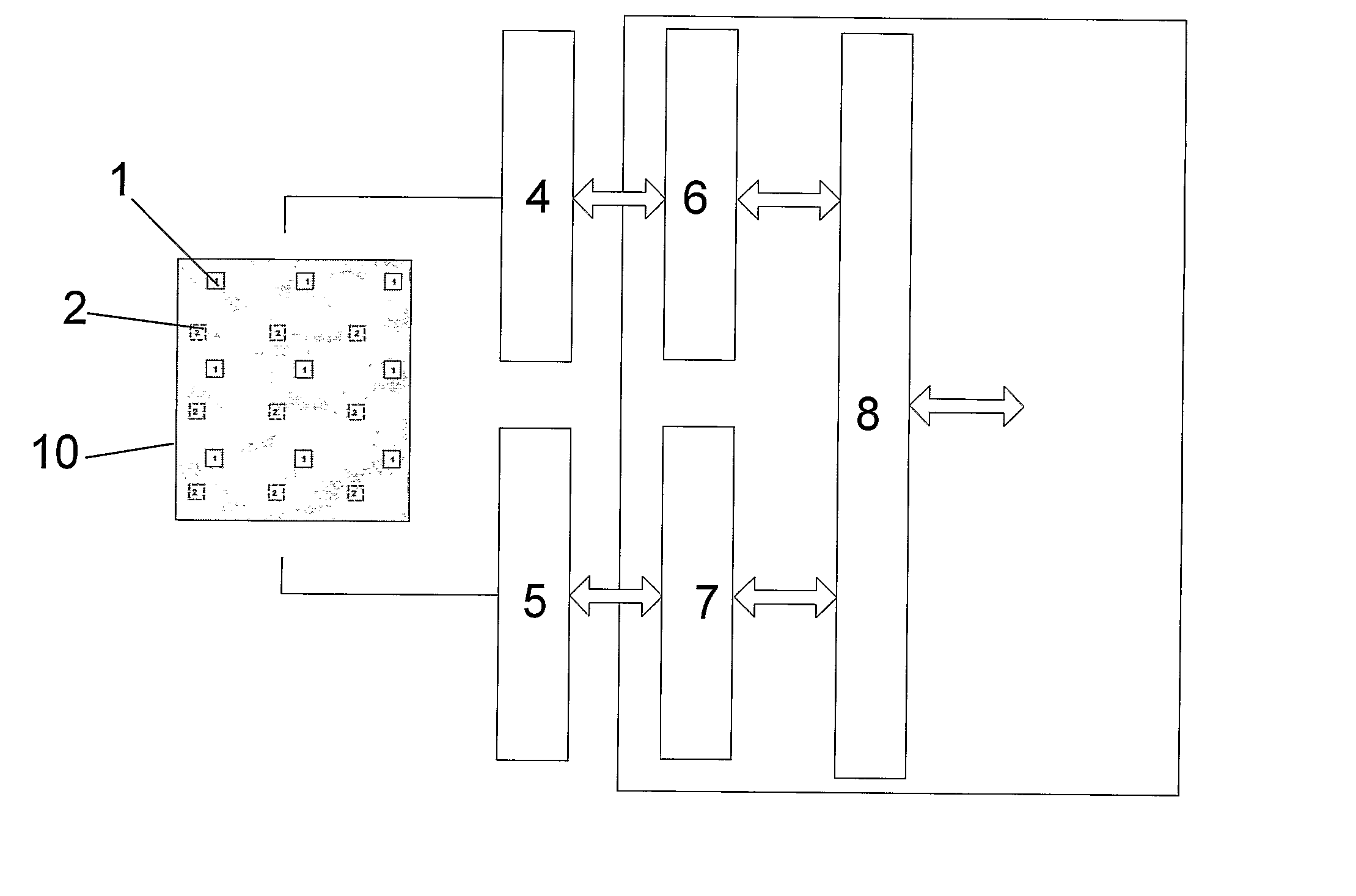Method And Arrangement For Determining The Spatial Frequency Of A Signal
a spatial frequency and signal technology, applied in the direction of wind-induced force reduction, linear waveguide fed arrays, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of increasing hardware costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0016] The invention will be described in reference to a composite layered antenna panel as disclosed in International Patent Application PCT / NO2004 / 000407 with title “An antenna arrangement” filed by the present applicant, even though the invention may be applied to any type of antenna array.
