Water Manifold System And Method
a technology of manifolds and manifolds, applied in the direction of drawing-off water installations, lighting and heating apparatuses, heating types, etc., can solve the problems of permanent assembly of manifolds, inability to expand or reconfigure easily, and high cost of manifold types
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
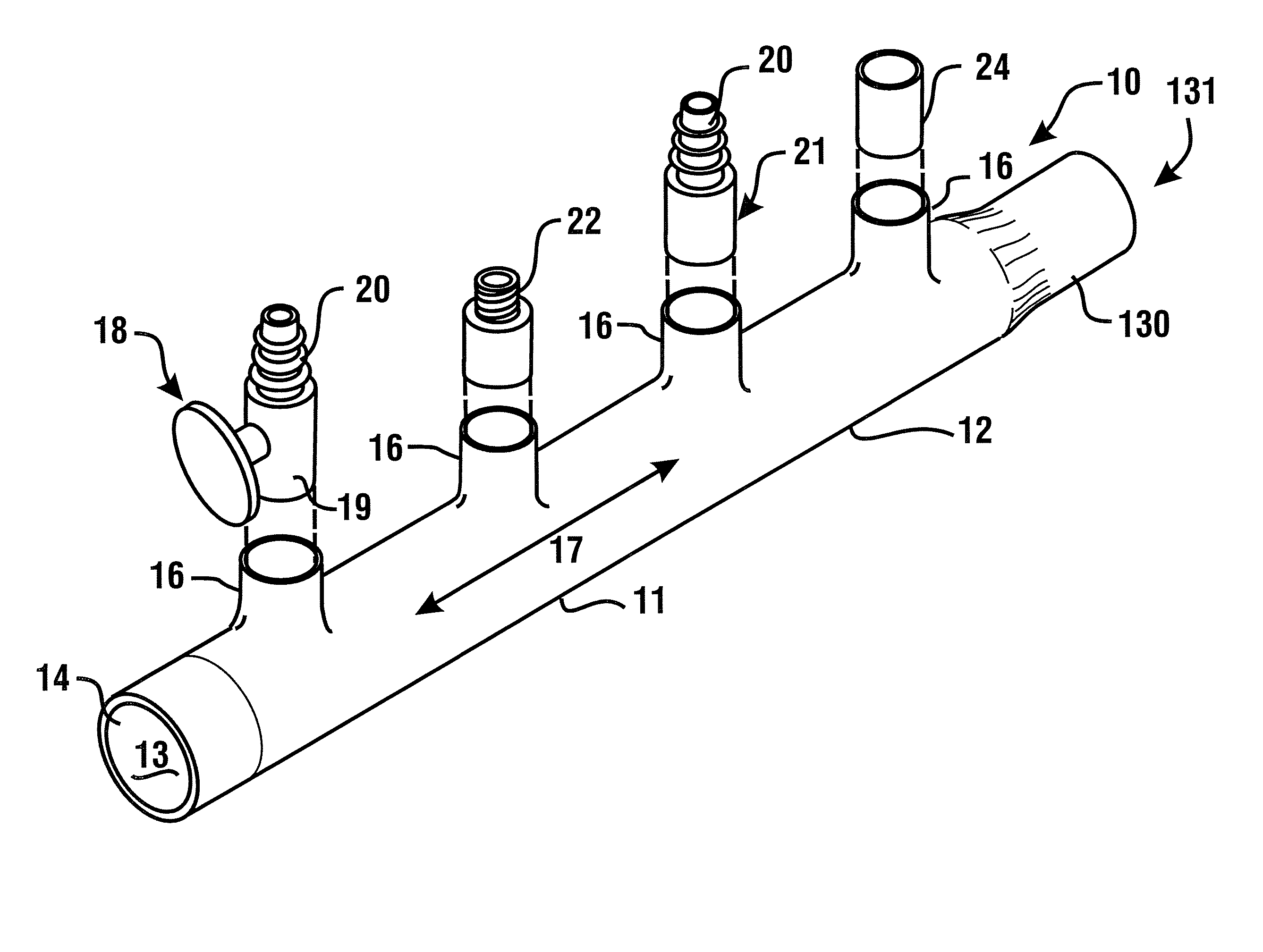
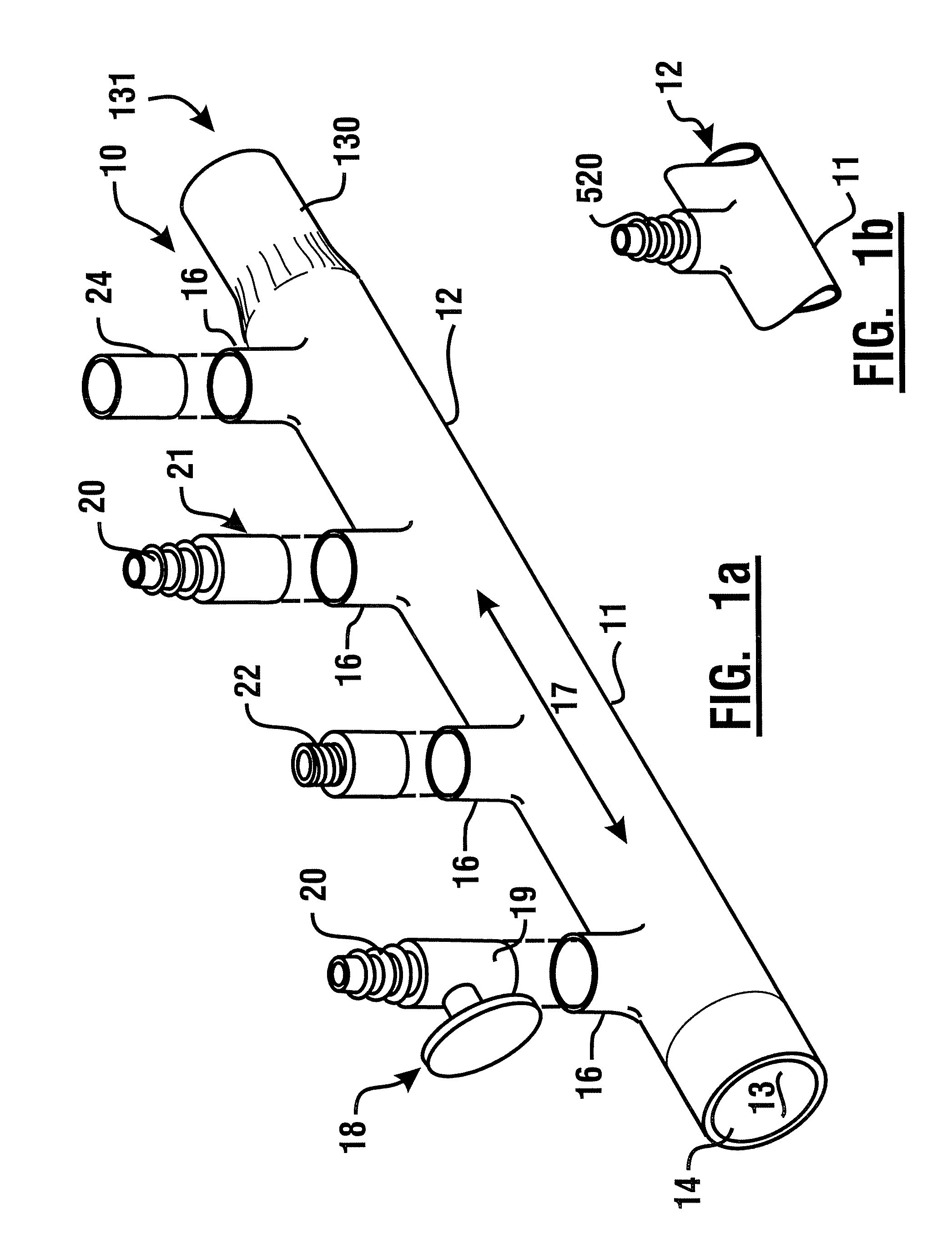
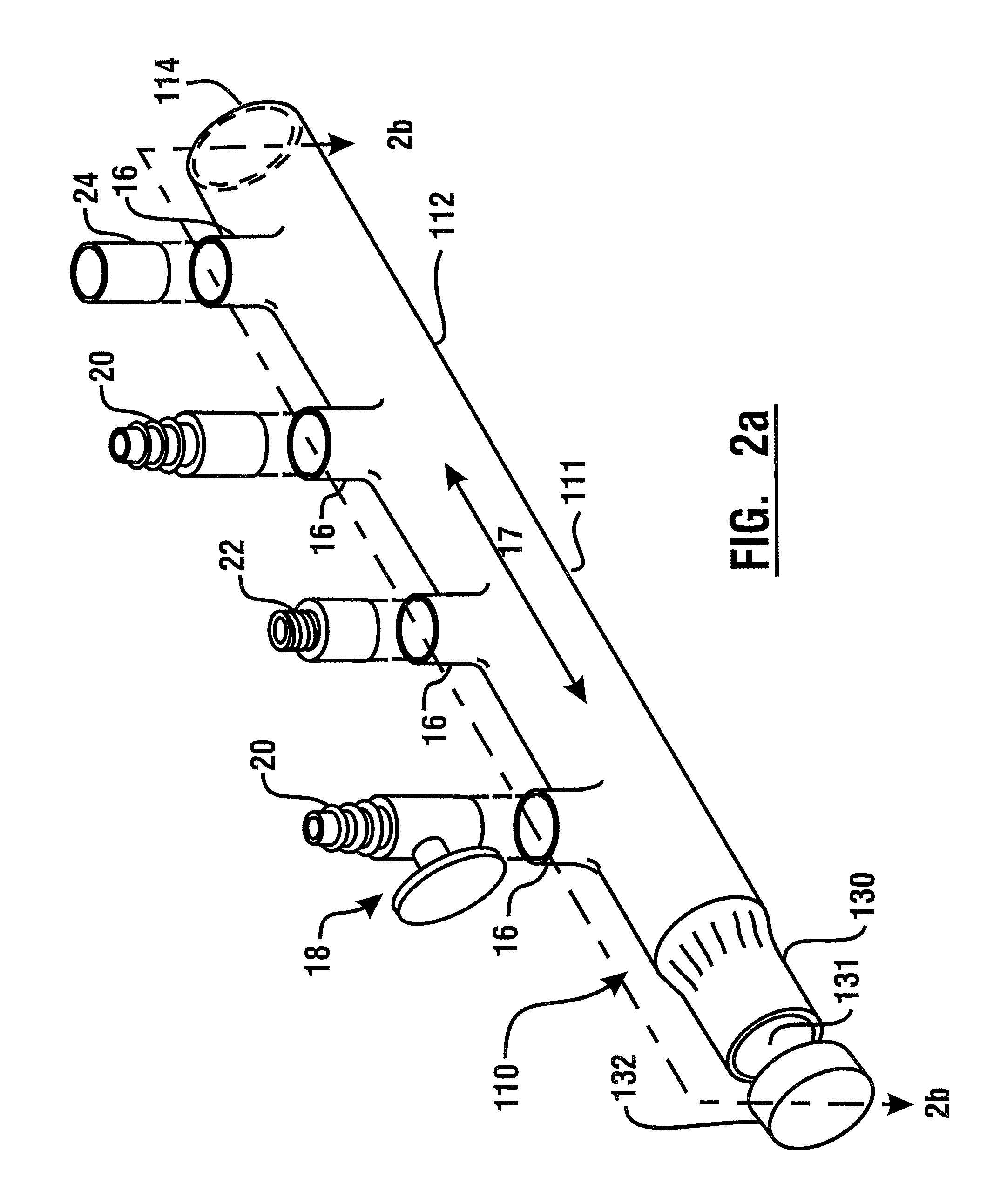
[0051]Referring now to the drawings, and particularly to FIG. 1a, there is shown therein a perspective view of an exemplary manifold system 10. In this exemplary embodiment, a manifold or distributor 12, is comprised of molded plastic material. In an exemplary embodiment, the manifold is comprised of a unitary molded CPVC manifold. Of course in other embodiments, other materials may be used. The manifold bounds a chamber 11 which defines an interior volume 13 of the manifold. The exemplary manifold further includes an entry port 14 and a plurality of liquid outlet ports 16, which are alternatively referred to herein as sockets. In an exemplary embodiment, the entry port may be configured to accept a standard copper tube size (CTS) outside diameter conduit therein. For example, in an exemplary embodiment the entry port 14 may be configured in the manner of a molded one inch CTS female coupling.
[0052]In the exemplary embodiment, the sockets 16 may be sized to accept standard CTS sized...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com