Formed core sandwich structure and method and system for making same
a metal core sandwich and sheet metal technology, applied in the direction of manufacturing tools, transportation and packaging, solvents, etc., can solve the problems of loss of structural integrity, inability to easily form into compound curves and other complex shapes, and other similar conventional formed metal core sandwich structures, etc., to achieve easy and more economical manufacturing, improve the effect of structural integrity and strong brazing joints
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0032] Preferred embodiments of the invention are described in detail below with reference to the figures wherein like elements are referenced with like numerals throughout. It is understood that the figures are not necessarily drawn to scale but intended to merely illustrate some of the novel aspects, features and processes of the invention.
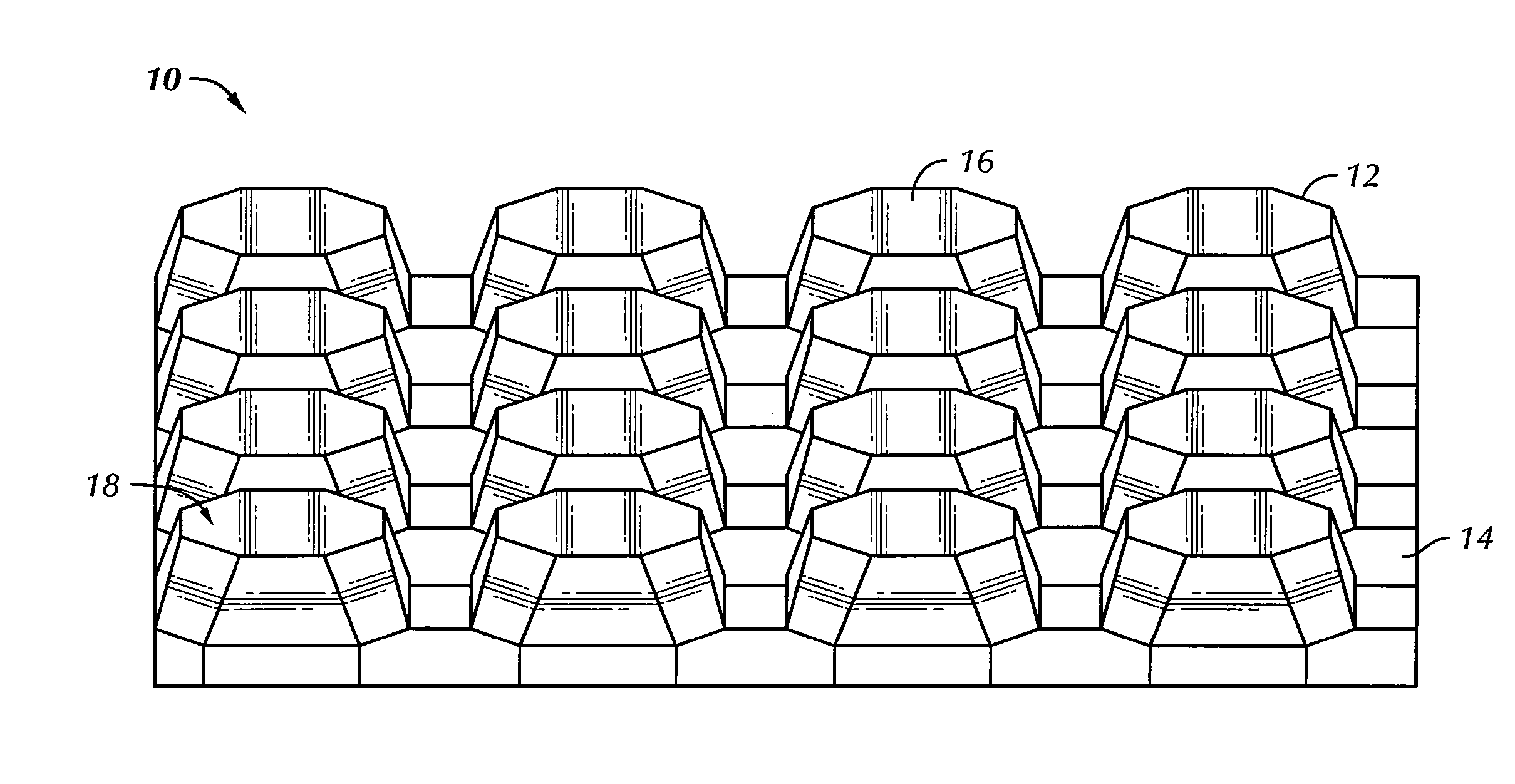
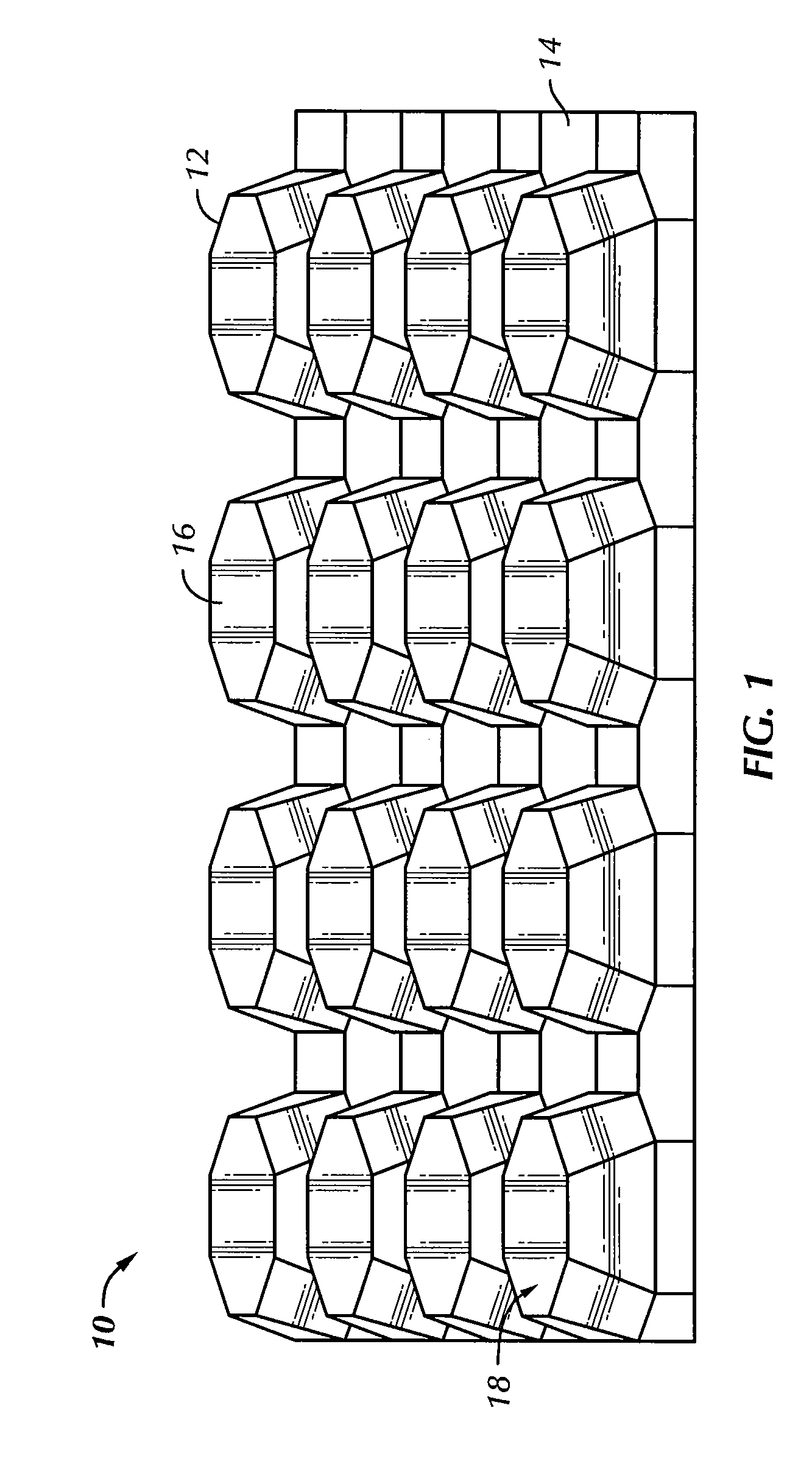
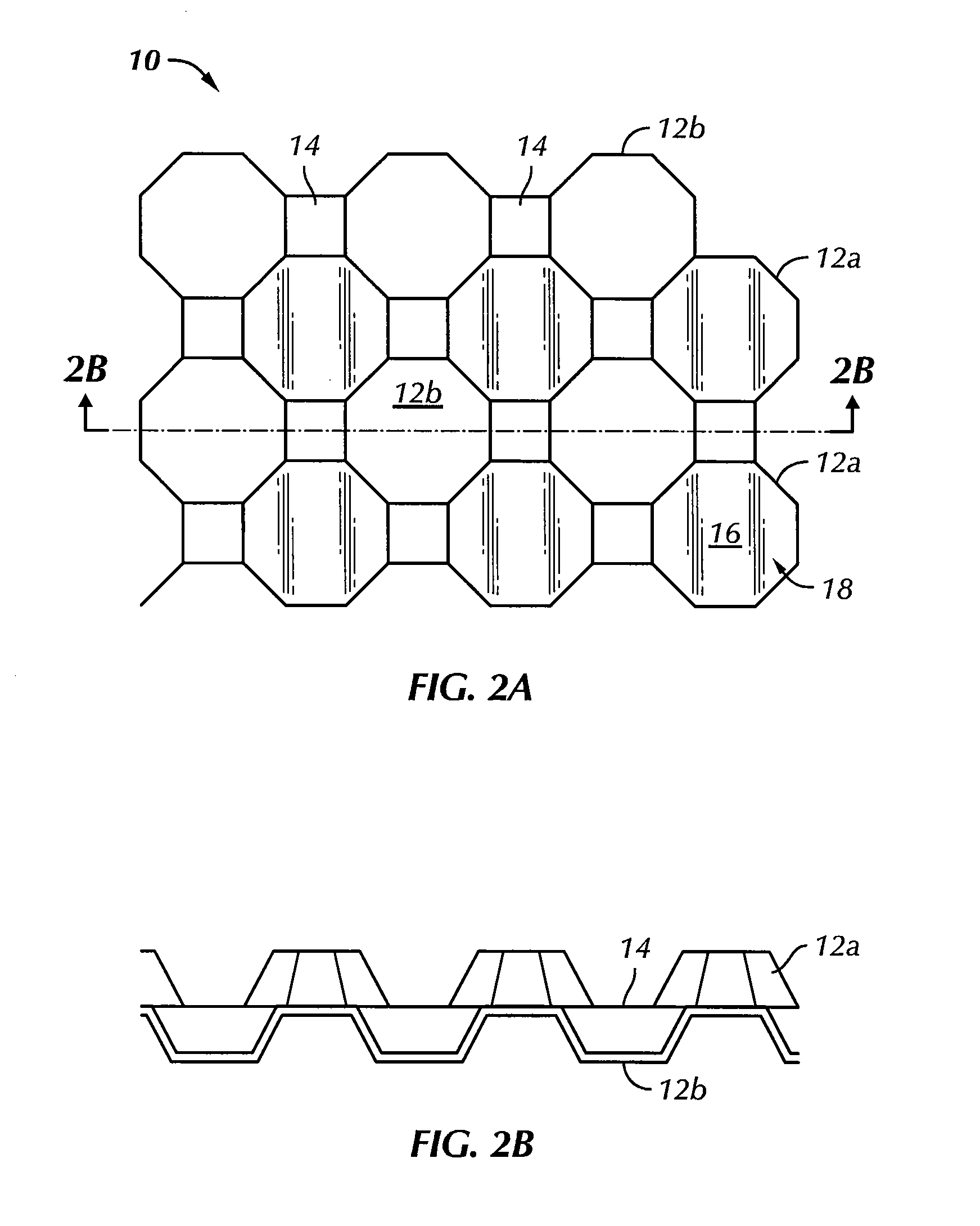
[0033]FIG. 1 illustrates a perspective view of a formed metal core 10 made in accordance with one embodiment of the invention. In this embodiment, the metal core 10 is formed in a corrugated pattern having a plurality of cells 12 comprising alternating front and rear projections extending outwardly in front of and behind a median plane 14, with each projection having a bonding surface area or land 16 configured to be brazed or bonded with corresponding external metal sheets (not shown) on both sides of the median plane 14. As shown in FIG. 1, a plurality of micro-abrasions or indentations 18 are formed on the bonding lands 16. As explained in f...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com