Adsorbent for Water Adsorption and Desorption
a technology of adsorbent and water, which is applied in the field of adsorbent, can solve the problems of increasing operation costs, reducing the humidity of a room, and no detailed explanation of the adsorbent used in the equipment, and achieves outstanding adsorption capacity and adsorption characteristics, and high adsorption capacity for water
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 2
Cr-BDCA-2
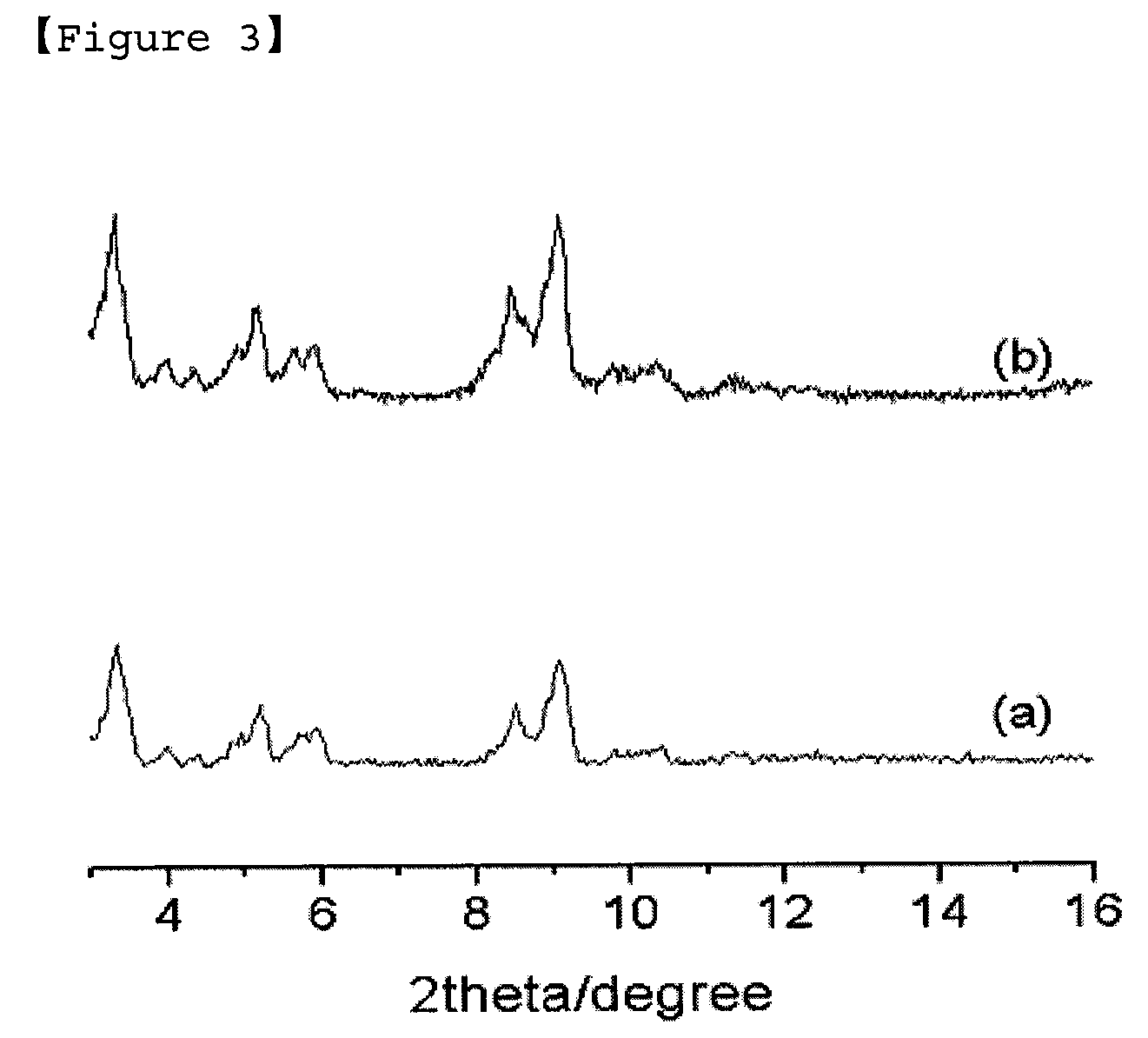
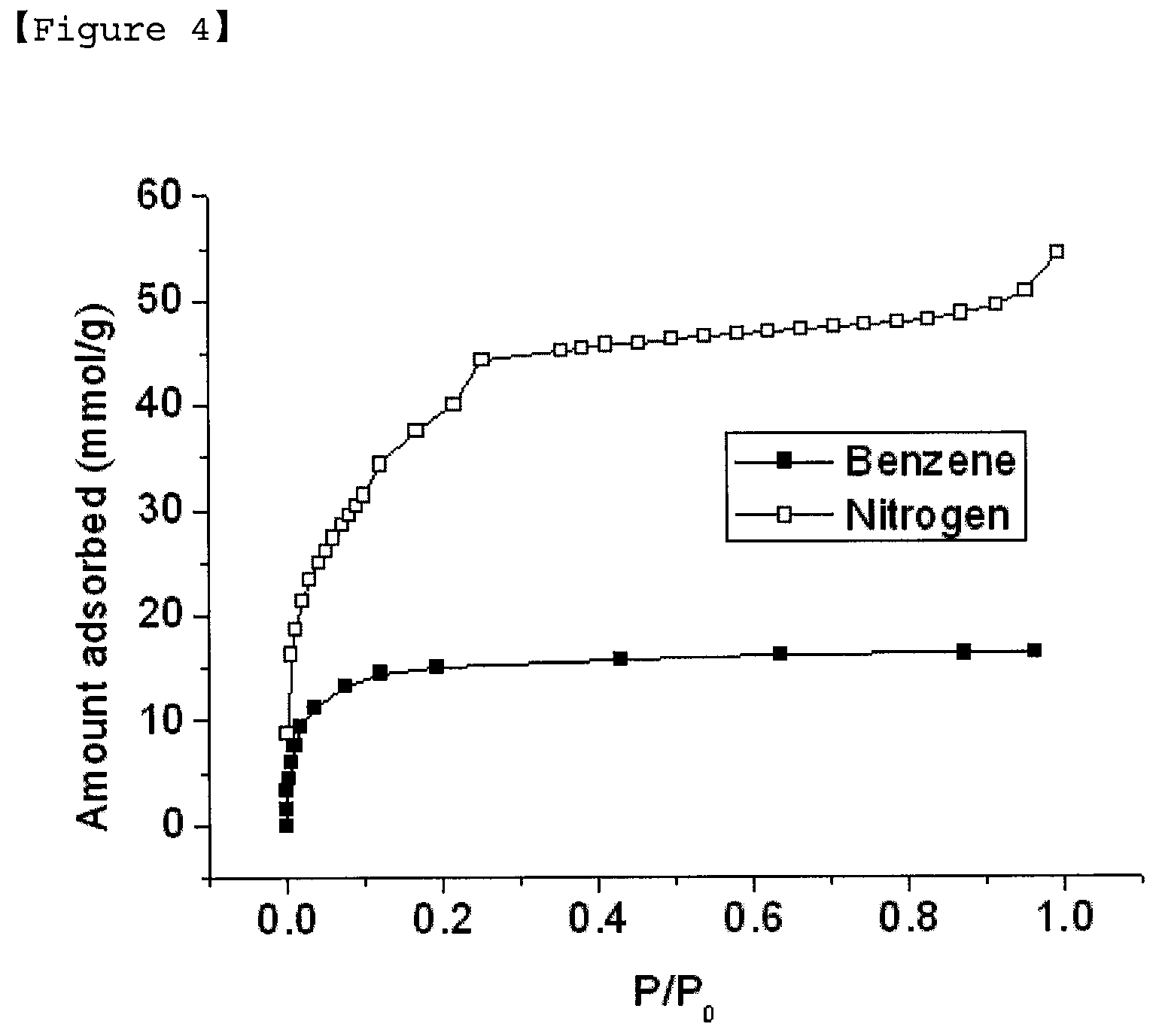
[0039]The synthesis of a porous hybrid inorganic-organic material was carried out as Example 1, except that ultrasonic pretreatment was omitted and the reaction time was 2 min. X-ray diffraction patterns of FIG. 3a show that a material with structure same as Example 1 was obtained, and SEM image confirms that a porous hybrid inorganic-organic material with homogeneous size of 40-50 nm was obtained. The porous hybrid inorganic-organic material, after evacuation at 150° C. under vacuum, has nitrogen adsorption capacity of 1050 mL / g or 46.9 mmol / g at relative pressure of 0.5 (P / Po=0.5, at liquid nitrogen temperature). Moreover, the porous hybrid inorganic-organic material has high benzene adsorption capacity (16 mmol / g) at 30° C. and relative pressure of 0.5 (P / Po=0.5). At this time, the average pore size of the hybrid inorganic-organic material is 1.3 nm. The adsorption isotherms of nitrogen and benzene are shown in FIG. 4.
[0040]The surface area and pore volume of the hybrid ...
example 3
Cr-BDCA-3
[0041]The synthesis of a porous hybrid inorganic-organic material was carried out as Example 2, except that the reaction time was 40 min. X-ray diffraction patterns of FIG. 3b show that a material with structure same as Example 1 was obtained, and SEM image (FIG. 2) confirms that a porous hybrid inorganic-organic material with homogeneous size of 200 nm was obtained even though the crystal size increased considerably compared with the size of Example 2. The surface area and pore volume of this material are 3900 m2 / g and 2.1 mL / g, respectively.
example 4
Fe-BDCA-1
[0042]The synthesis of a porous hybrid inorganic-organic material was carried out as Example 2, except that FeCl3 was used instead of Cr(NO3)3-9H2O. X-ray diffraction patterns showed that a material with structure same as Example 1 was obtained, and SEM image confirmed that a porous hybrid inorganic-organic material with homogeneous size of 50-100 nm was obtained.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com