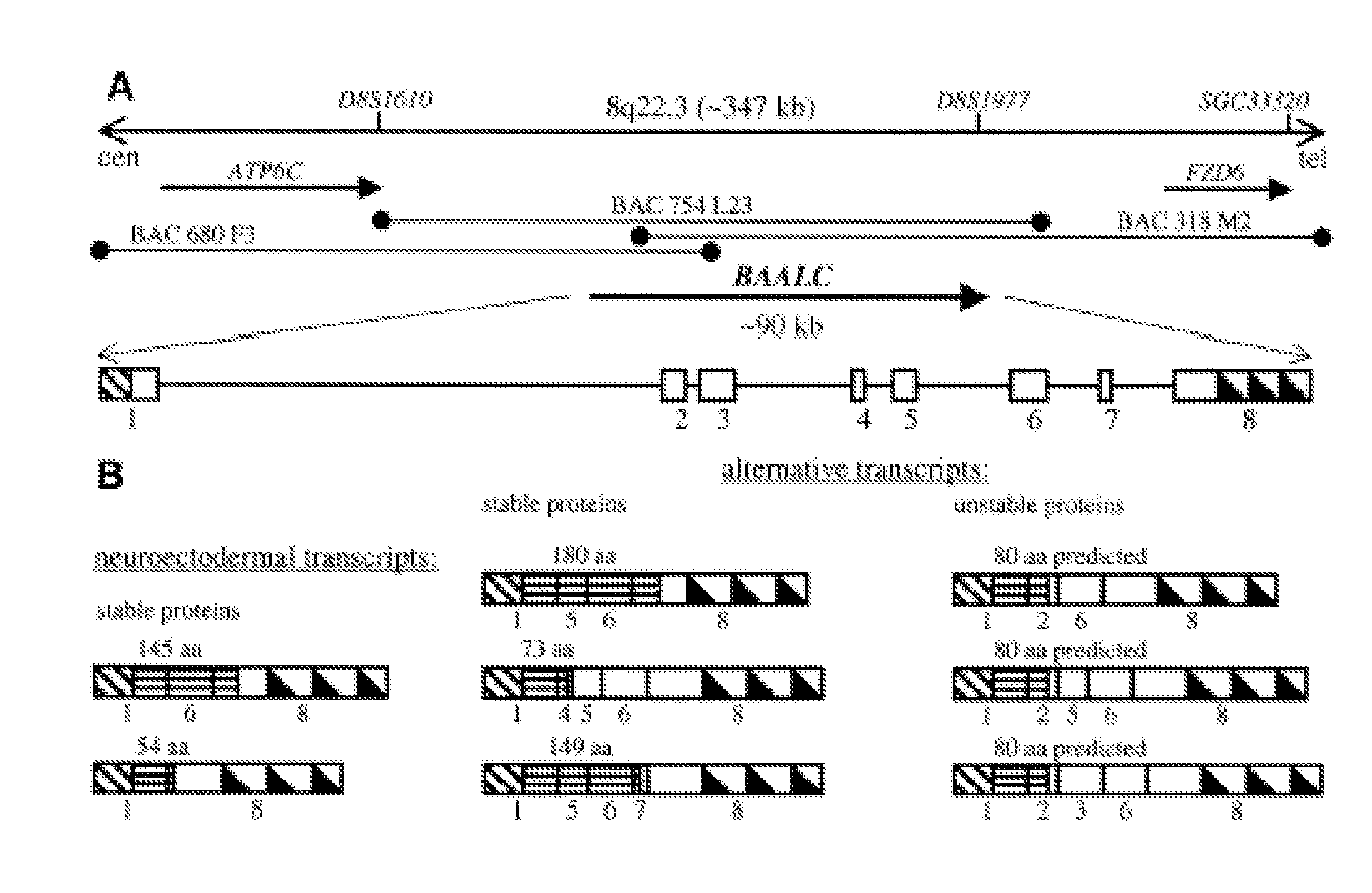
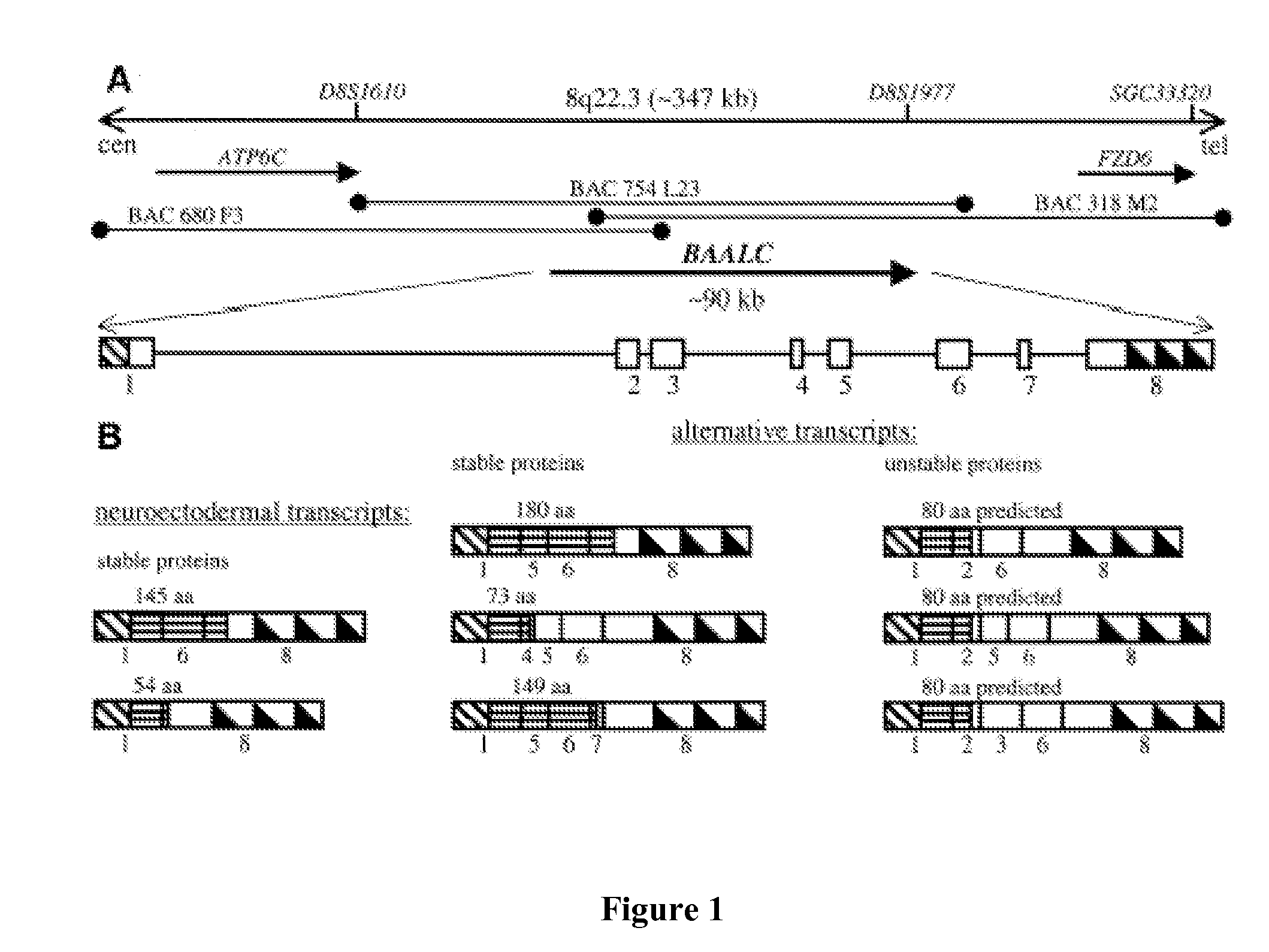
Baalc expression as a diagnostic marker for acute leukemia
a leukemia and diagnostic marker technology, applied in the field of acute leukemia leukemia leukemia leukemia leukemia leukemia leukemia leukemia leukemia leukemia leukemia leukemia leukemia leukemia leukemia leukemia leukemia leukemia leukemia leukemia leukemia leukemia leukemia leukemia leukemia leukemia leukemia leukemia leukemia leukemia leukemia leukemia l
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Alternative Splicing of BAALC in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Samples
[0094]Blasts from BM or peripheral blood (PB) were collected from patients with AML. Total RNA was isolated using Trizol (Invitrogen). Total RNA from AML cells from these patients was reverse-transcribed with avian myeloblastosis virus reverse transcriptase (Roche Diagnostics) using oligo(dT) as primer. The reverse transcriptase reaction mixture contained 10 mM Tris (pH 8.3), 40 mM KCl, 1.5 mM MgCl2, 1 mM dithiothreitol, 200 μM each of dATP, dCTP, dTTP and dGTP, 200 ng of the primer, 10 U of AMV reverse transcriptase from Boehringer Mannheim Biochemicals, and 20 units of RNASIN from Promega. The reverse transcriptase reaction was then performed at a temperature of 60° C.
[0095]PCR was then performed using the cDNA from the reverse transcriptase reaction as template. Primer sequences from exons 1 and 8 of human BAALC were used. The primer from exon 1 was ES100, 5′-GTGCGGTACCAAGCTTCCGCGGCGCAGGAGGATG-3′ (SEQ ID NO: 38), The ...
example 2
BAALC Overexpression in Normal Cells and Various Cancer Samples, Including Glioblastoma Samples
