Exhaust particulate matter measuring apparatus
a technology of particulate matter and measuring apparatus, which is applied in the direction of exhaust treatment electric control, electrical control, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of inability to accurately combust the soot particles settled on the molded member, and inability to measure the amount of soot with high accuracy, and achieve the effect of accurate measuremen
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
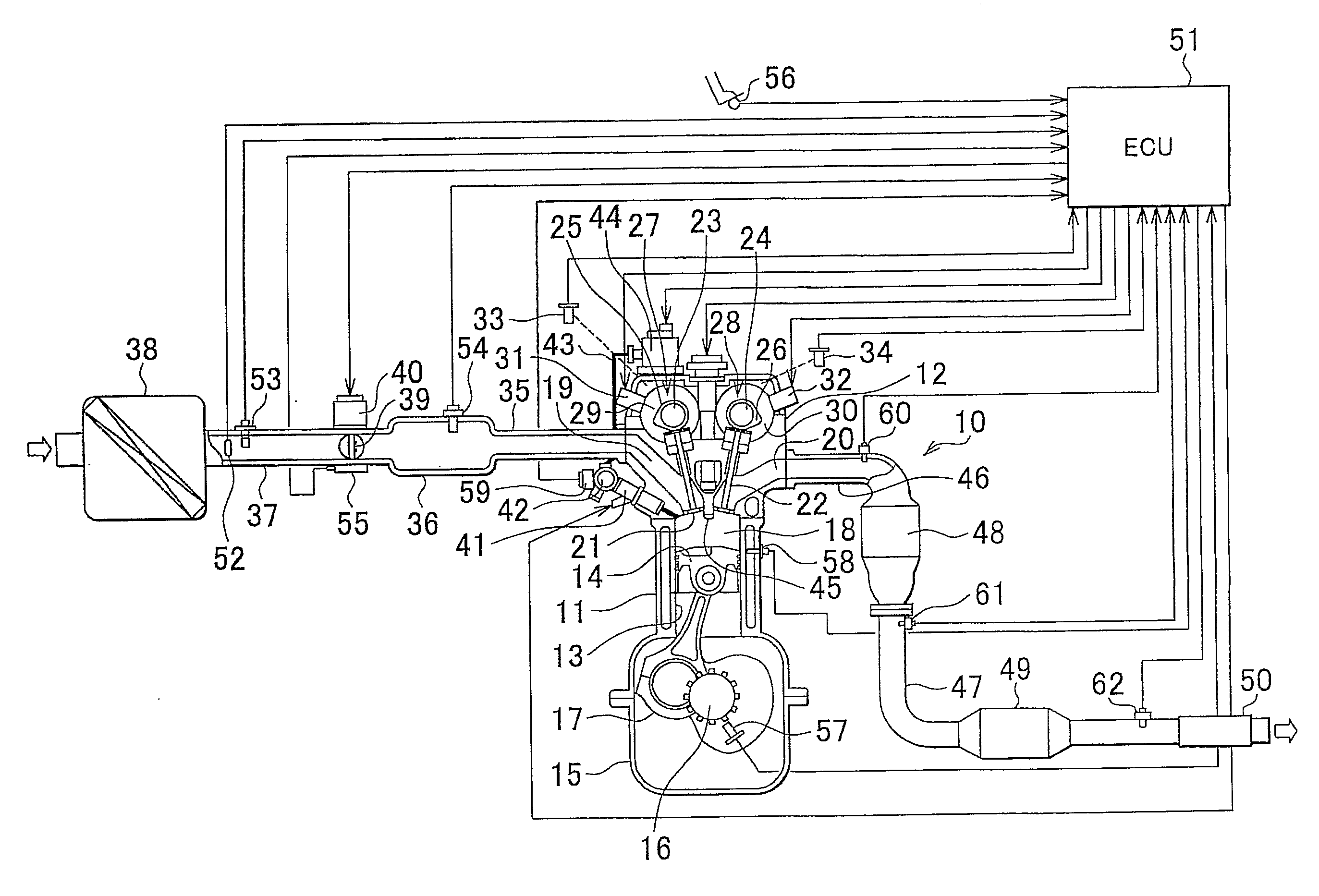
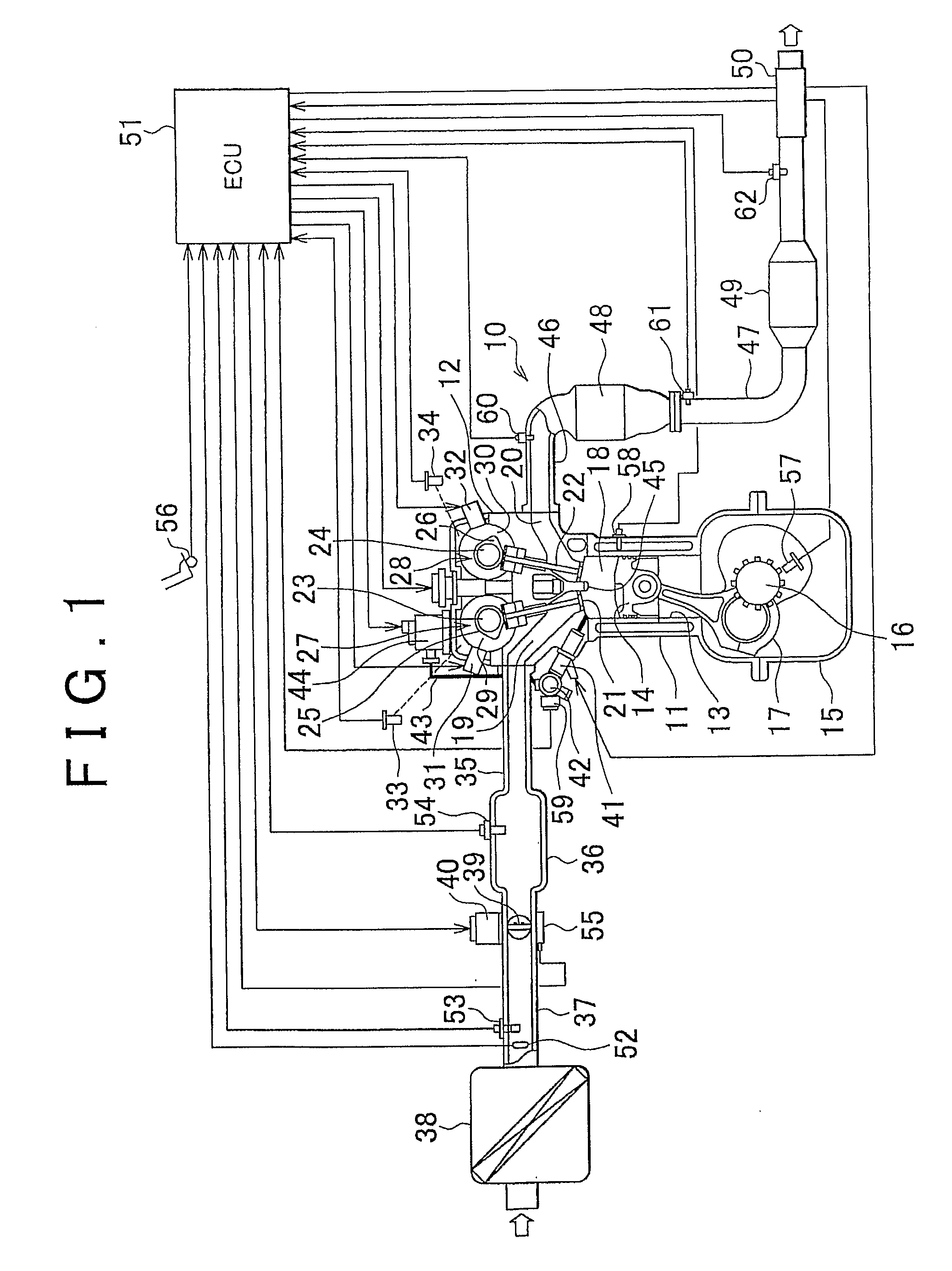
[0033]In an internal combustion engine to which the exhaust particulate matter measuring apparatus of the first embodiment is applied, as shown in FIG. 1, the engine 10 may be a four-cylinder direct-injection type engine, in which a cylinder head 12 is fitted tightly onto a cylinder block 11, wherein a pistons 14 are fitted into a plurality of cylinder bores 13 formed in the cylinder block 11 to enable up-and-down movement within the cylinder block 11. A crankcase 15 is fitted tightly to the bottom of the cylinder block 11. A crankshaft 16 is rotatably supported inside the crankcase 15, and each of the pistons 14 is linked to the crankshaft 16 via a connecting rod 17. In FIG. 1, only one cylinder and cylinder bore of four cylinders is shown.
[0034]A combustion chamber 18 is formed by the wall surface of the cylinder bore 13 of the cylinder block 11, the lower surface of the cylinder head 12, and the upper surface of the piston 14. This combustion chamber 18 is a pent-roof shaped, in ...
second embodiment
[0067]The method of measuring the exhaust particulate matter with the exhaust particulate matter measuring apparatus is described in detail below, with reference being made to the flowchart of FIG. 8.
