Method for conditioning a polishing pad
a polishing pad and polishing technology, applied in the field of integrated circuit fabrication, can solve the problems of increasing the production cost per substrate, increasing reducing the processing cost per substrate, so as to increase the removal rate and increase the removal rate of conductive materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
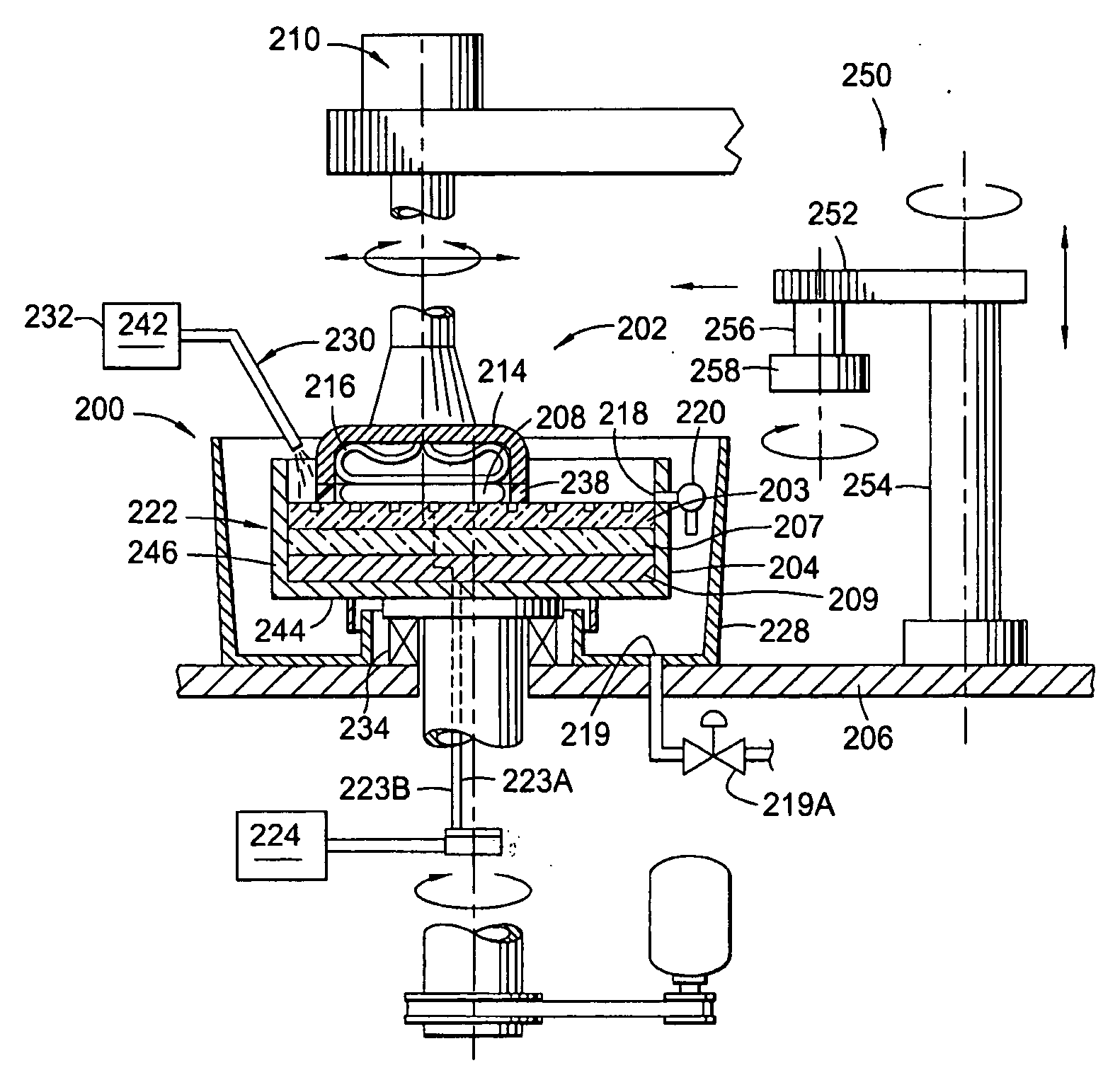
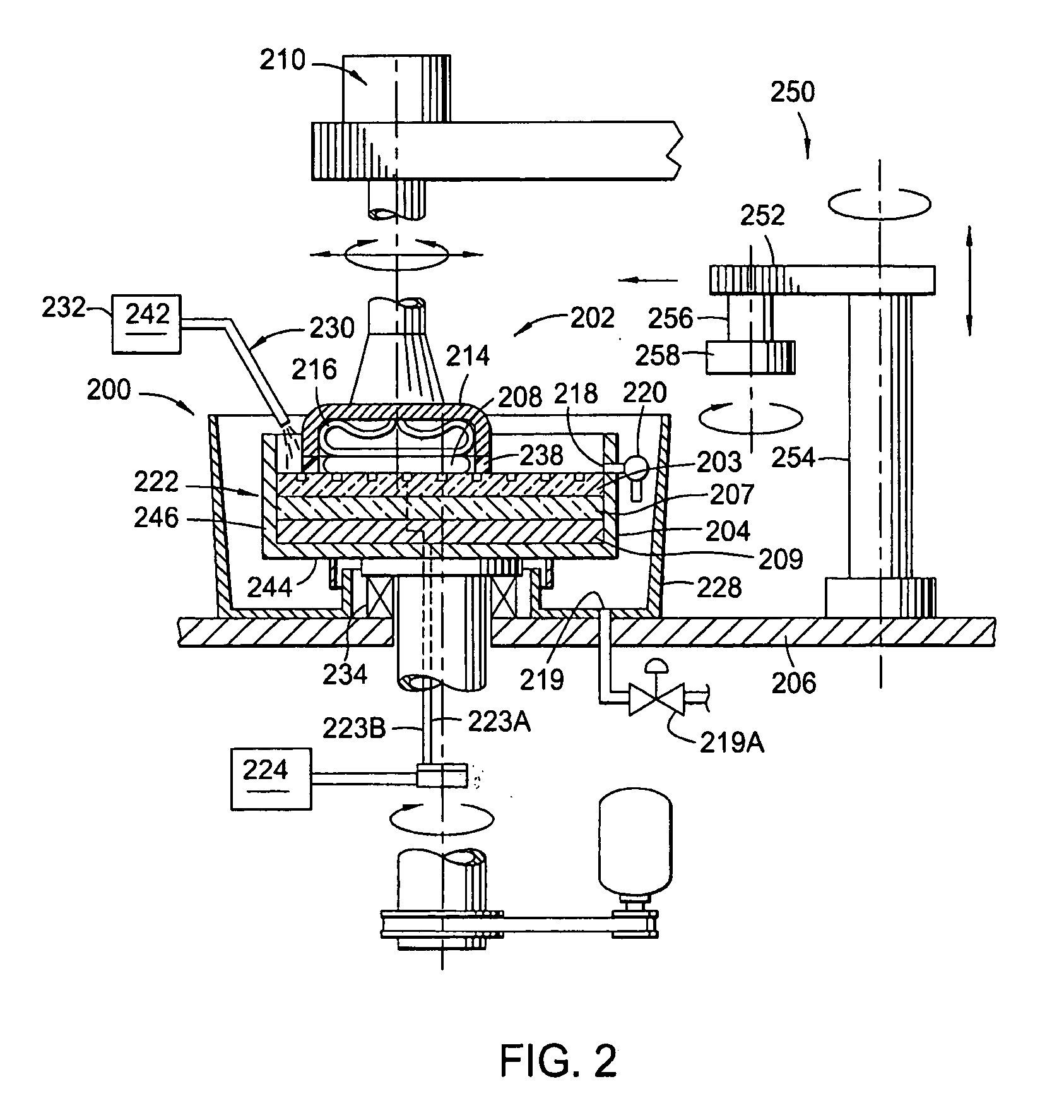
[0026]FIG. 2 is a cross-sectional view of one example of an ECMP station 200 that may be used to practice aspects of the invention. The process cell 200 generally includes a basin 204 and a polishing head 202. A substrate 208 is retained in the polishing head 202 and lowered into the basin 204 during processing in a face-down, i.e., production side down, orientation. An electrolyte, as described herein, flows into the basin 204 and is in contact with the surface of substrate 208 and a processing pad assembly 222, while the polishing head 202 places the substrate 208 in contact with the processing pad assembly 222. The basin 204 includes the processing pad assembly 222, a bottom 244 and sidewalls 246 that define a container that houses the processing pad assembly 222. The sidewalls 246 include a port 218, formed therethrough to allow removal of polishing composition from the basin 204. The port 218 is coupled to a valve 220 to selectively drain or retain the polishing composition in ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| voltage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| radial velocity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| velocity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com