Deployment of polysaccharide markers
a polysaccharide and marker technology, applied in the field of polysaccharide markers, can solve the problems of inaccuracy, misdirected follow-up treatment to an undesired portion of the patient's tissue, and rapid hemostasis, and no long-term irritation or inflammation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
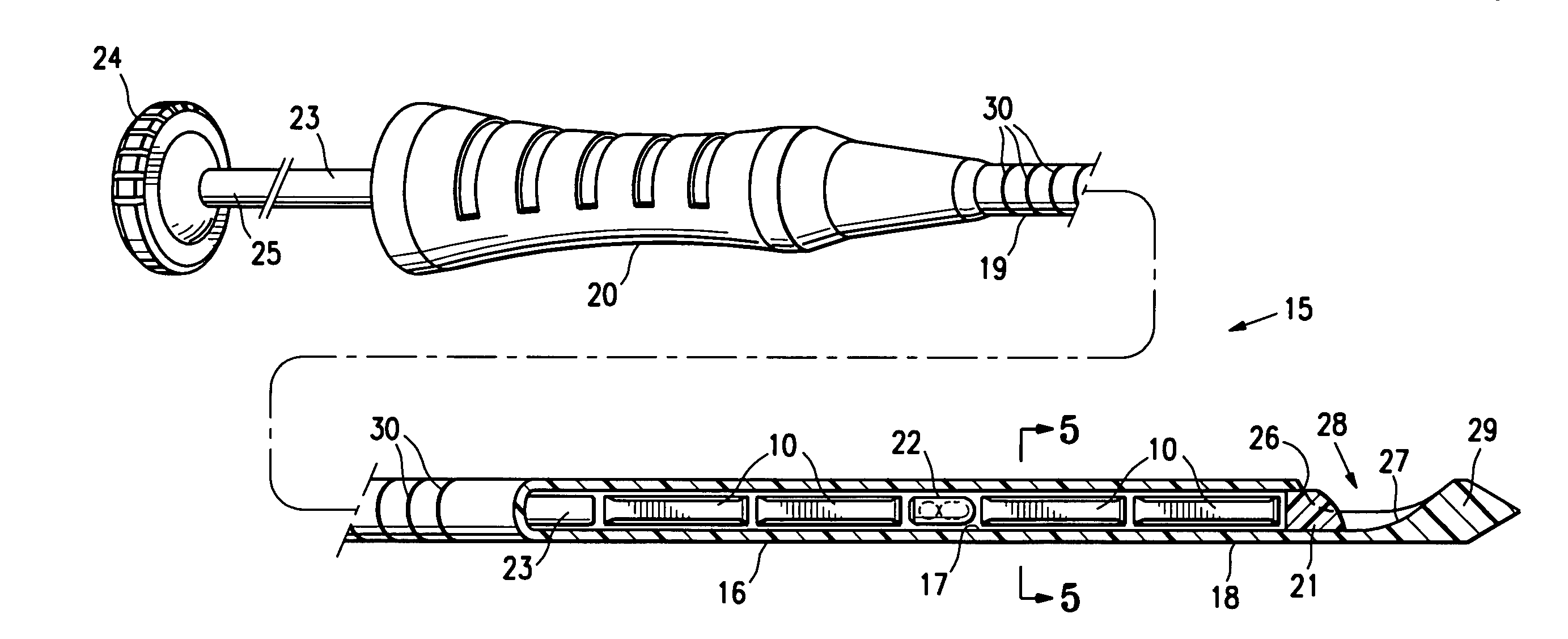
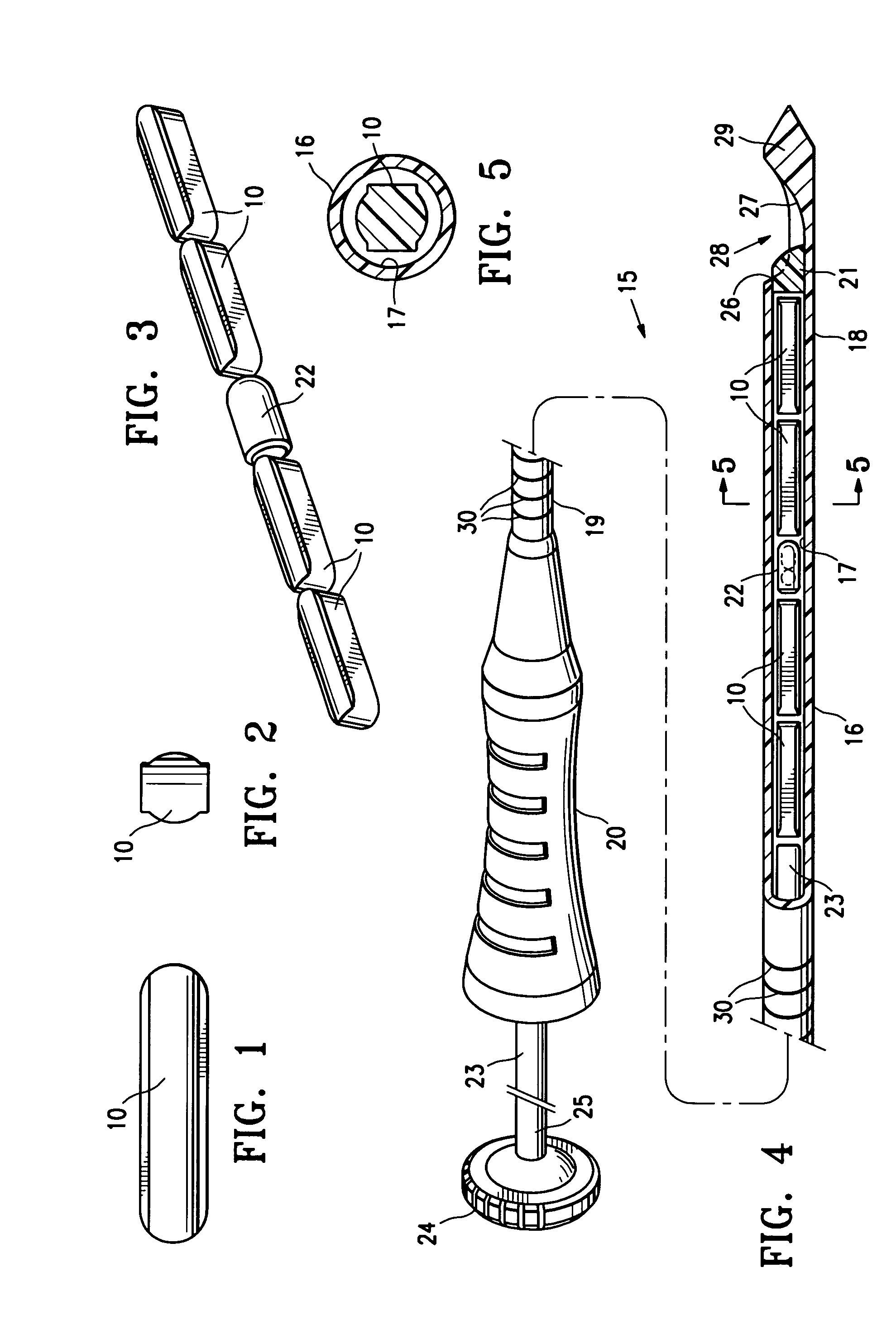
[0030]FIGS. 1 and 2 illustrate a press-formed marker member 10 embodying features of the invention which is formed of a mixture of polysaccharide powder and methylcellulose powder. The press-formed marker member 10 has sufficient polysaccharide powder so as to quickly form thrombus when coming into contact with blood at an intracorporeal site. Typically, the marker member 10 will have 65% (by wt.) polysaccharide and 35% (by wt.) methylcellulose. The marker member 10 is preferably formed by mixing polysaccharide powder (corn starch or potato starch) and methylcellulose powder in appropriate amounts, placing the mixed powder in a pellet die and subjecting the powder within the pellet die to a pressure of about 6 to 40 ksi, typically about 12 ksi.
[0031]One suitable polysaccharide material is U.S.P. Topical Starch. Alternatively, Hemaderm™, which is available from Medafor, Inc. located in Minneapolis, Minn., may also be used. This product is described at least in part in U.S. Pat. No. 6...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com