Blood Pressure Reduction in Salt-Sensitive Hypertension
a salt-sensitive hypertension and blood pressure reduction technology, applied in the field of mammals' blood pressure reduction methods, can solve the problems of poor control rate in all countries, refractory to presently available treatments, and disorder cannot be cured, so as to achieve less magnitude, prolong the effect of life and reduce the severity of the diseas
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
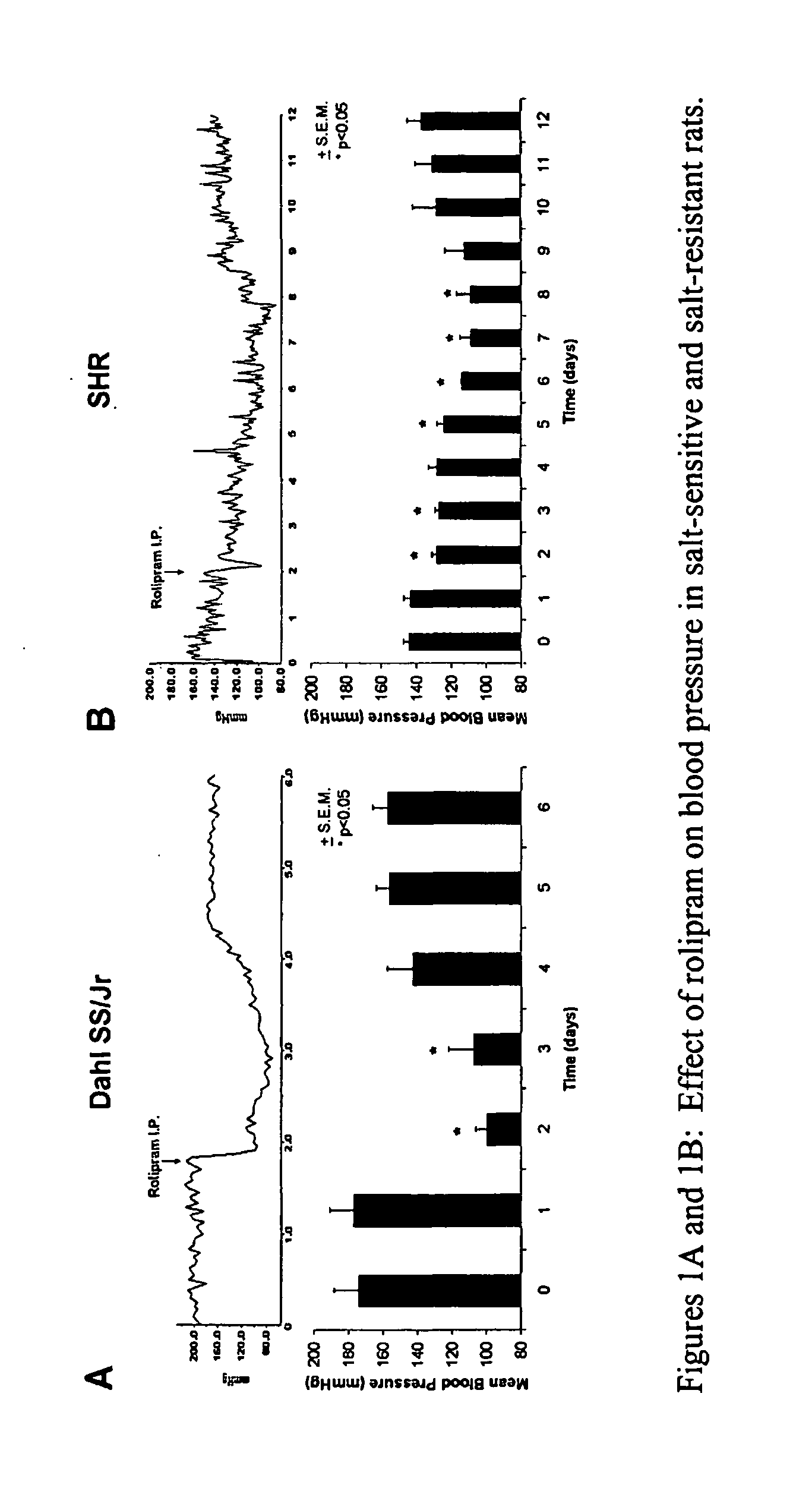
Effect of PDE4 Inhibitors on Blood Pressure
[0063]The effect of PDE4 inhibitors on salt-sensitive hypertension was demonstrated using male Dahl salt-sensitive (SS / Jr) rats (250-300 gm, Harlan, Indianapolis, Ind.) that were placed on basal (0.3%) or high (8%) NaCl rat chow diets (Purina series 5500) beginning ten days prior to the start of the experiments. Male Dahl salt-resistant (SR / Jr) rats (250-300 gm, Harlan, Indianapolis, Ind.) were used as controls. Non-salt-sensitive, spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) were also employed in some experiments. Each rat was housed individually with a 12 hour light / 12 hour dark cycle. The animal use protocols were approved by the Chicago—West Side Veterans Administration Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee.
