Sliding material composition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
Reference Example 1
[0084]As the porous silica, Sunsphere H33 (commercial name) produced by Asahi Glass Co. Ltd. was prepared. As the silicone oil serving as the lubricant, KF96H (commercial name) produced by Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd. was prepared. Five parts by volume of the silicone oil was sufficiently mixed with one part by volume of the porous silica to impregnate the porous silica with the silicone oil. Thereby the oil-containing porous silica (abbreviation in table 1: Si) was prepared. The obtained oil-containing porous silica was powdery and could be used as a mixing agent with the resin material.
examples 1 through 4
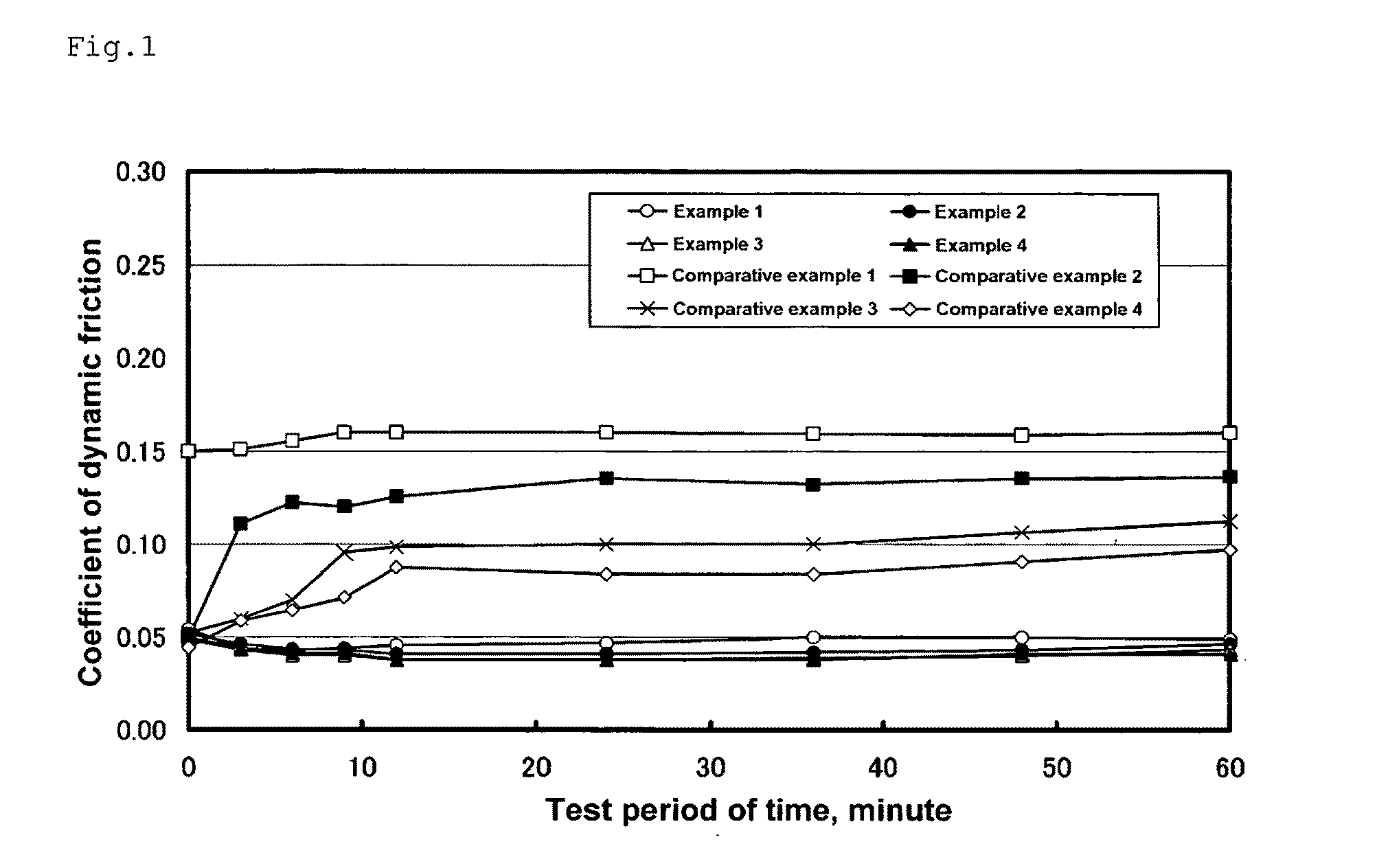
[0085]As polyethylene resin serving as the material of the base resin, Mipelon XM220 (commercial name, abbreviation in table 1: PE) produced by Mitsui Chemicals Co., Ltd. was mixed with the oil-containing porous silica prepared in the reference example 1 at the ratio shown in table 1. Mixed powder was supplied to a mold and molded by heat compression molding method. As the molding condition, temperature: 220° C., pressure: 40 MPa. Turning processing was used for each obtained molding to prepare a ring-shaped sliding material specimen which is the sliding material composition having a dimension of φ17×φ21×10 mm. By using the obtained specimen, the end face of the ring was brought into contact with a rotating disk (ring-on-disk testing machine) to conduct a friction test in conditions and an evaluation method shown below. Results are shown in FIG. 1. The abscissa axis and the ordinate axis in FIG. 1 show a test period of time (minute) and a coefficient of dynamic friction respectively...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com