Piston ring having improved scuffing, cracking and fatigue resistances, and its production method, as well as combination of piston ring and cylinder block
a technology of scuffing, cracking and fatigue resistance, which is applied in the field of piston rings, can solve the problems of scuffing of the piston ring and the liable roughness of the surface of the block by grinding, and achieve the effect of suppressing the initiation and propagation of cracks and reducing the size of grain boundary lamellar compounds
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples 1-11 (
J1-J11) and COMPARATIVE EXAMPLES 1-8 (H1-H8)
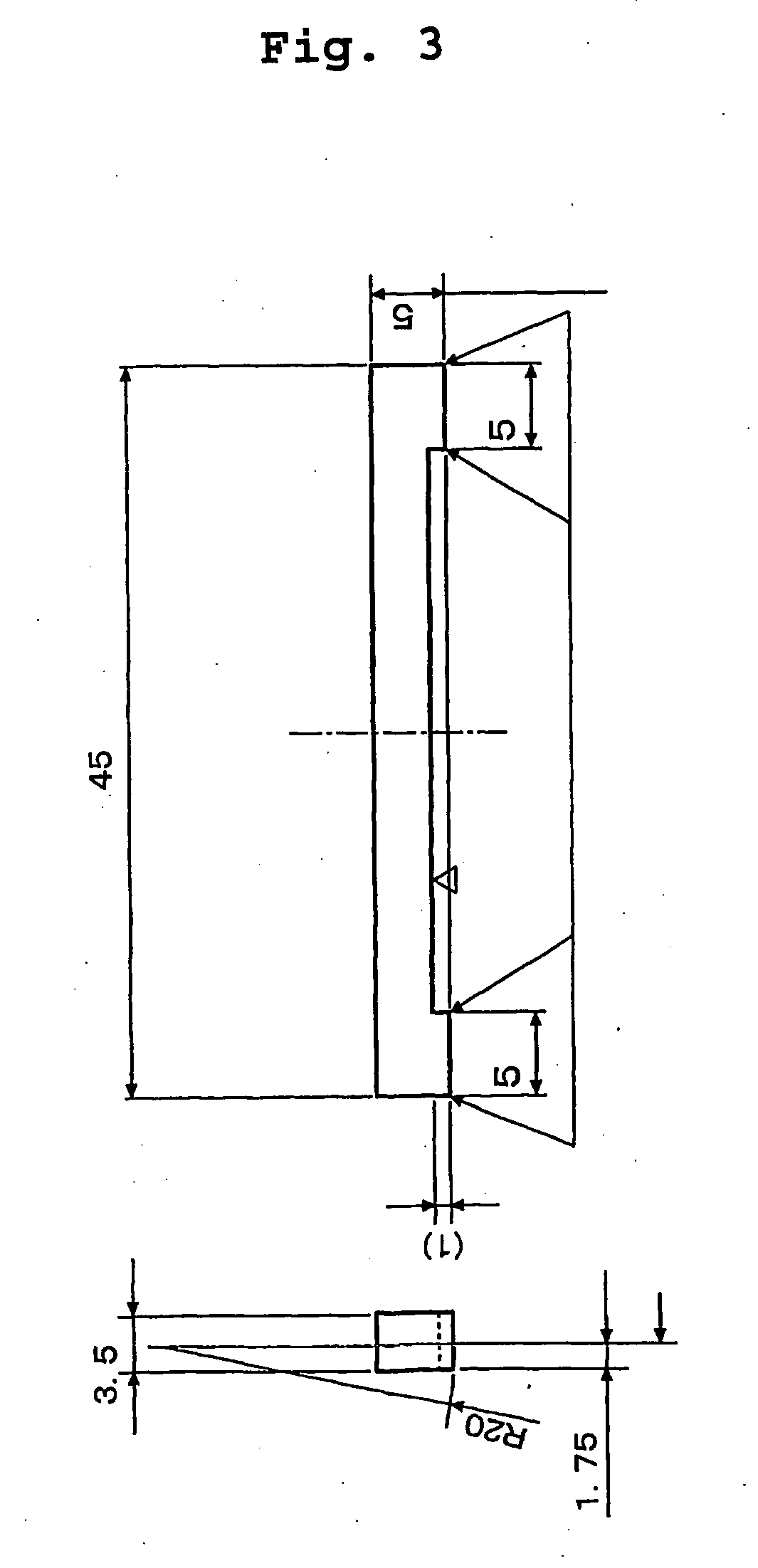
[0053] The high chromium martensitic stainless steels having a composition shown in Table 1 were melted in an amount of 10 kg in a vacuum induction melting furnace. However, less than 0.2% of N was added to the steel during melting under the normal pressure, while 0.2% or more of N was added to steel during melting under pressure N2 gas atmosphere. Wire material having 12 mm of diameter was obtained by hot working. After acid cleaning, spheroidizing annealing was carried out at 750° C. for 10 hours. A wire having a rectangular cross section of 3.5 mm×5.0 mm was produced through working steps. The wire was passed through a quenching furnace (Ar protective atmosphere) and a tempering furnace (Ar protective atmosphere). The air quenching was carried out from 930° C. after keeping approximately 10 minutes at that temperature. The tempering was carried out at 620° C. for approximately 25 minutes. The wires were cut into 50 mm long samples for t...