[0064]Arterial blood pressures in unrestrained rats were monitored using a model TA11PA-C20 (Data Science, International, St. Paul, Minn.) implantable telemetric blood pressure monitoring system. The rats were anesthetized using an in...
example 2
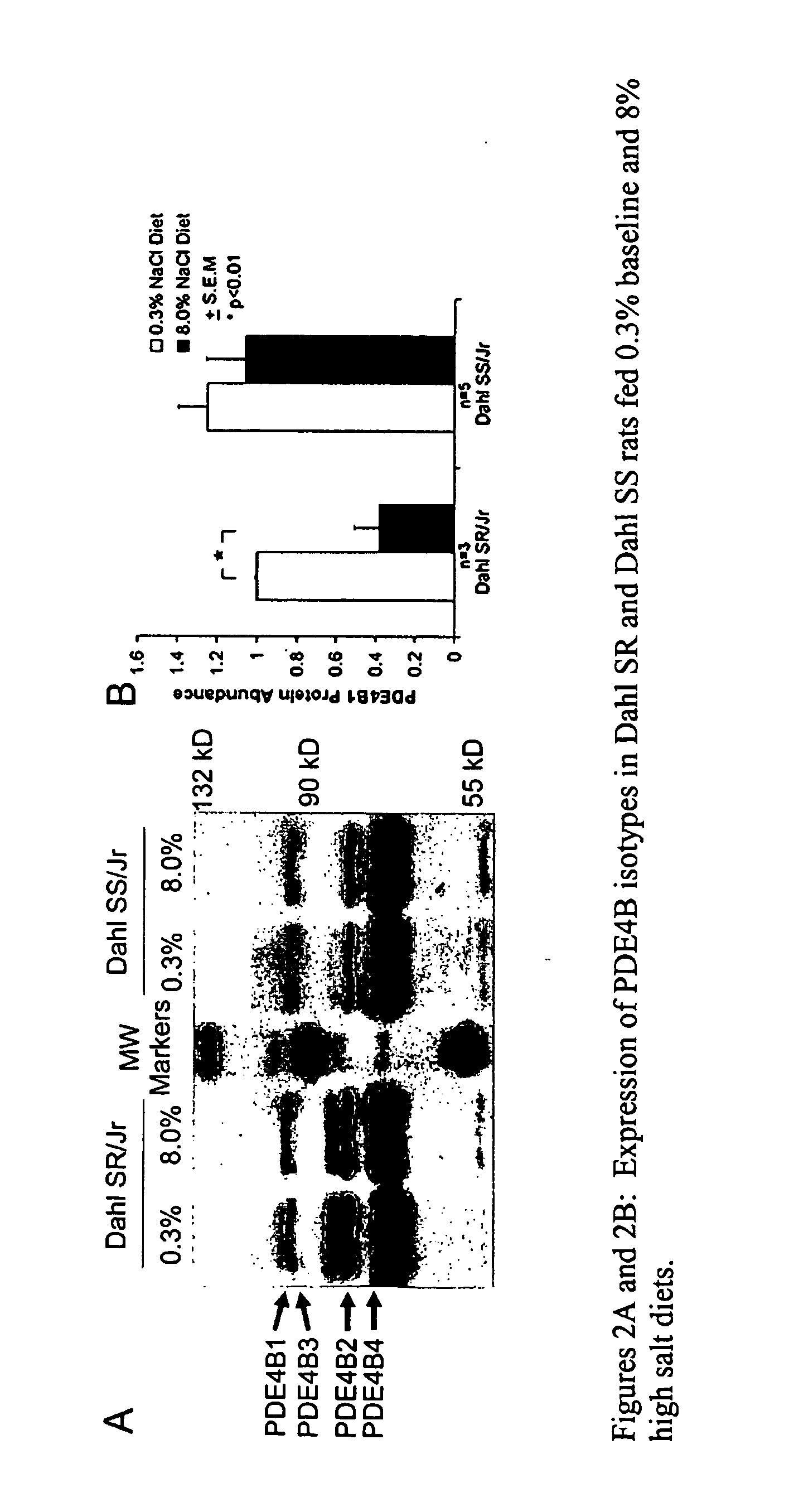
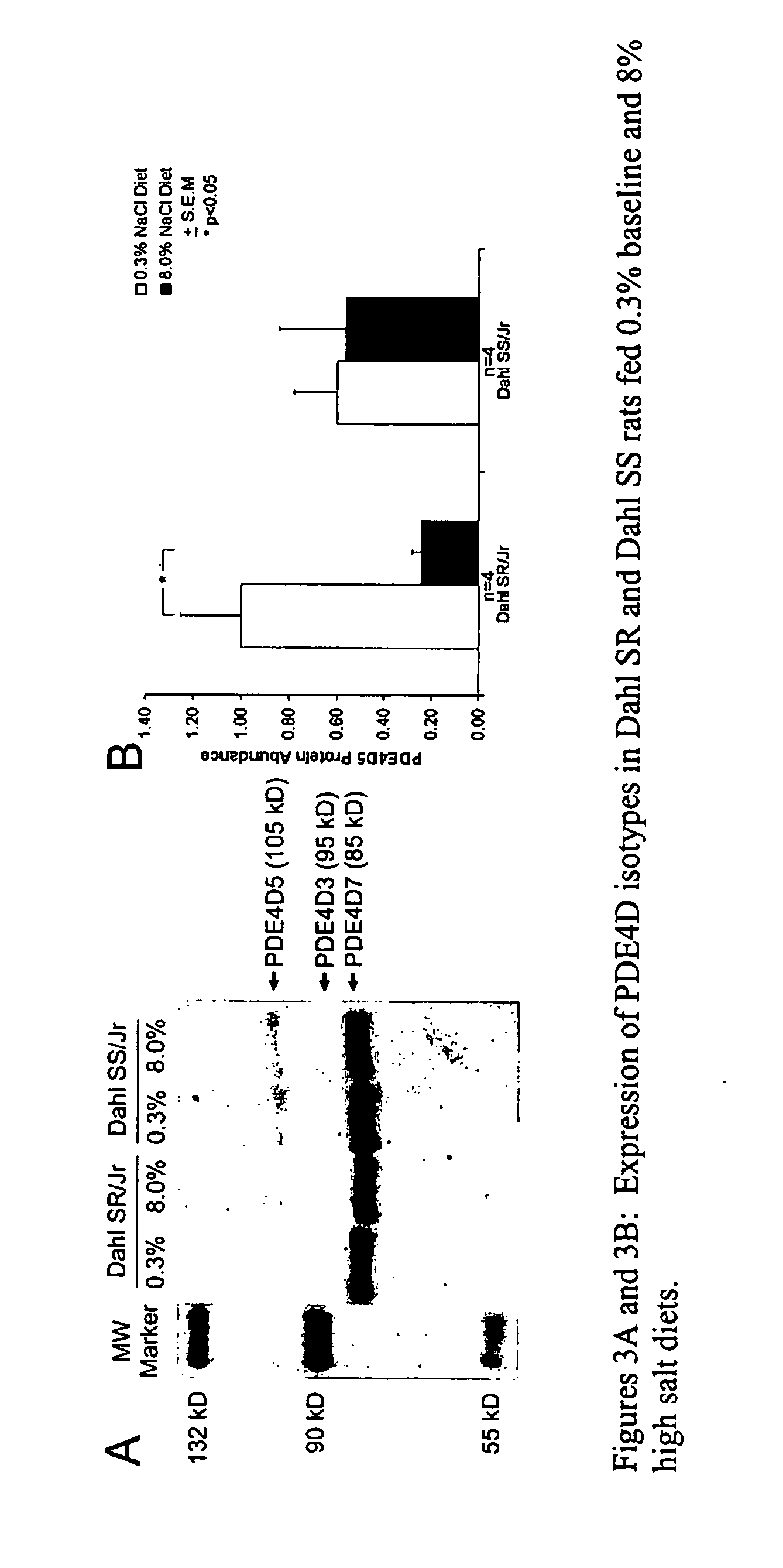
Expression of PDE4 Isotypes
[0067]Male Dahl salt-sensitive (SS / Jr) and salt-resistant (SR / Jr) rats (250-300 gm, Harlan, Indianapolis, Ind.) that were fed basal (0.3%) and high (8%) NaCl rat chow diets (Purina series 5500) for ten days were sacrificed and their kidneys excised. The kidneys were washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS, pH 7.4) and homogenized in a lysis buffer (20 mmol / L Tris-HCl, 150 mmol / L Na2EDTA, 1 mmol / L EGTA 1% Triton 2.5 mmol / L sodium pyrophosphate, 1 mmol / L b-glycerolphosphate-1 mmol / L Na3VO4 ) supplemented with 1 mmol / L phenylmethanesulfonylfluoride (PMSF) and 1× protease inhibitors (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, Mo.). The homogenate was spun at 14 000 rpm for 30 minutes at 4° C., and the supernatant was collected and stored in aliquots at −80° C. until use. Protein concentrations were estimated on each lysate with Bradford's reagent (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, Calif.). Samples were separated on a 10% SDS-polyacrylamide gel and the protein bands transferre...
example 3
Immunobistochemical Localization of PDE4 Isotypes
[0073]PDE4 activity has been reported in inflammatory cells, gonads, cardiac muscle, liver, tracheal smooth muscle, various regions of the brain, and in kidney, but little information on the localization of PDE4 isotypes is available. Immunohistological methods were employed to verify the localization of PDE4, PDE4B, PDE4D, PDE4B1 and PDE4D5 activity in rat kidneys. A standard three-stage indirect immunoperoxidase technique was used for this purpose.
[0074]Briefly, tissue sections that had been fixed in 10% formaldehyde were rehydrated in graded alcohols (from 100% to 80%) and then rinsed in a running water bath. Endogenous peroxidase activity was quenched by preincubating the specimens in 3% hydrogen peroxide for 5 minutes at room temperature (RT). After washing in TBST, the specimens were incubated in serum-free protein blocking solution (DakoCytomation, Carpinteria, Calif.) for 30 minutes at RT and washed again in TBST. Three hundre...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| body weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| body weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com