Composite regenerated cotton and bast fiber yarn and method for making the same
a technology of composite regenerated cotton and bast fiber yarn, which is applied in the direction of yarn, continuous wounding machines, drafting machines, etc., can solve the problems of certain inherent drawbacks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
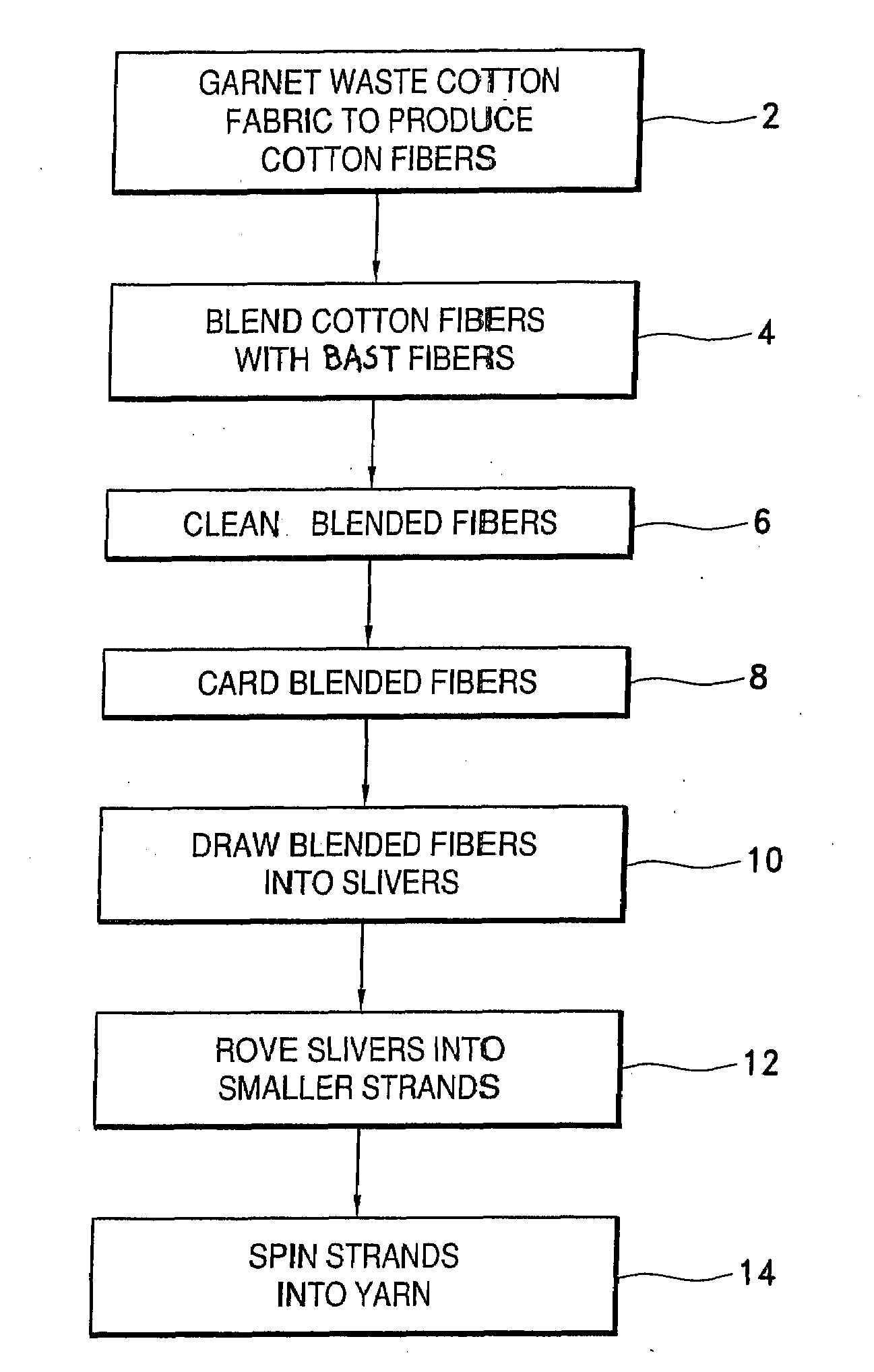
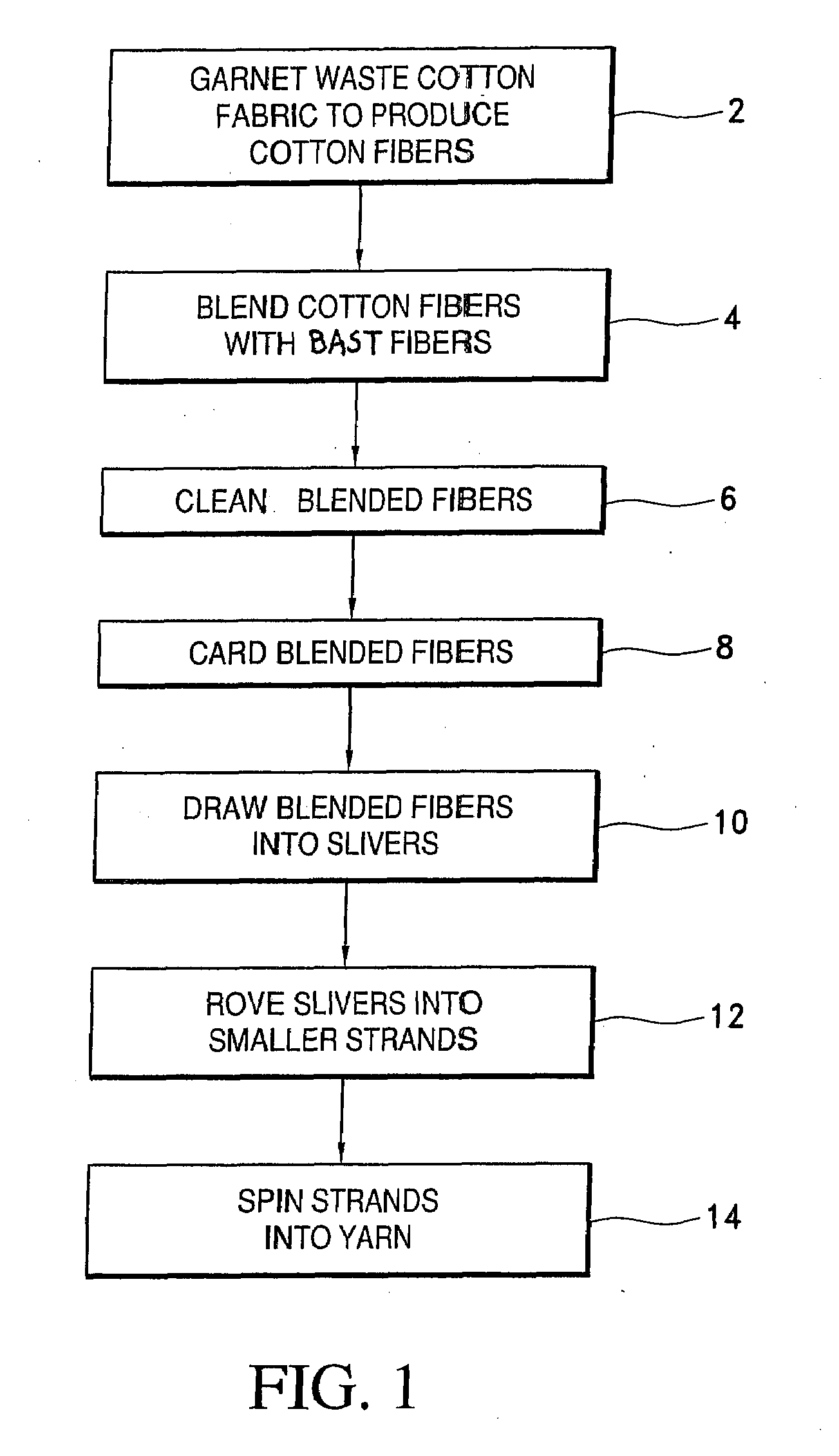
[0010]Textile waste in the form of cuttings, trimmings and clippings is collected from manufacturing facilities around the world before it is discarded for deposit in a landfill or incinerated. The waste cotton fabrics have previously been bleached and dyed, so additional treatment or dyeing is not required and therefore no additional industrial effluents which could add to additional pollution of the environment are produced. The waste materials are sorted by color and cleaned to remove any foreign material such as paper or metal from labels, buttons, or the like.
[0011]Bast includes herbaceous plants of dicoeyledons such as flax or linen, hemp, sunn, kenaf, jute and ramie, which are grown and cultivated for their long sinuous fibers. The fibers are very strong with a very high tensile strength and extremely absorbent. Bast fibers are naturally organic and do not require the use of herbicides or pesticides which are used extensively in the traditional cultivation of cotton. One acre...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thick | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com