Exhaust emission control device
a technology of exhaust emission control and control device, which is applied in the direction of exhaust treatment electric control, machines/engines, mechanical equipment, etc., can solve the problems of deteriorating the purification performance of the catalytic converter
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
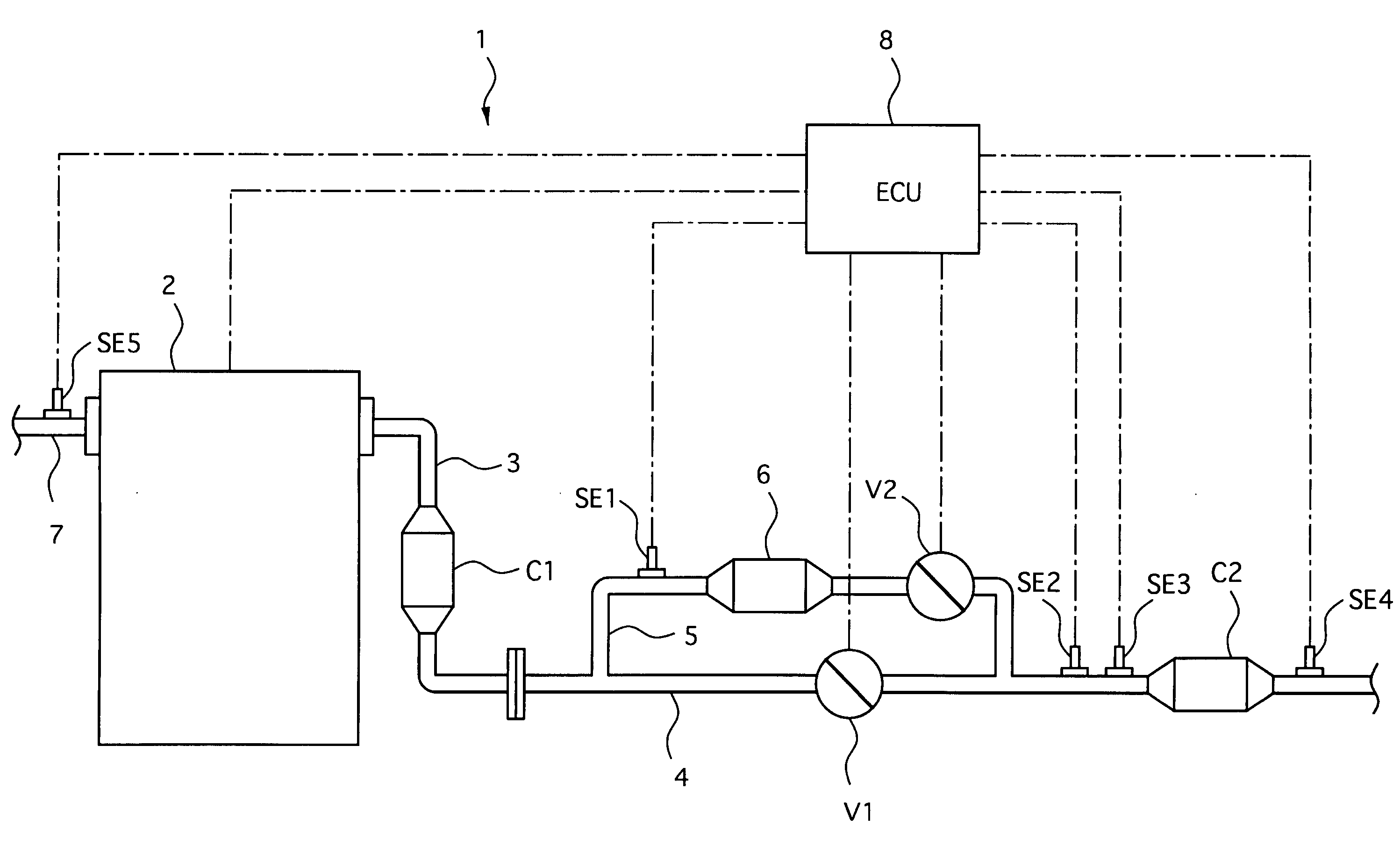
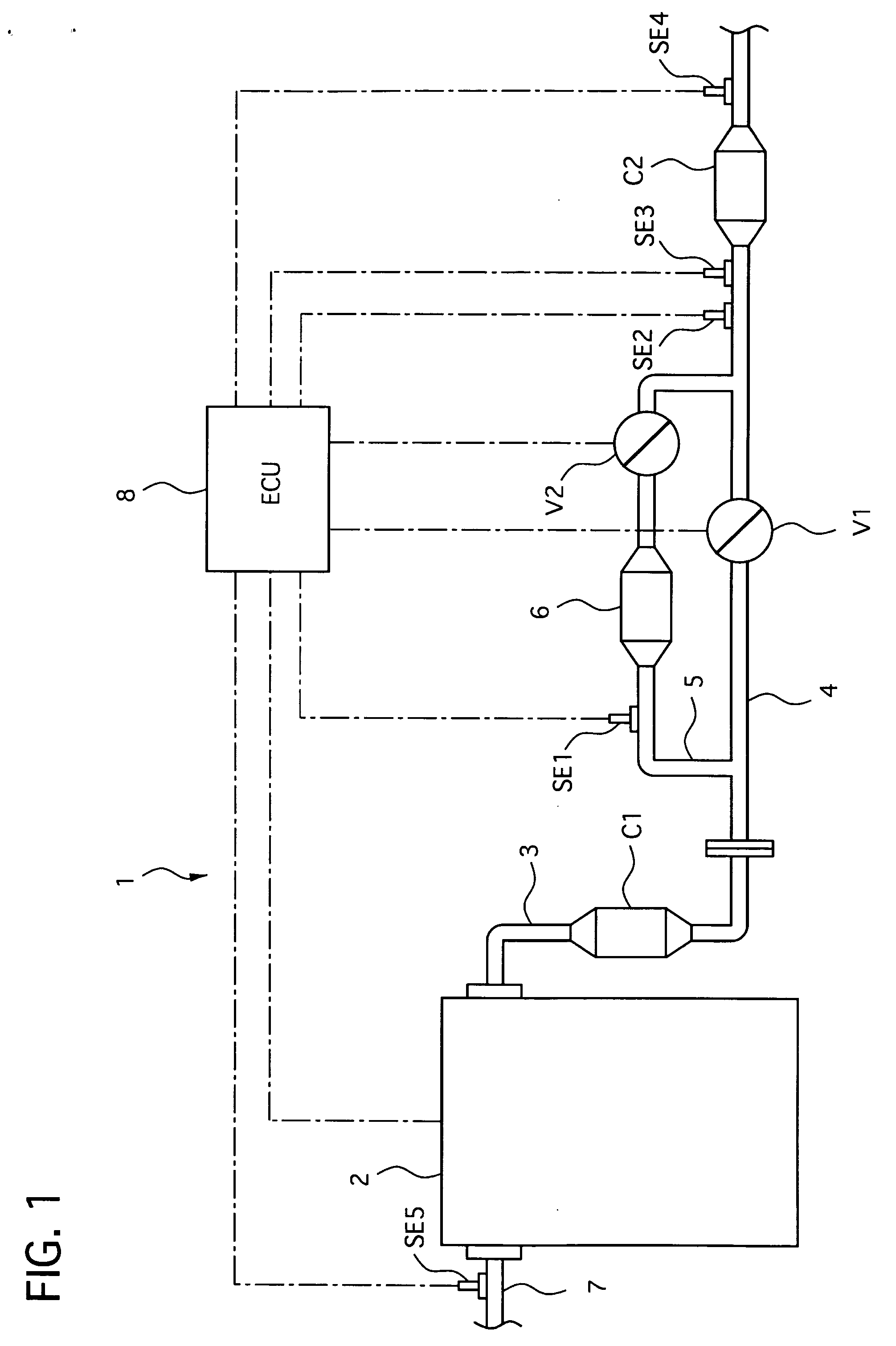
[0044]The operation and effects of the exhaust emission control device 1 of the first embodiment will be described.
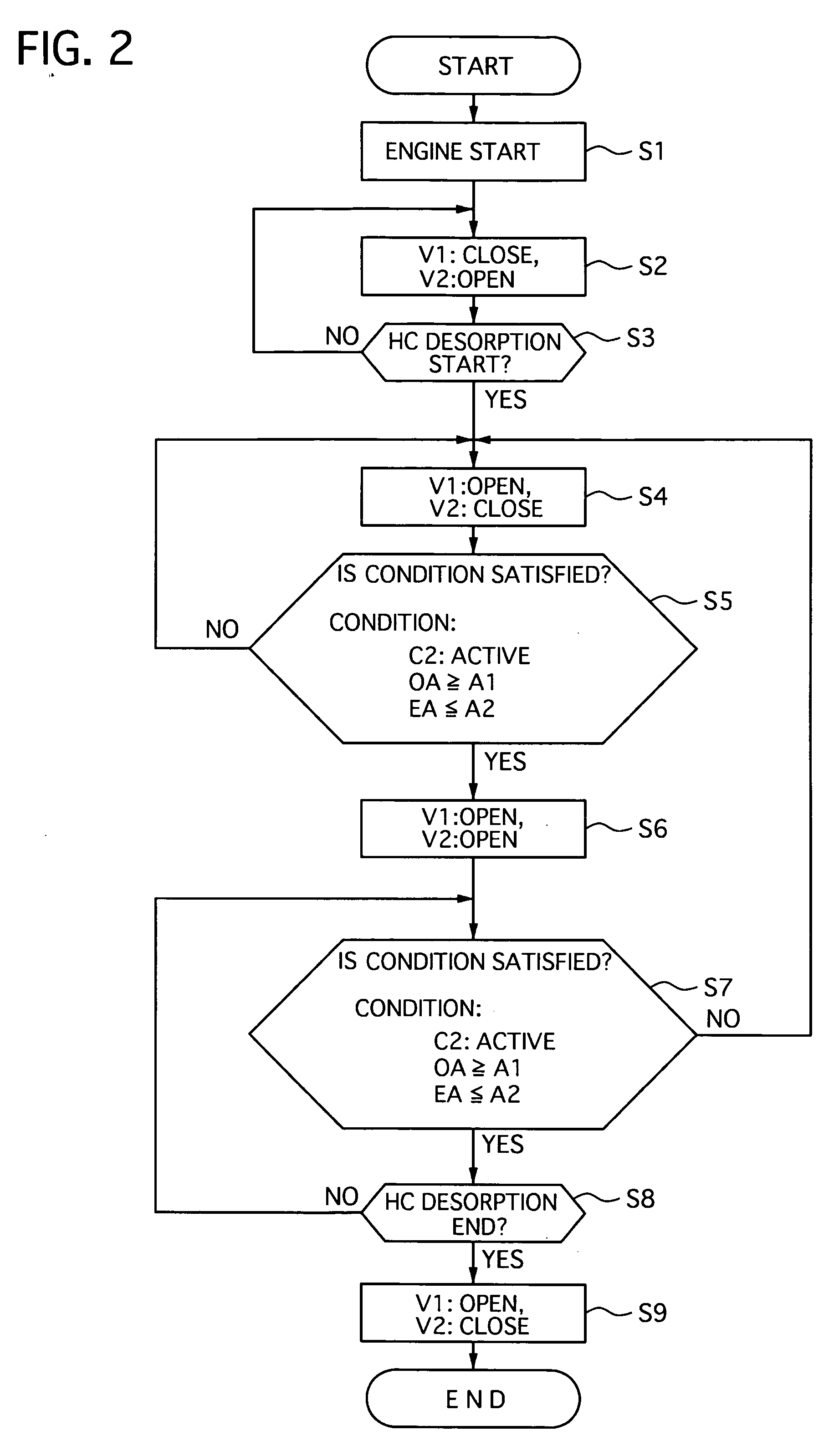
[0045]In the exhaust emission control device 1 of the first embodiment, the engine control unit 8 controls the first valve V1 and the second valve V2 to open and close according to a flowchart shown in FIG. 2 of valve open / close control executed by the engine control unit 8.
[0046]At step S1, the engine control unit 8 starts the open / close control when it detects a start of the engine 1, and then the flow goes to step S2.
[0047]At the step S2, the first valve V1 is closed to shut the main exhaust passage 4, the second valve V2 being opened to flow the full amount of the exhaust gas discharged from the engine 2 through the bypass exhaust gas passage 5, and then flow goes to step S3.