[0098]Real-time PCR (TaqMan®, Applied Biosystems) was used to quantify the relative levels of BAALC transcripts in various tissues and cancers using total RNA isolated from the cells using Trizol (Invitrogen). Initially, RNA samples from several organs including BM, PBL, brain and fetal brain, plus different human tumor samples were analyzed. Additionally, RNA samples from 10 normal human tissues, 10 colorectal cancer-normal colonic mucosa-matched sample pairs, 3 esophageal cancer-normal esophagus-matched sample pairs, 3 lung tumor samples, 5 glioblastoma samples, 2 thyroid carcinoma-normal thyroid-matched sample pairs, 1 thyroid carcinoma sample, and 3 testicular and 3 mammary tumor samples were analyzed for expression of BAALC.
[0099]Reverse transcription was performed using the total RNA isolated from the cells. Separate primers for reverse transcription were used to synthesize cDNA for ...
example 3
BAALC Overexpression in Leukemia Samples
[0106]Real-time PCR (TaqMan®, Applied Biosystems) was used to quantify the relative levels of BAALC transcripts in different leukemia samples, using total RNA isolated from the cells in real-time PCR, as described in Example 2. Blasts from BM or peripheral blood from 130 diverse AML patients, 31 ALL patients, 4 Burkitt's lymphoma (BL) patients, 5 chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) patients, 5 chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) patients, plus the 7 leukemia cell lines HL-60, KG-1, KG-1a, MC-1010, K-562, D1.1, and RS4;11, were analyzed. Pretreatment BM aspirate or peripheral blood samples from patients with the different leukemias were collected after prior consent. CD34-positive progenitor cells were enriched twice from normal BM aspirates by immunomagnetic separation, using MiniMACS columns (Miltenyi Biotec, Auburn, Calif.). Cell lines were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection. Total RNA was isolated using Trizol (Invitrogen).
[01...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com