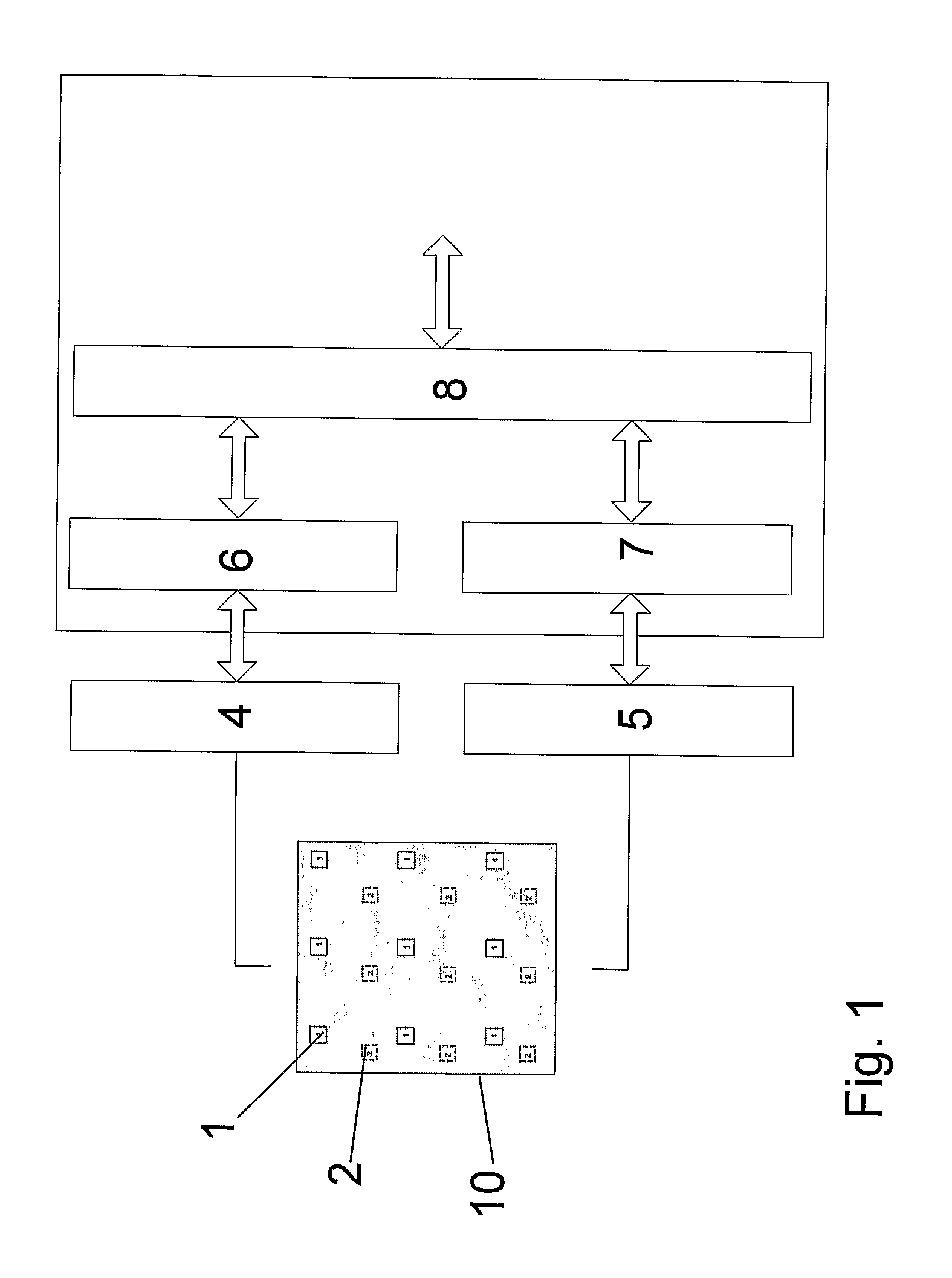
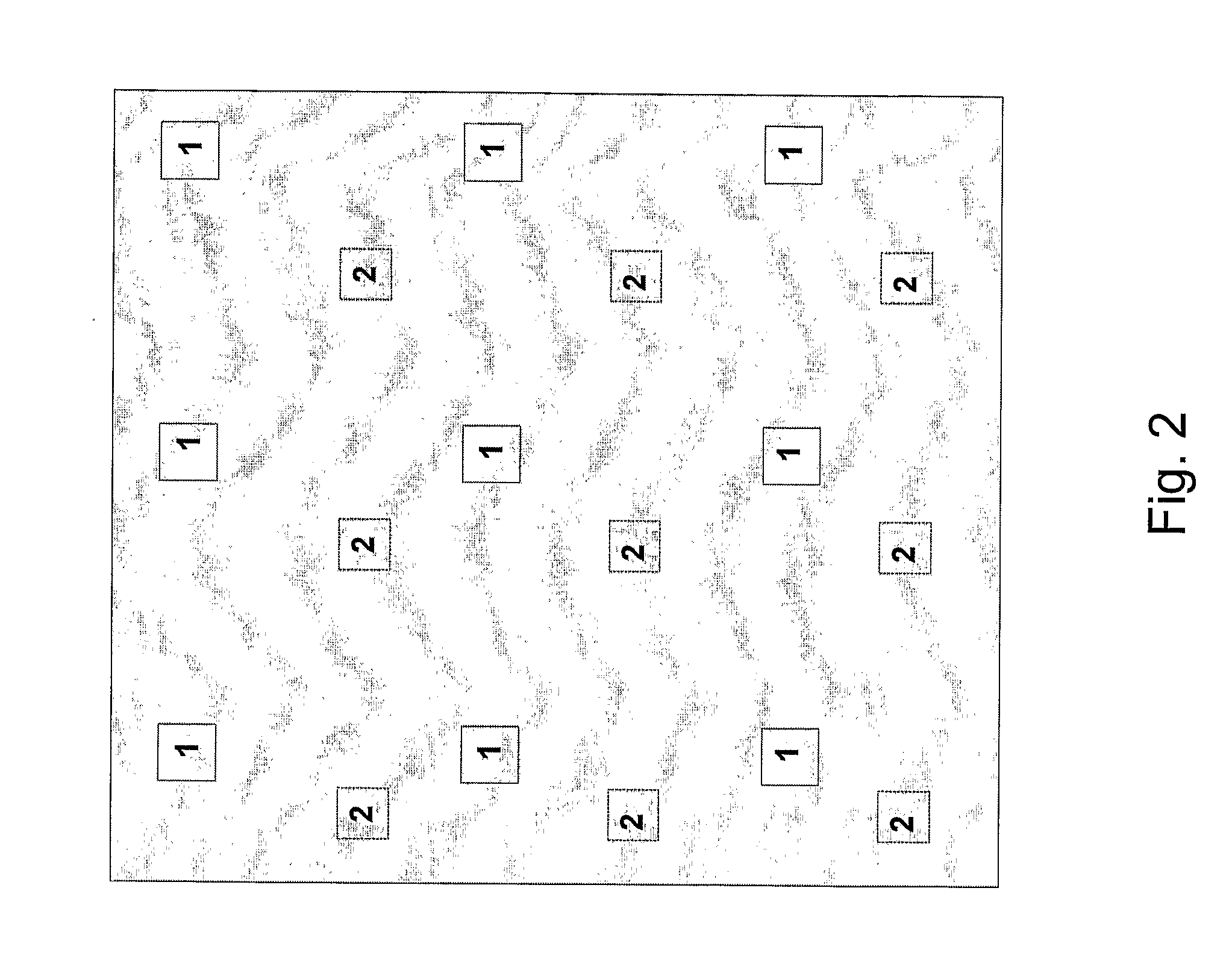
[0017]FIG. 1 shows a direction finder system including an antenna panel 10. The antenna panel includes two set of patches 1, 2 organized in separate matrices. The signals picked up by each patch set are processed in separate receiver chains 4, 5. The receiver chains output digitized signals. Preferably, each receiver chain comprises separate receivers for each individual patch if economy and space permits. The digitized signals are combined in beamforming circuitry 6, 7. The signals from the patch sets 1, 2 are compared in signal processing circuitry 8 in order to determine the direction of arrival for a signal received by the antenna panel 10. The beamforming properties of the antenna is amon...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com