examples 12-14 (
J12-J14) AND COMPARATIVE EXAMPLES 9-11 (H9-H11)
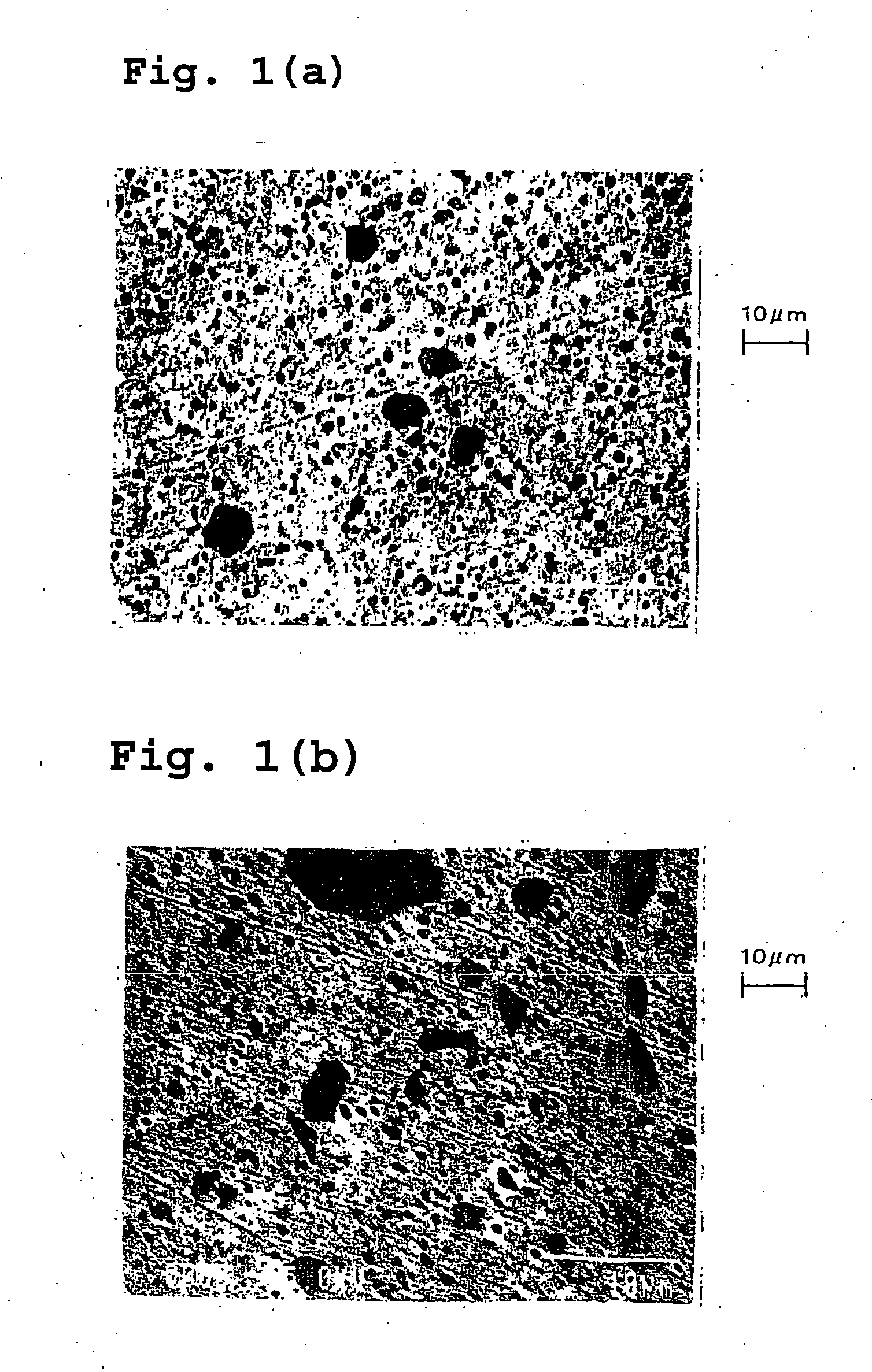
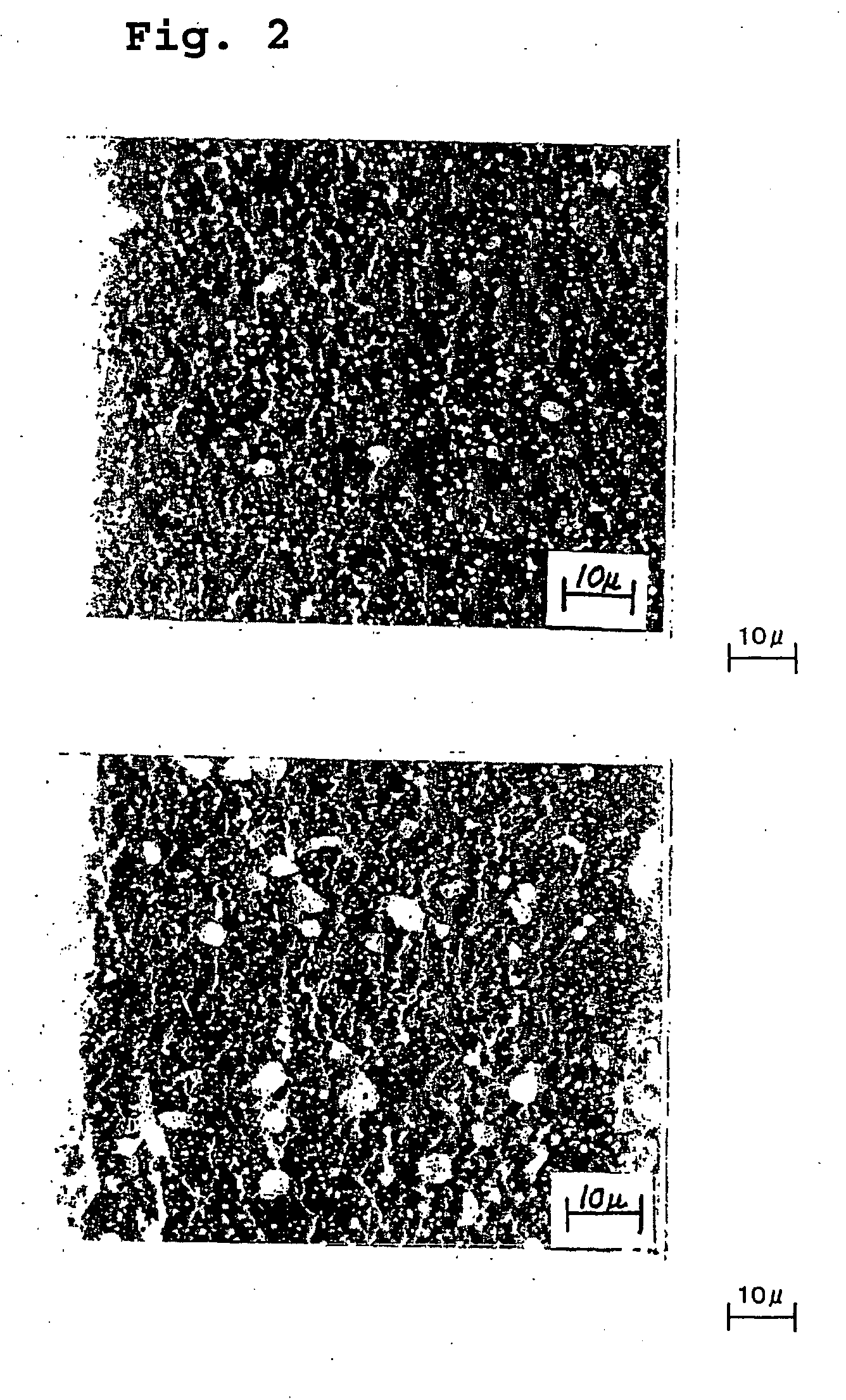
[0065] The materials having the chemical composition of Example 1 were worked into a wire and air quenched from the temperature shown in Table 4. The gas nitriding treatment was carried out by the same method as in Example 1. The microstructure of the nitriding layer was quantitatively analyzed. The results are shown in Table 4.
TABLE 4Longest LengthHard Particles of Slidingof GrainNitriding LayerBoundaryAverageLargestCompound inQuenchingParticleParticleAreaCross SectionTemperatureDiameterDiameterRatioof Nitriding(° C.)(μm)(μm)(%)Layer (μm)H9*8000.3515.414J128700.5519.411J139201.3618.515J149801.8617.418H1010302.3914.731H1110802.81111.549
*The hardness of the nitriding layer of Comparative Example 9 (H9) was low of Hv 860.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size(length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com