Fluid-specimen collecting and testing device and method for recording chromatographic assay test results
a technology for chromatographic assay and specimen collection, which is applied in the field of fluid specimen collection and testing devices and methods for recording chromatographic assay test results, can solve the problems of limited devices, difficult to locate a proper place for discarding excess specimens, and health risks of the person conducting the test, etc., and achieves convenient use, reliable results, and cost-effective
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
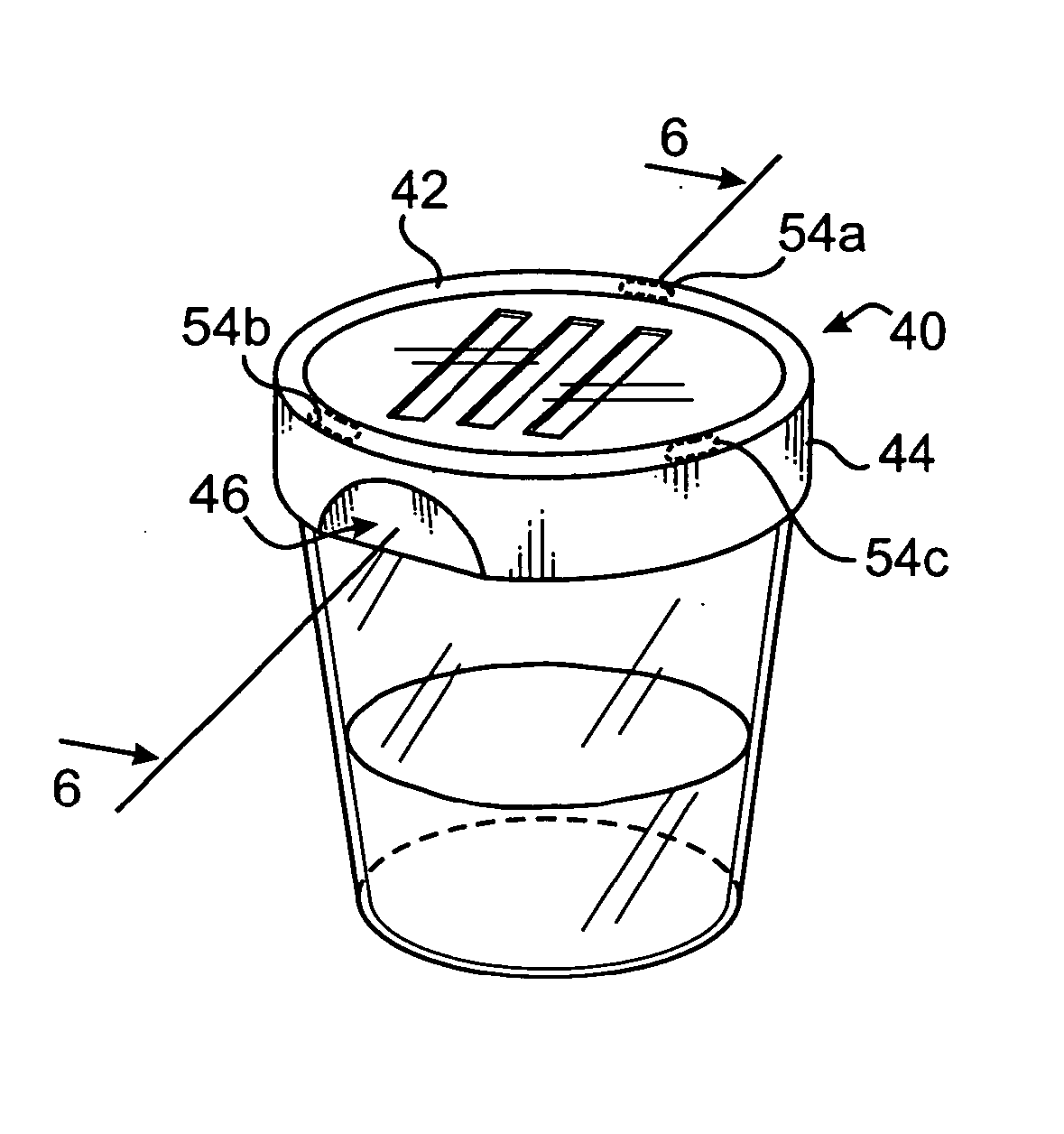
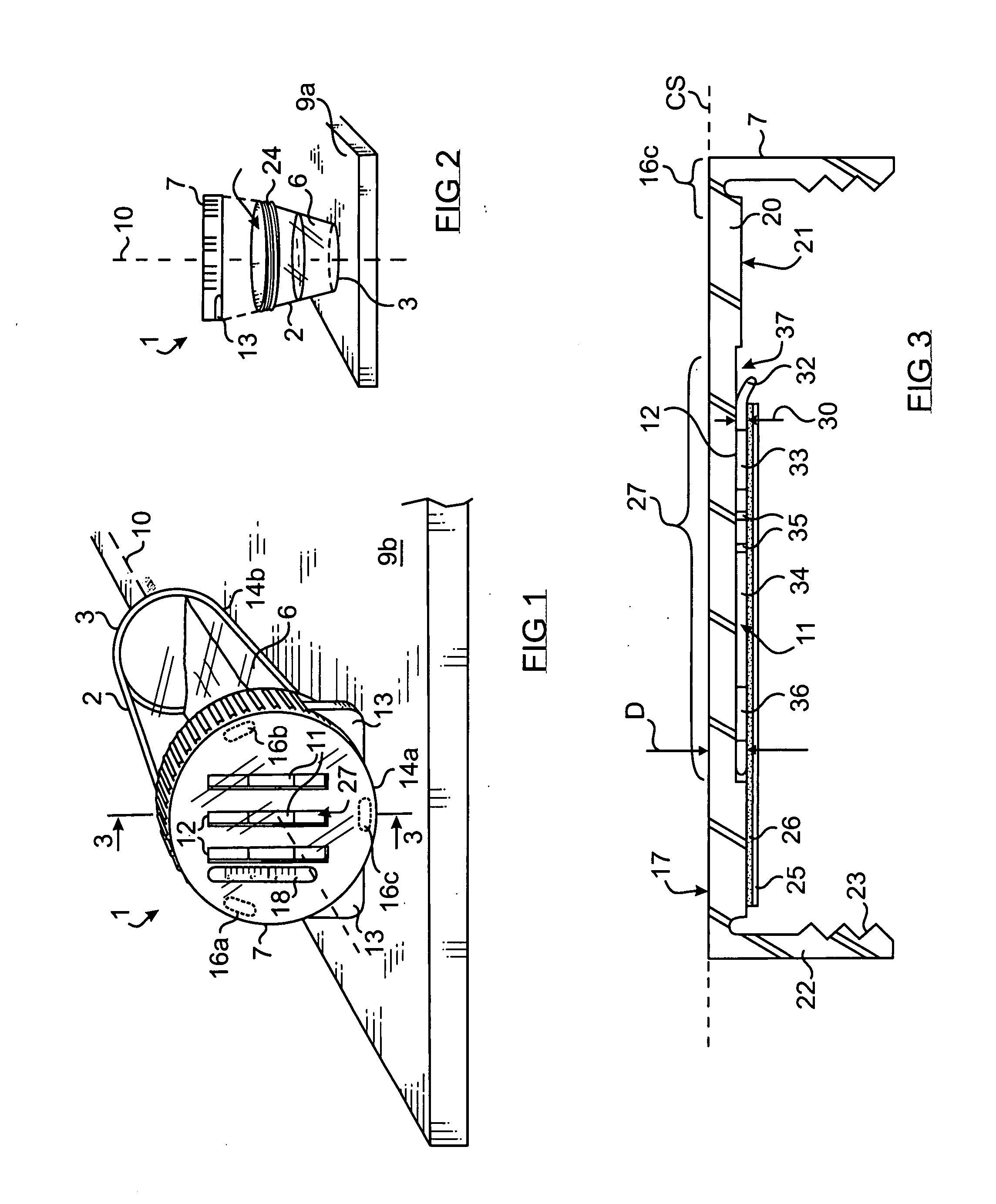
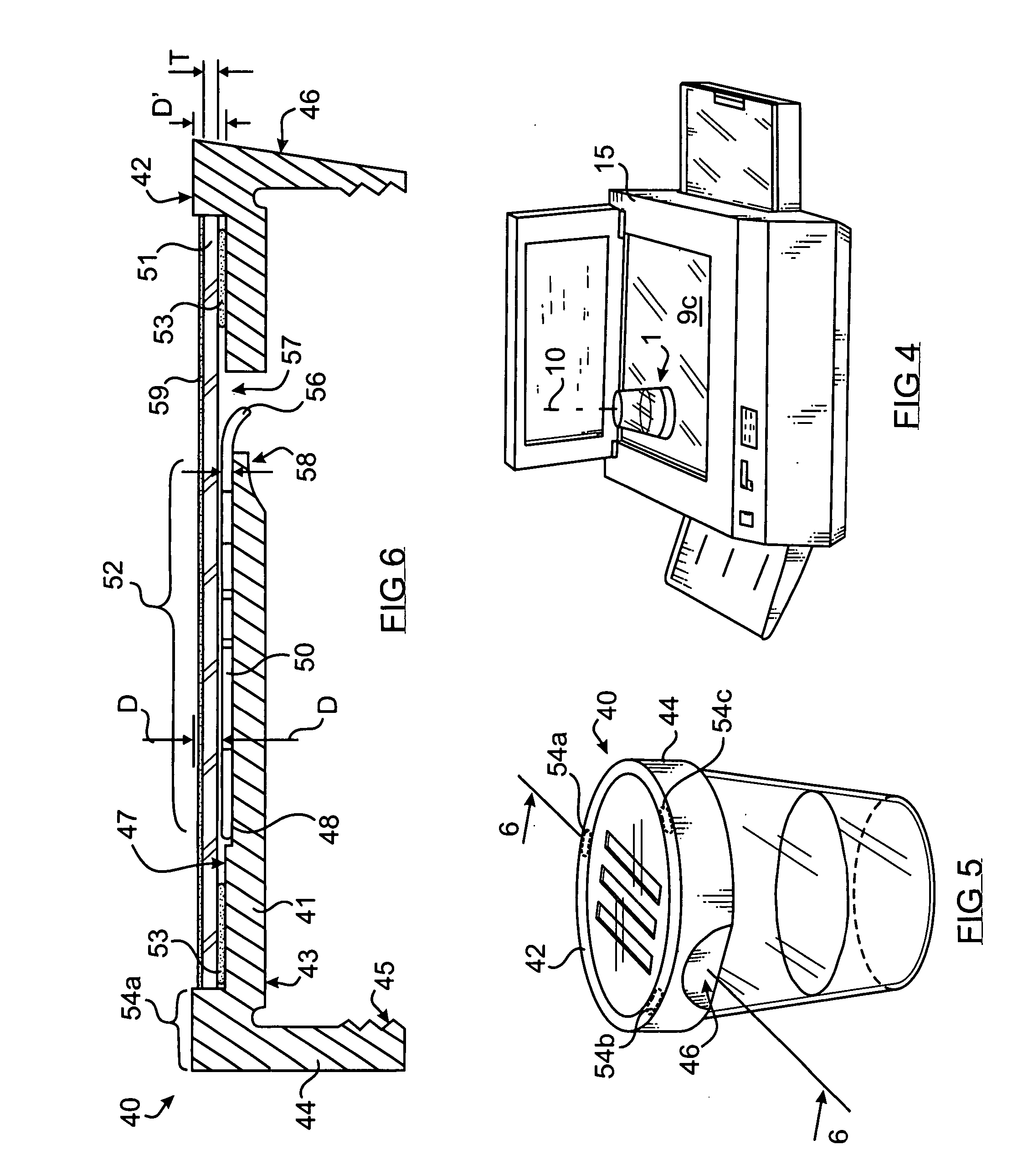
[0024] Referring now to the drawing, there is shown in FIG. 1 through 4 a first embodiment of a fluid-specimen containing and testing device 1 having a cup portion 2 having a closed bottom end 3 and an opposite top opening 4 defining an inner chamber 5 for collecting a fluid specimen 6, and a lid 7 sized and shaped to seal the opening by corresponding threading 8. Other means well known in the art may be used to seal the lid to the cup.
[0025] As shown in FIG. 2, the bottom end 3 of the cup is flattened to allow it to rest on a substantially horizontal surface 9a in a stable, upright position and contain the specimen. The major axis 10 of the device is substantially vertical when the device is in an upright orientation.
[0026] The lid 7 has a substantially rigid, disk-shaped top portion 20 having a substantially planar outer, upper surface 17 and inner, lower surface 21. A substantially cylindrical flange 22 extends downward from the periphery of the top portion having inner threads...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com