Polymorphisms in the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Gene Promoter
a technology of epidermal growth factor and gene promoter, which is applied in the field of molecular biology and oncology, can solve the problems that the variable expression of egfr may directly affect drug response and toxicity, and achieve the effect of reducing the toxicity of egfr-targeting therapeutic agents
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Discovery of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) in EGFR Regulatory Region
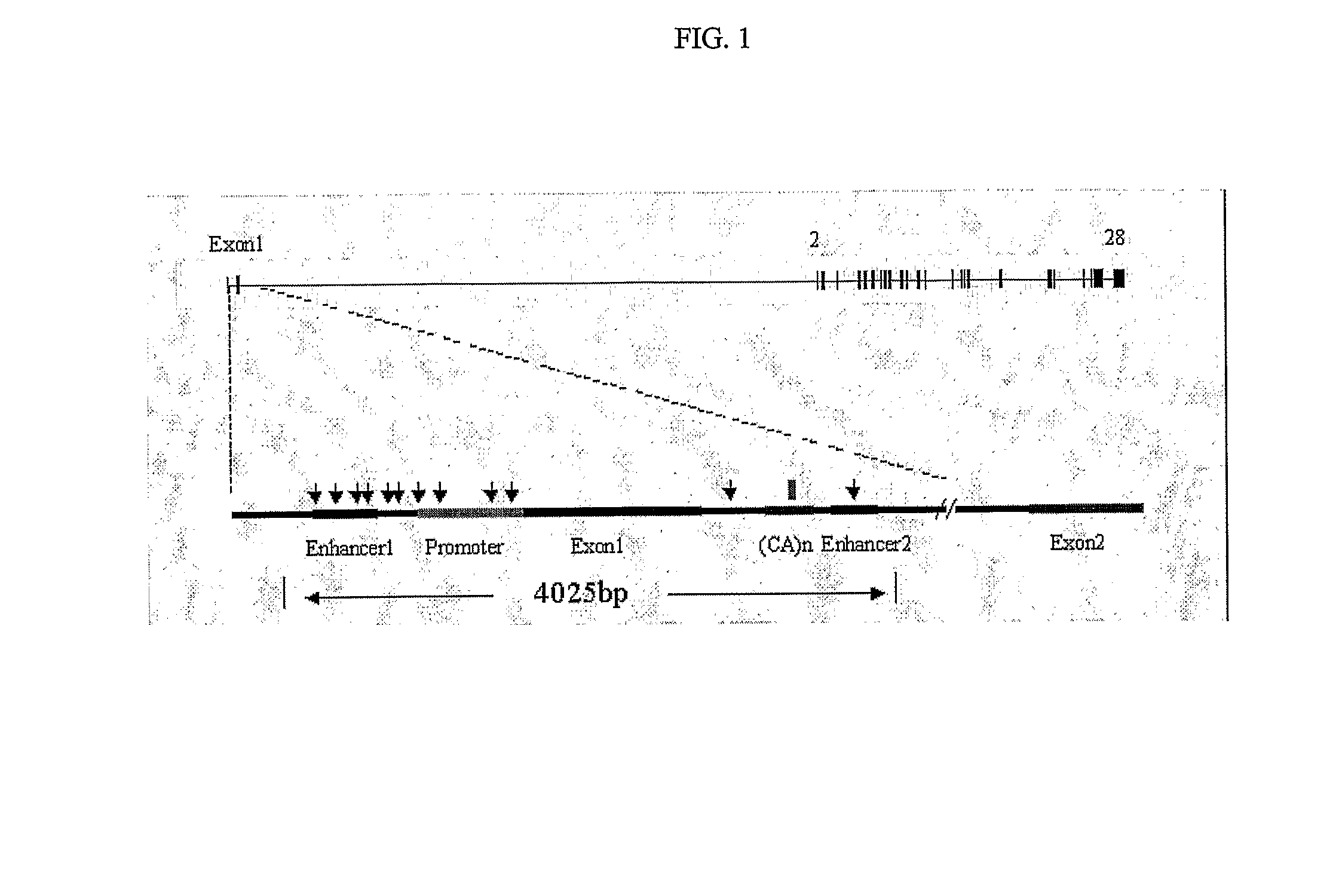
[0158] DNA samples from Coriell Cell Repository were used for resequencing. The samples include 22 Caucasians, 23 African-Americans and 23 Asians. For SNP discovery, PCR was used to amplify the approximately 4.5 kb fragment containing the upstream and downstream enhancer, promoter, exon 1 and part of intron 1 using the primers in Table 1. Purified PCR products were directly sequenced from both ends. ABI-3700 capillary sequencer and a phred / phrap / polyphred / consed pipeline (World Wide Web at phrap.org / ) were used to identify the polymorphisms.
