Sheet metal forming process
a metal sheet and forming technology, applied in metal-working apparatus, manufacturing tools, shaping tools, etc., can solve the problems of metal failure or fatigue, inability to use or scrap parts, and limited processes, so as to improve the forming aspect ratio, reduce the forming time, and improve the forming efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
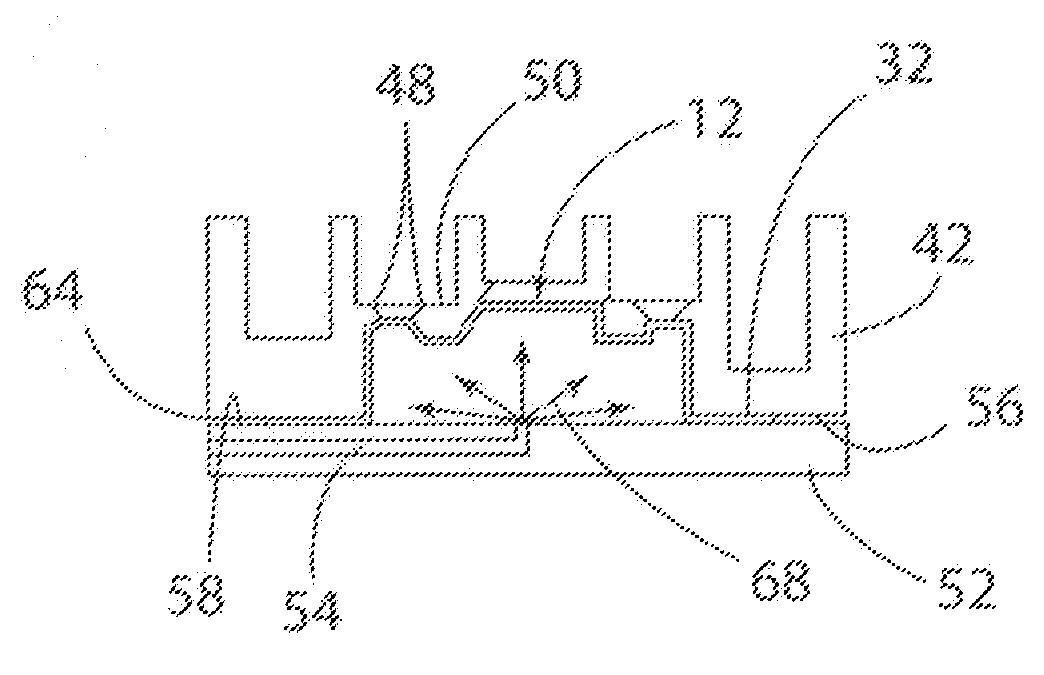
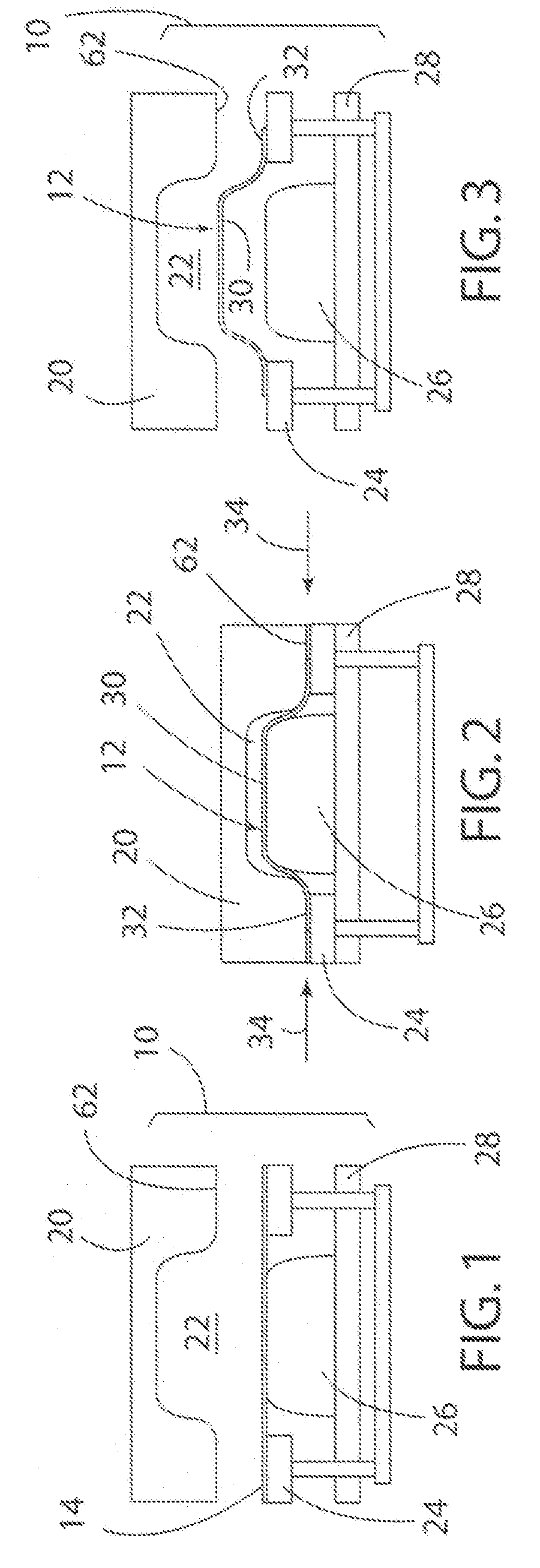
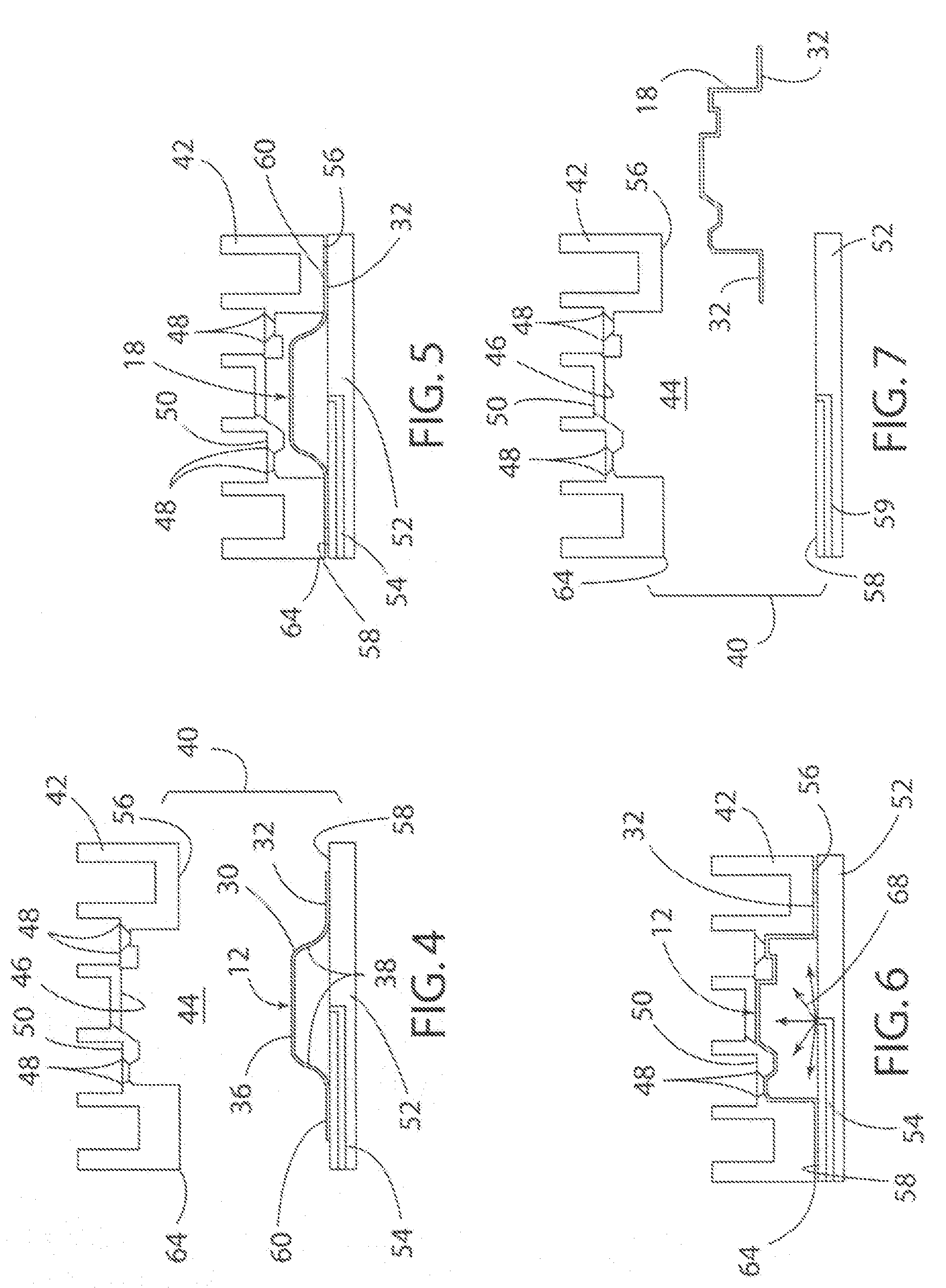
[0022]Referring now to the drawings, FIGS. 1-3 schematically illustrate a double-action draw die 10 used to create a preform 12 from a blank 14 according to a first stage of the present invention. FIGS. 4-7 schematically illustrate a second stage of the present invention using a superplastic forming tool 40 to complete the forming process on the preform 12 to create a finished workpiece 18. Typically, the process of the present invention is utilized with a blank 14 made of a lightweight sheet material, including a sheet of material formed of various aluminum and magnesium alloys. As shown in FIG. 1, the draw die 10 includes an upper die member 20 having a die cavity 22, a blank holder 24 and a punch 26 located on a lower die platen or member 28. Prior to beginning the forming process the draw die 10 is placed in a dual or double-action press (not shown) that operates to move the blank holder 24 independent of the punch 26.
[0023]A first step in the forming process is to place or load...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| gas pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com