[0048]At the step S3, the engine control unit 8 judges whether or not the adsorbent in the adsorbent trapper 6 begins to desorb the exhaust gas therefrom based on the temperature signal outputte...
second embodiment
[0082]In addition, although the NOx amount in the exhaust gas increases only in a case where the engine 2 is driven merely at the lean mixture, the exhaust emission control device 1 of the second embodiment uses the lean mixture control with the fuel injection cut-off, so that the oxygen can be supplied to the second catalytic converter C2 without increase in NOx because the air fuel ratio is not changed.
[0083]FIG. 7 shows experiment results, of a conventional exhaust emission device and that of the second embodiment, showing a relationship between the amount of HC emission, a vehicle speed and an elapsed time since the engine 2 is started. The vehicle speed is set according to a speed model that is used for experiments. The conventional exhaust emission control device is constructed in such a way that a first valve V1 and a second valve V2 are opened to flow the exhaust gas through the main exhaust gas passage 4 and the bypass exhaust gas passage 5 immediately after a second cataly...
third embodiment
[0085]Next, an exhaust emission control device of a third embodiment according to the present invention will be described with the accompanying drawings.
[0086]As shown in FIG. 8, the exhaust emission control device 11 includes a first catalytic converter C1, a main exhaust gas passage 4, a bypass exhaust gas passage 5, a second catalytic converter C2 with an adsorbent trapper, a first valve V1, a second valve V2, a center muffler MF, a rear muffler MR and an emission control unit 12. The emission control unit corresponds to the control unit of the present invention.
[0087]The first catalytic converter C1 is constructed similarly to that of the first embodiment, and is connected with an engine 2 at its upstream portion through an exhaust manifold 3 and with a connecting pipe 3a at its downstream portion.
[0088]A downstream side end portion of the connecting pipe 3a is provided with a flange that is joined with a flange 25 of an upstream side end portion of the main exhaust gas passage ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com