Nanoparticulate based lubricants
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
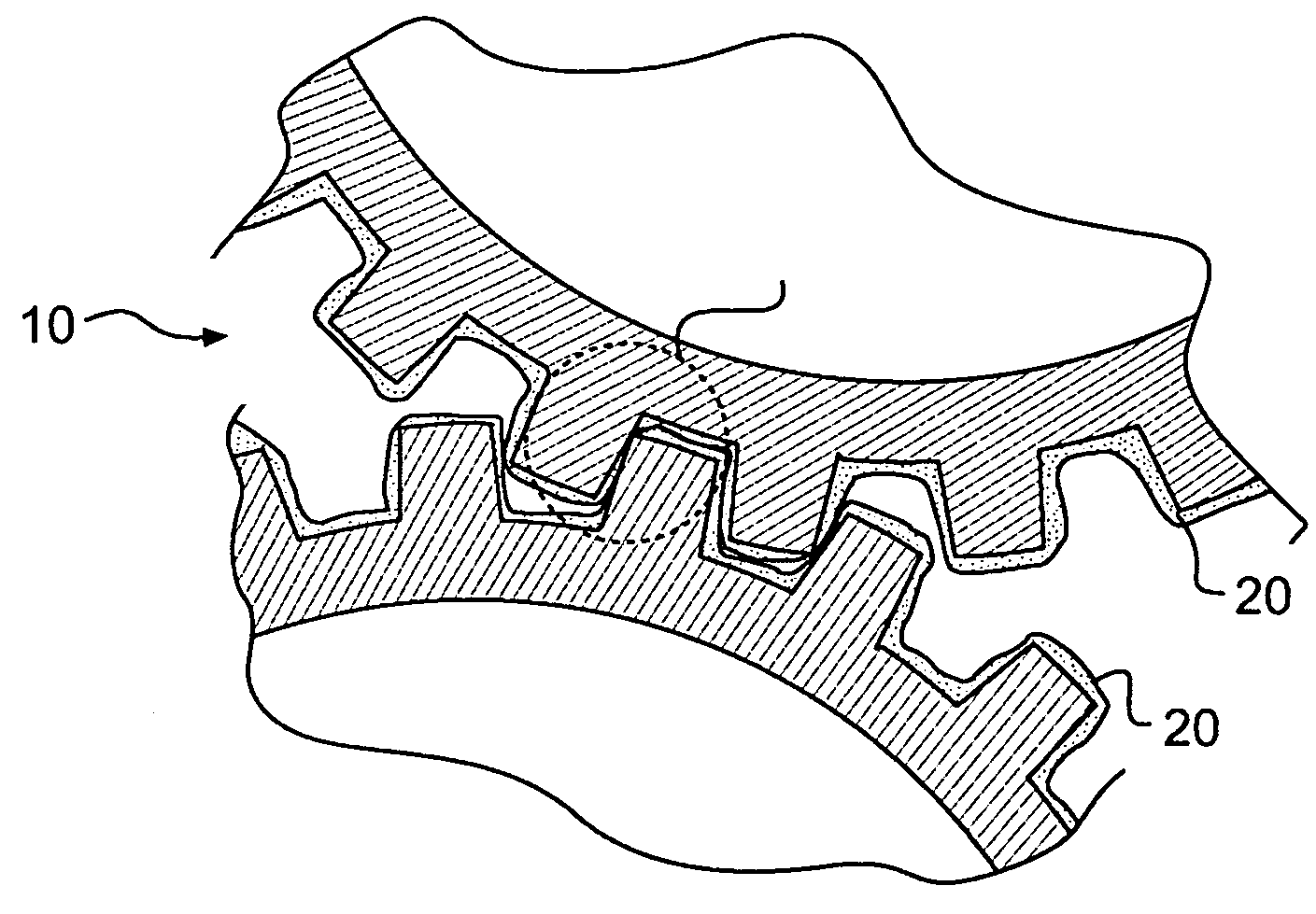
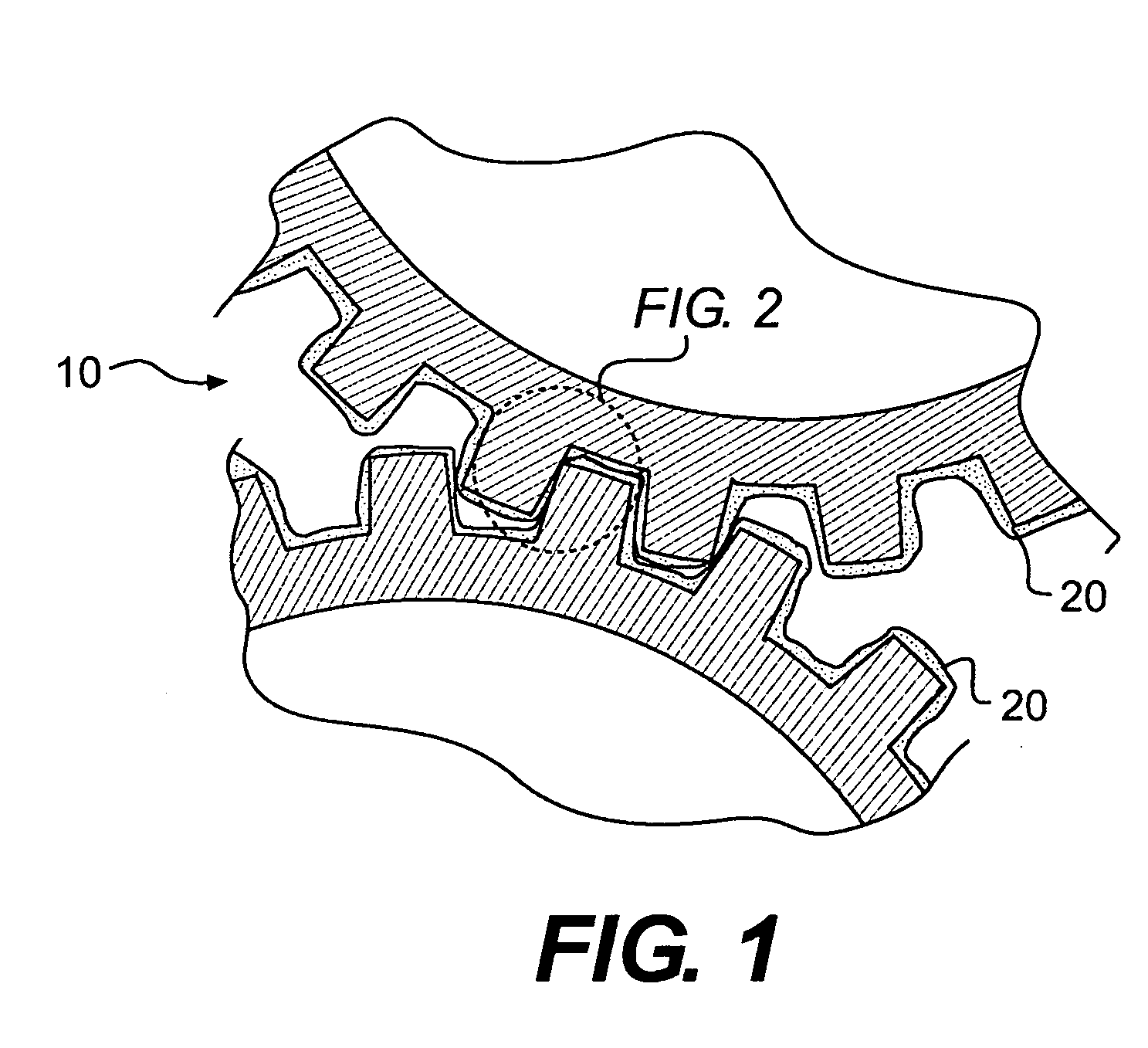
[0015]FIG. 1 illustrate exemplary surfaces 10 under frictional contact. These surfaces 10 may be part of a machine that performs some sort of operation associated with an industry. Non limiting examples of surfaces 10 may include, contacting surfaces of a piston and a cylinder within an internal combustion engine, mating surfaces of a transmission gear assembly, etc. A lubricant 20 is disposed between the surfaces 10 under frictional contact. The lubricant 20 may be a substance introduced between the surfaces 10 to reduce the friction and wear therebetween. In some cases, this reduction in friction may be accomplished by the lubricant 20 forming a protective film on the surfaces 10.