TABLE 1SEQ ID NO: 3EGFR1L-FGTTCCACTGTTGTGCTTCCC 4EGFR1L-RAAGAAAGTTGGGAGCGGTTC 5EGFR1L-AFGGGTGGACTTGCCAAAGGA 6EGFR1L-ARCTTAGAGCCAGCGTCGGATA 7EGFR1L-1FGCATGACTTCAACGCACAGT 8EGFR1L-1RGAGGCTAAGTGTCCCACTGC 9EGFR1L-2FTCGGACTTTAGAGCACCACC10EGFR1L-2RGAGGAGGAGAATGCGAGGAG11EGFR1L-3FAAATTAACTCCTCAGGGCACC12EGE11L-3RCGCCCTTACCTTTCTTTTCC13EGFR1L-4FCCCTGACTCCGTCCAGTATT14EGFR2L-FCGTC...
example 2
Functional Characterization of Two Promoter SNPs (−216G>T and −191 C>A).
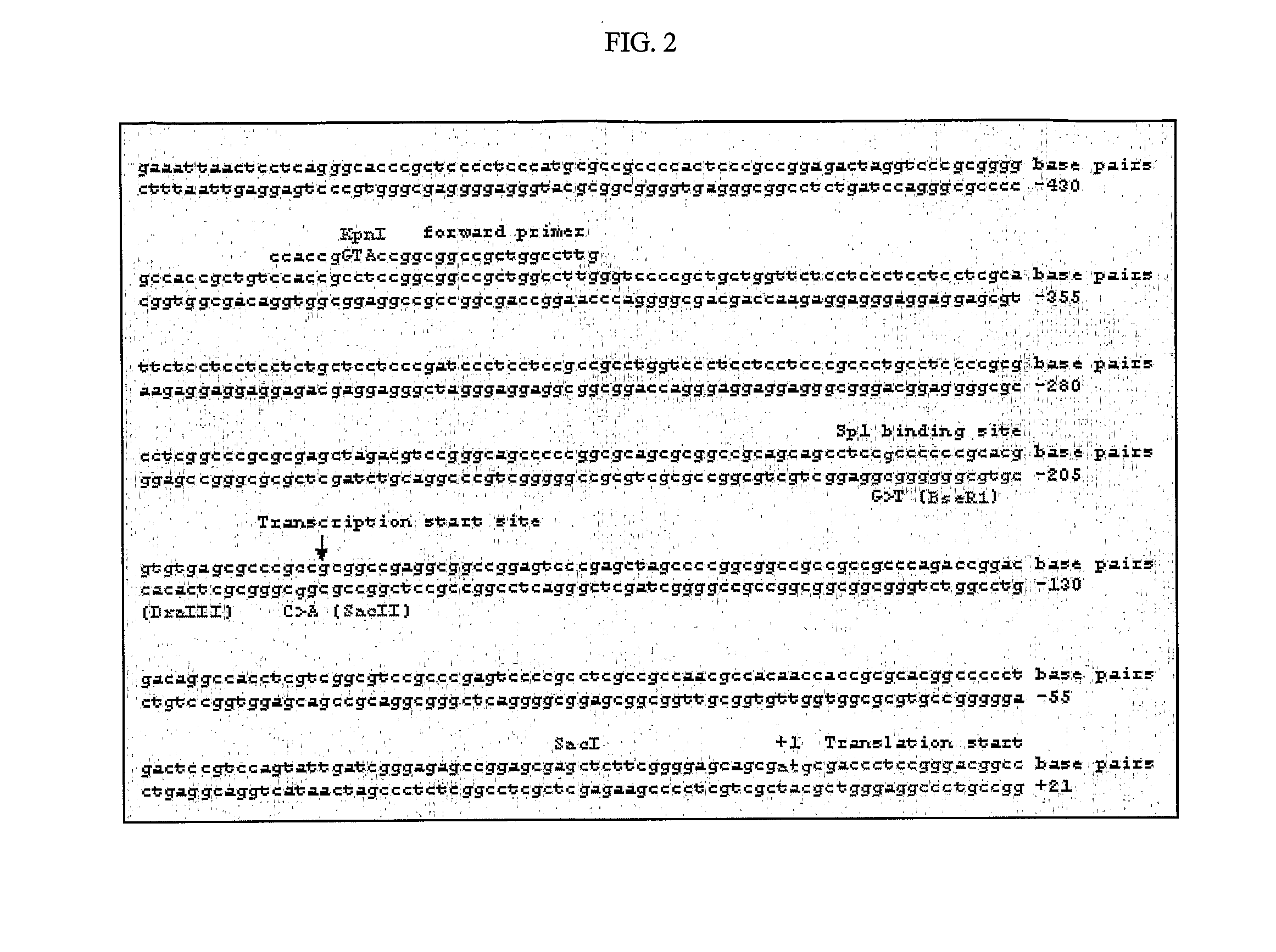
[0160] Potential function of two SNPs (−216 G>T and −191 C>A) in the EGFR promoter region were characterized by in vitro transient transfection assay and electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA).
