[0149] Unless stated otherwise, the following terms and phrases as used herein are intended to have the following meanings:
[0150] The terms “phosphonate” and “phosphonate group” mean a fumctional group or moiety within a molecule that comprises at least one phosphorus-carbon bond, and at least one phosphorus-oxygen double bond. The phosphorus atom is further substituted with oxygen, sulfur, and nitrogen substituents. These substit...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle sizes | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle sizes | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle sizes | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com