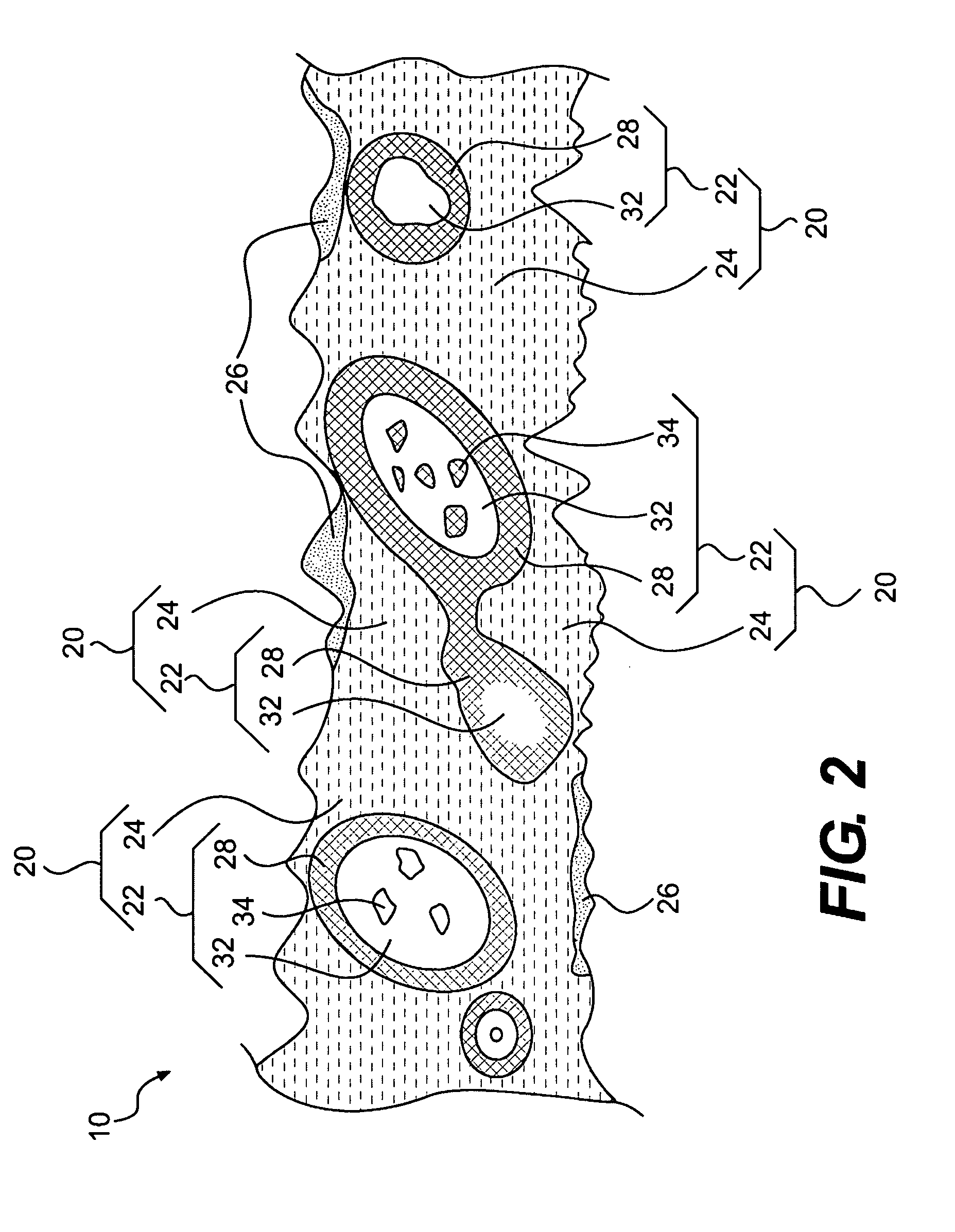
[0016]The lubricant 20 may, in some cases, be composed of several different materials. The lubricant 20 may include a liquid such as organic oils (for example, vegetable oils, seed oils and mineral oils), hydrocarbon base oils (for example, fossil fuel based oils), synthetic liquids (for example, hydrogen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com