Method and device for determining a gradient-limited cumulative setpoint torque from a setpoint torque of a closed-loop speed control
a technology of closed-loop speed control and cumulative setpoint torque, which is applied in the direction of motor/generator/converter stopper, electric control, dynamo-electric converter control, etc., can solve the problems of delay in torque generation and reduction, annoy the driver, and affect the driving comfort. , to achieve the effect of high control quality and high dynamic performan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
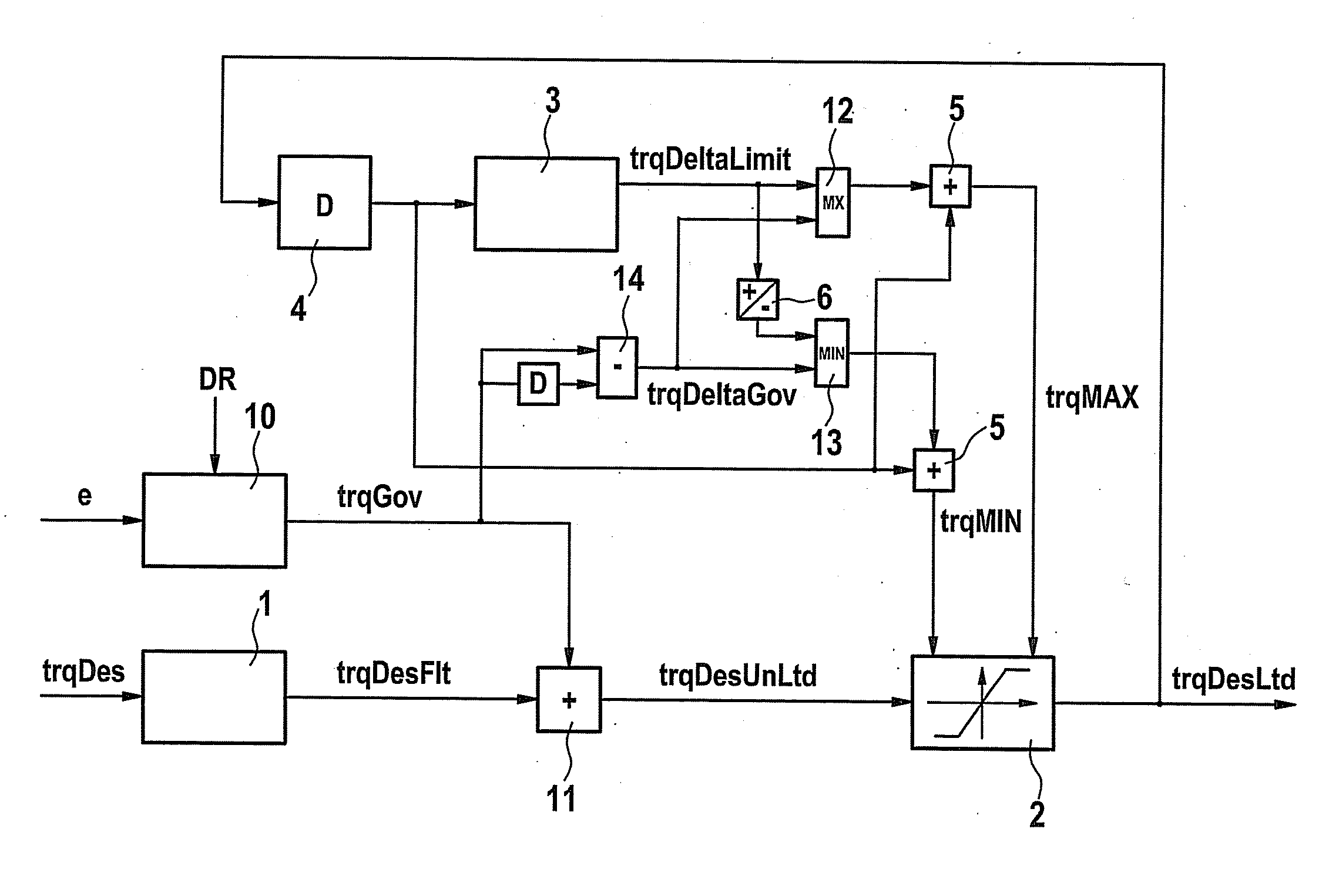
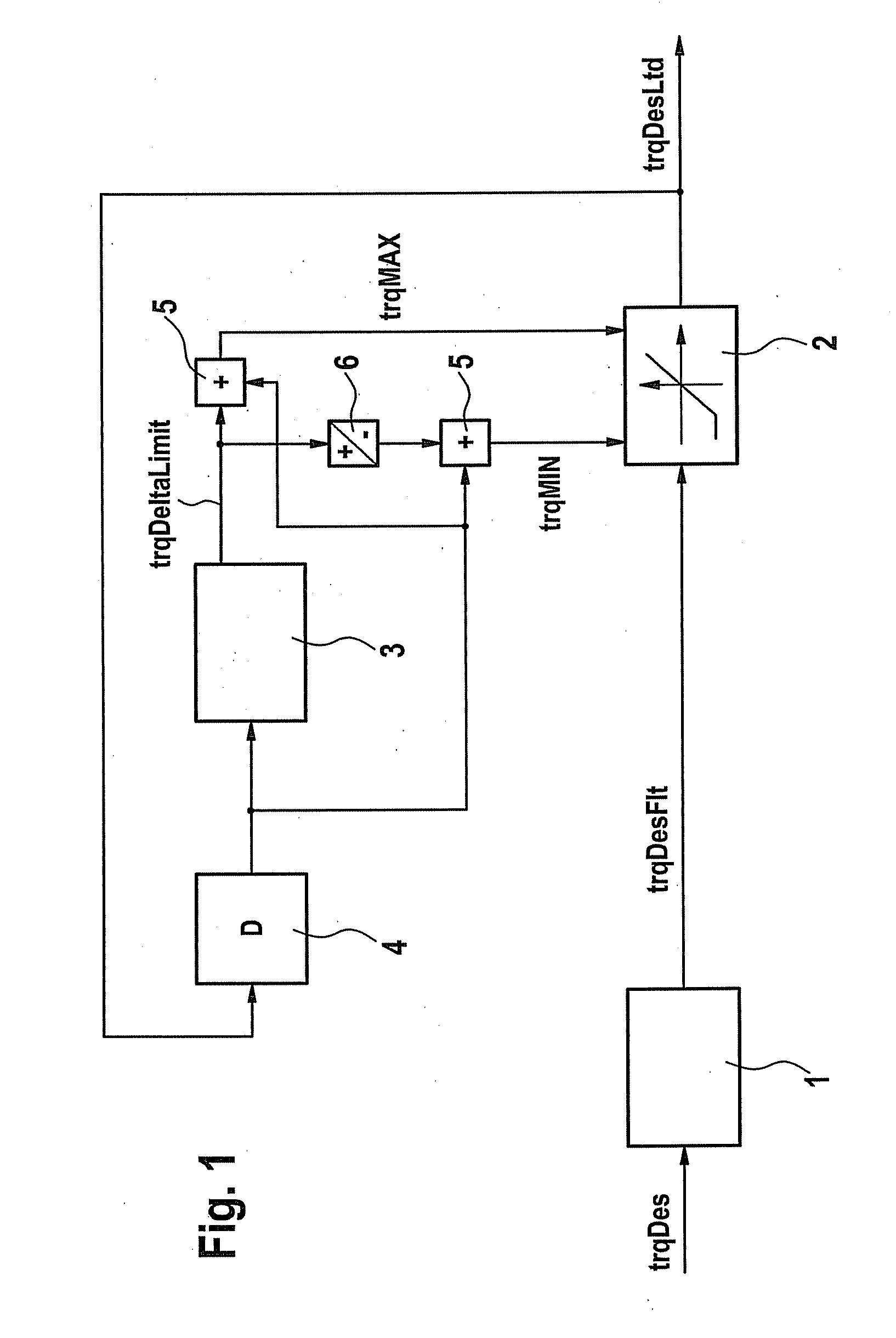
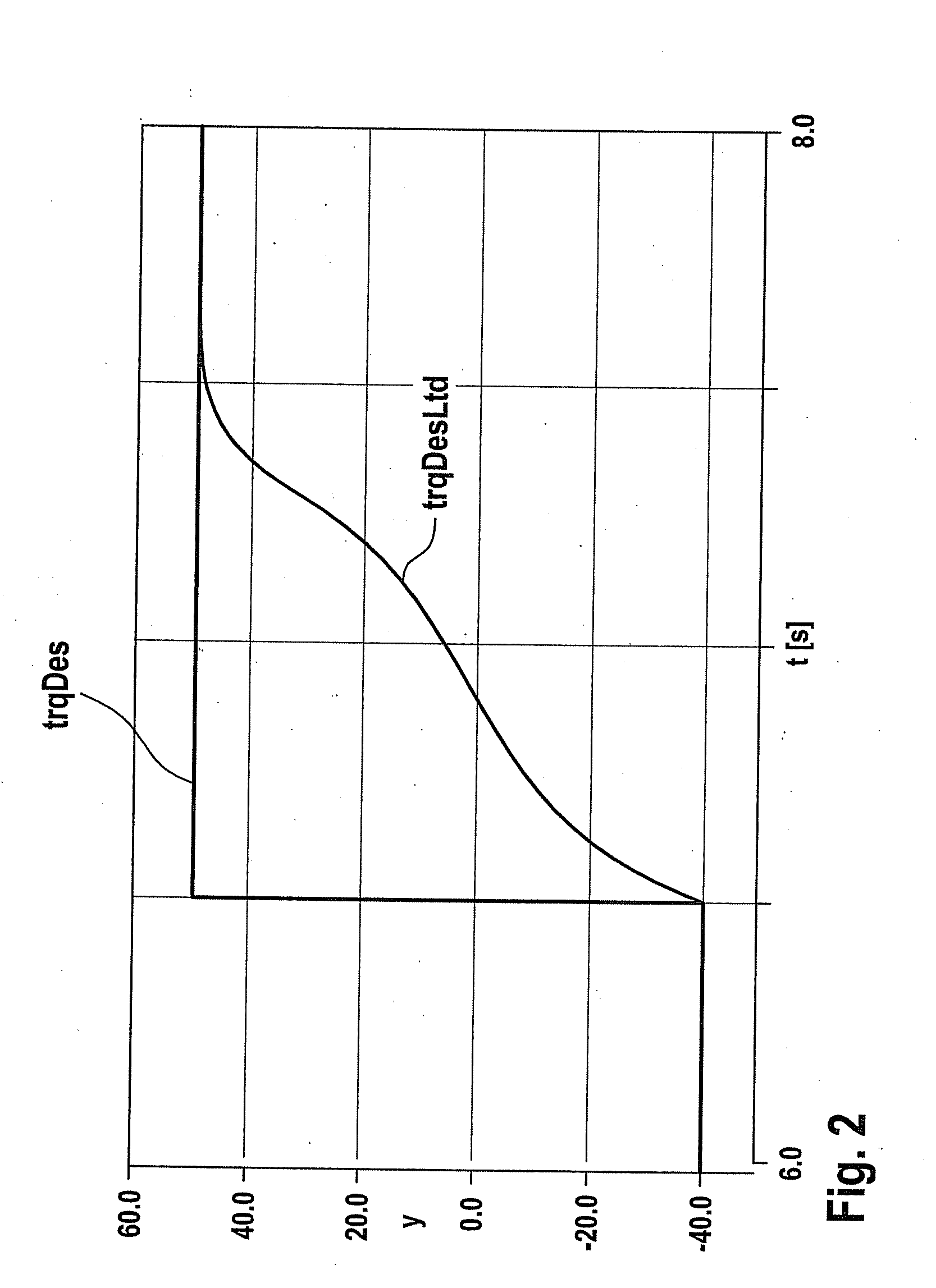
[0027]One possible realization of torque formation is shown in FIG. 1. A setpoint drive torque trqDes requested by, for instance, a driver (via the gas pedal position) or requested by other vehicle devices is forwarded to a filter stage 1 where it is low-pass-filtered. Filtered setpoint drive torque trqDesFlt obtained in this manner is then forwarded to a rate-of-change limiter 2, which implements a rate-of-change limitation (limitation of the first derivative) of filtered setpoint drive torque trqDesFlt. A limited setpoint torque trqDesLtd is obtained as output of rate-of-change limiter 2.
[0028]Rate-of-change limiter 2 implements the rate-of-change limitation by being supplied with a highest permitted value trqMAX and a lowest permitted value trqMIN for limited setpoint torque trqDesLtd. If filtered setpoint drive torque trqDesFlt transmitted to rate-of-change limiter 2 exceeds the highest permitted value trqMAX for limited setpoint torque trqDesLtd, or if it undershoots lowest per...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com