[0161] Haplotypes.
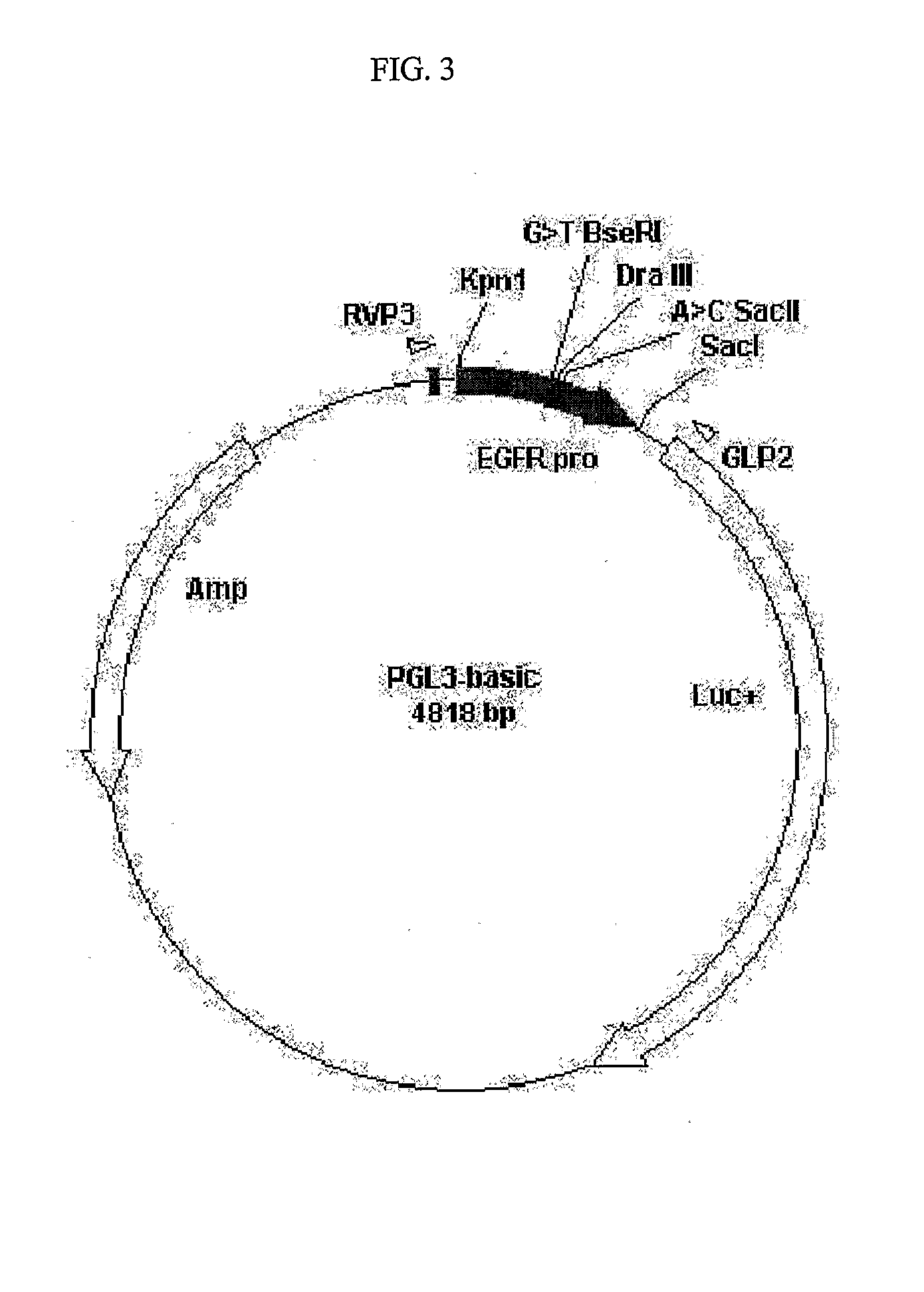
[0162] The SNP −216 G>T was found to be frequent in African-Americans (29%) and Caucasians (34%) but relatively rare in Asians (9%), while −191 C>A was only found in Caucasians (18%) when the inventors sequenced the 68 samples from different ethnic groups (Table 3). Linkage disequilibrium and haplotype analysis showed that −216 G>T and −191 C>A are not in strong LD (D′=0.5562, p>0.05,) and three haplotypes were observed in the samples: G-C, G-A and T-C, see Table 3 below. DNA fragments containing these three haplotypes were amplified and cloned while the T-A haplotype was constructed by ligating the T fragment and A fragment from the Dra III digested G-A and T-C haplotypes (FIG. 3).
TABLE 3The ha...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Magnetic field | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Magnetic field | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Magnetic field | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com