Systems And Methods For Formation And Harvesting of Nanofibrous Materials
a nanofibrous material and nanotechnology, applied in the field of systems for forming and harvesting nanofibrous materials, can solve the problems of affecting the overall reaction kinetics, blocking the exit of nanomaterials from the chamber, etc., to avoid avoiding compromising the integrity of yarn, and minimizing the bonding of non-woven sheets
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
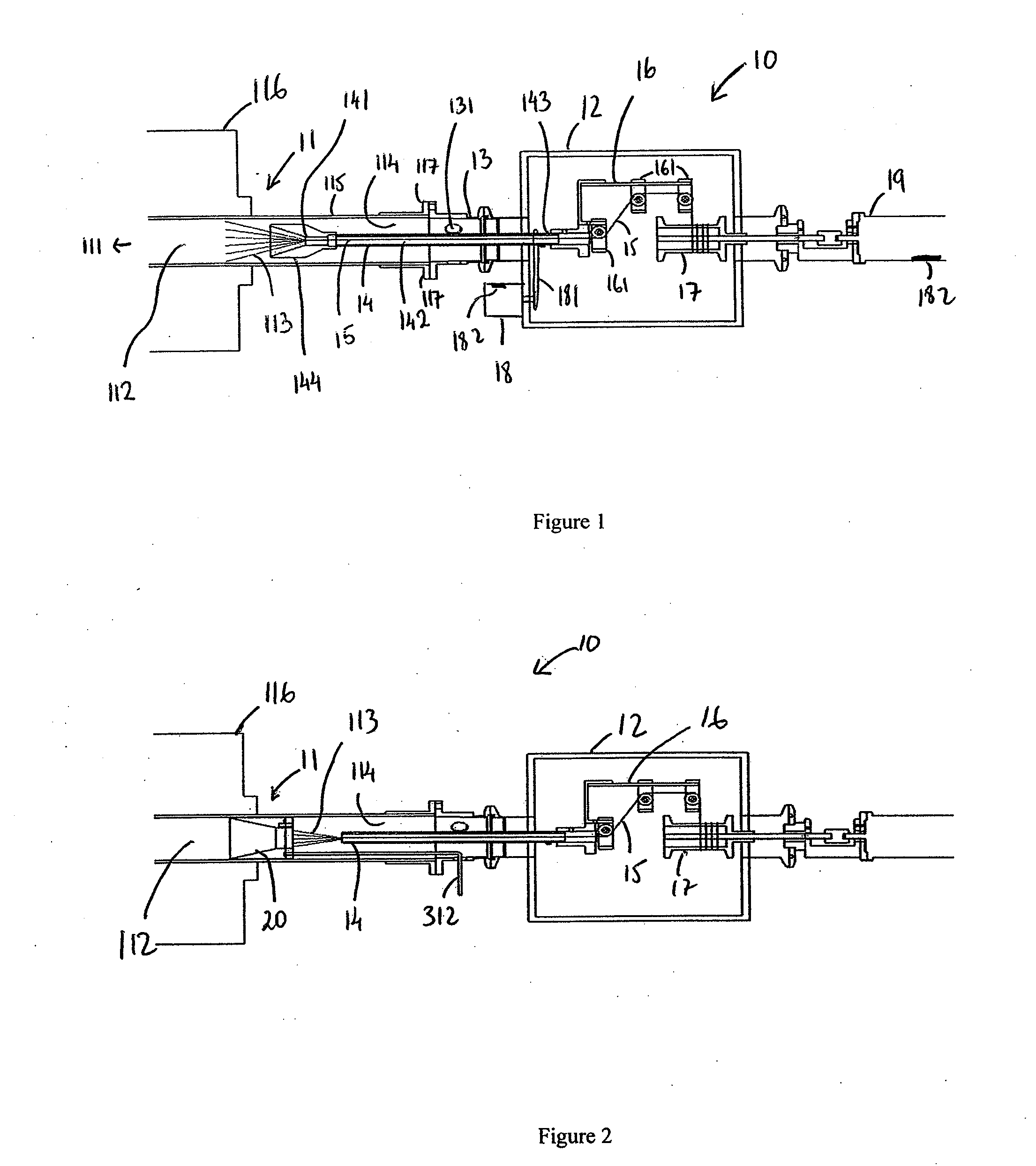
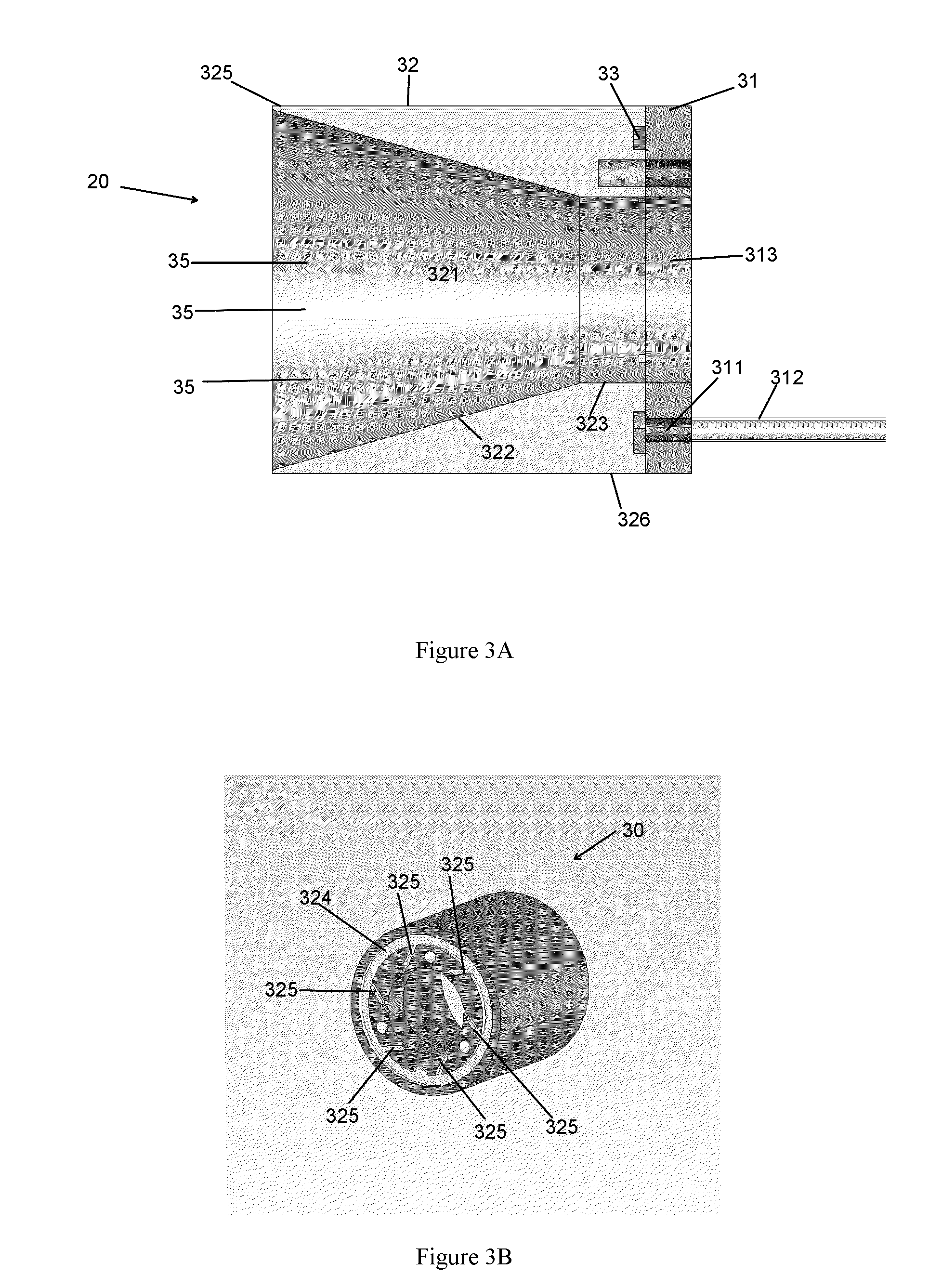