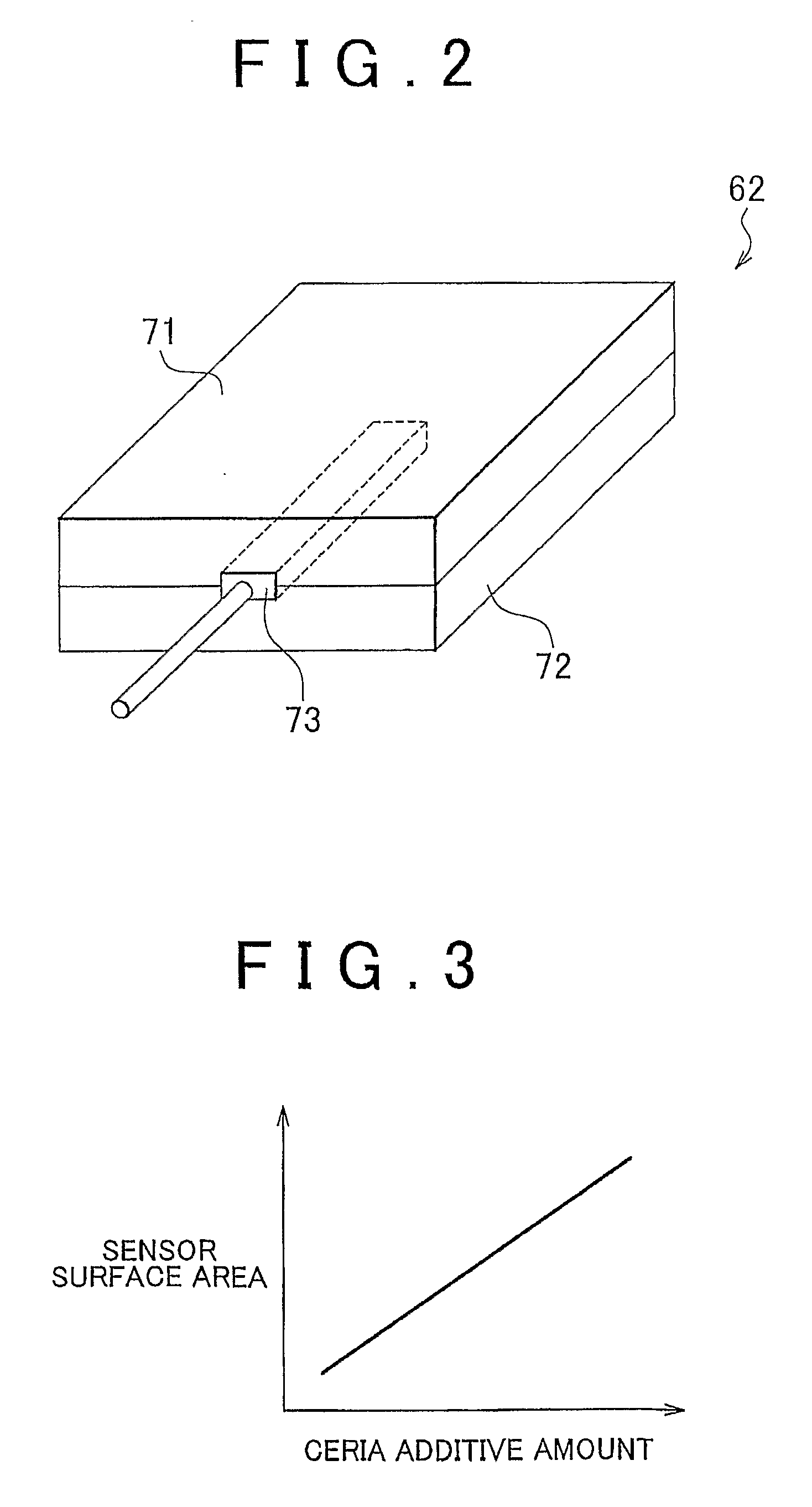
[0068]At step S31, a determination is made of whether the engine 10 is completed warmed-up, that is, whether the engine coolant temperature detected by the coolant temperature sensor 58 is at least a prescribed engine warm-up coolant temperature. At this point, if the determination is made that the engine coolant temperature has reached the engine warm-up coolant temperature, at step S32, the electrical heater 72 in the PM sensor 62 is electrically powered to heat the oxidation catalyst 71, thereby combusting the exhaust particulate matter settled in the oxidation catalyst 71. Then, at step S33, a determination is made of whether the exhaust particulate matter settled in the oxidation catalyst 71 of the PM sensor 62 has been completely combusted, based on the temperature change of the ...
third embodiment
[0081]The method of measuring the exhaust particulate matter with the exhaust particulate matter measuring apparatus is described in detail below, with reference being made to the flowchart of FIGS. 9A and 9B.
[0082]At step S51, a determination is made of whether the engine 10 is completed warned-up, that is, whether the engine coolant temperature detected by the coolant temperature sensor 58 is at least a prescribed engine warm-up coolant temperature. At this point, if the engine coolant temperature has reached the engine warm-up coolant temperature, at step S52, the electrical heater 72 in the PM sensor 62 is electrically powered to heat the oxidation catalyst 71, thereby combusting the exhaust particulate matter settled in the oxidation catalyst 71. Then, at step S53, a determination is made of whether the exhaust particulate matter settled in the oxidation catalyst 71 of the PM sensor 62 has been completely combusted, based on the temperature change in the oxidation catalyst 71....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com