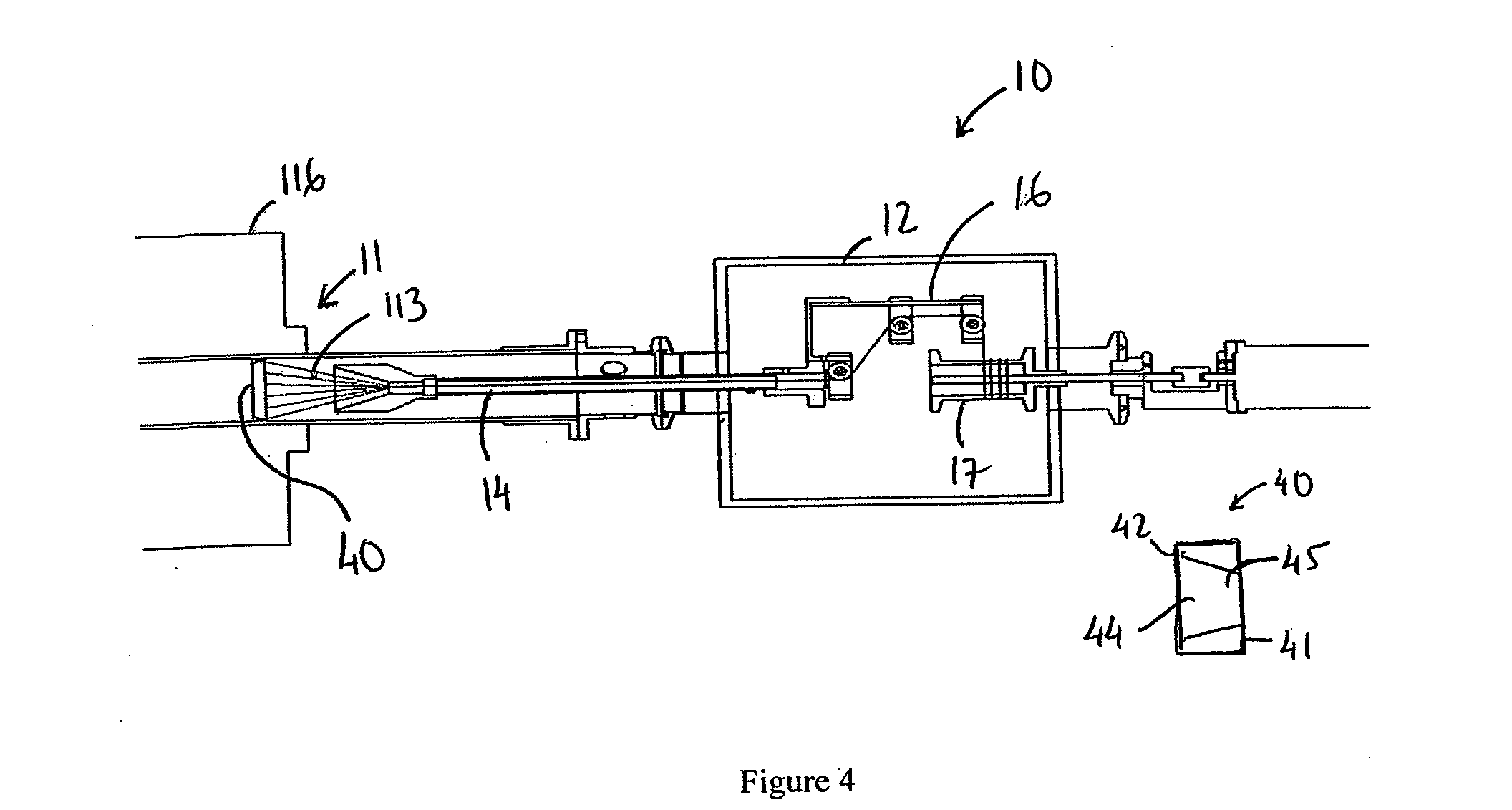
[0024]Nanotubes for use in connection with the present invention may be fabricated using a variety of approaches. Presently, there exist multiple processes and variations thereof for growing nanotubes. These include: (1) Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), a common process that can occur at near ambient or at high pressures, (2) Arc Discharge, a high temperature process that can give rise to tubes having a high degree of perfection, and (3) Laser ablation. It should be noted that although reference is made below to nanotube synthesized from carbon, other compound(s) may be used in connection with the synthesis of nanotubes for use with the present invention.
[0025]The present invention, in one embodiment, employs a CVD process or similar gas phase pyrolysis procedures well known in the industry to generate the appropriate nanotubes. In particular, since growth temperatures for CVD can be comparatively low ranging, for instance, from about 600° C. to about 1300° C., carbon nanotubes, bot...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| aspect ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com