Irrigation System With Soil Moisture Based Seasonal Watering Adjustment
a technology of irrigation system and seasonal watering schedule, which is applied in the direction of process and machine control, instruments, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve the problems of large amount of wasted water, and adjustment feature not producing the optimum watering schedule, so as to maintain plant health and conserve water
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
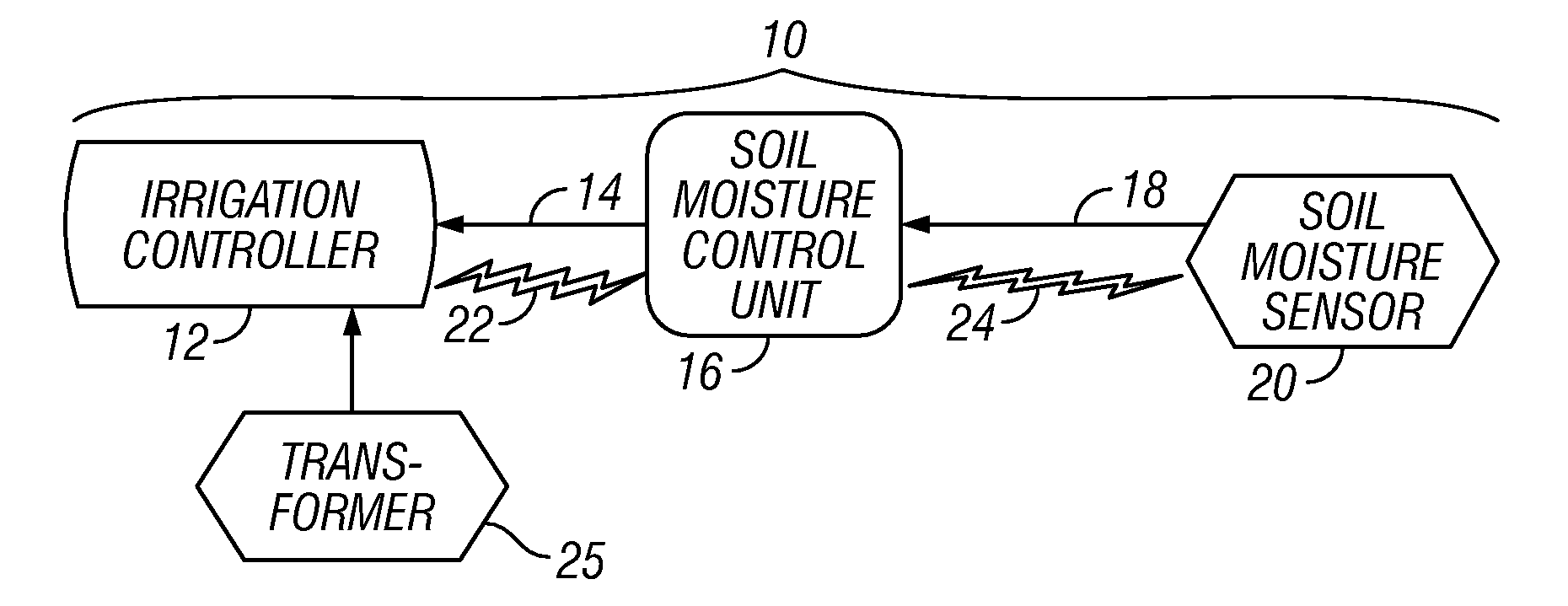
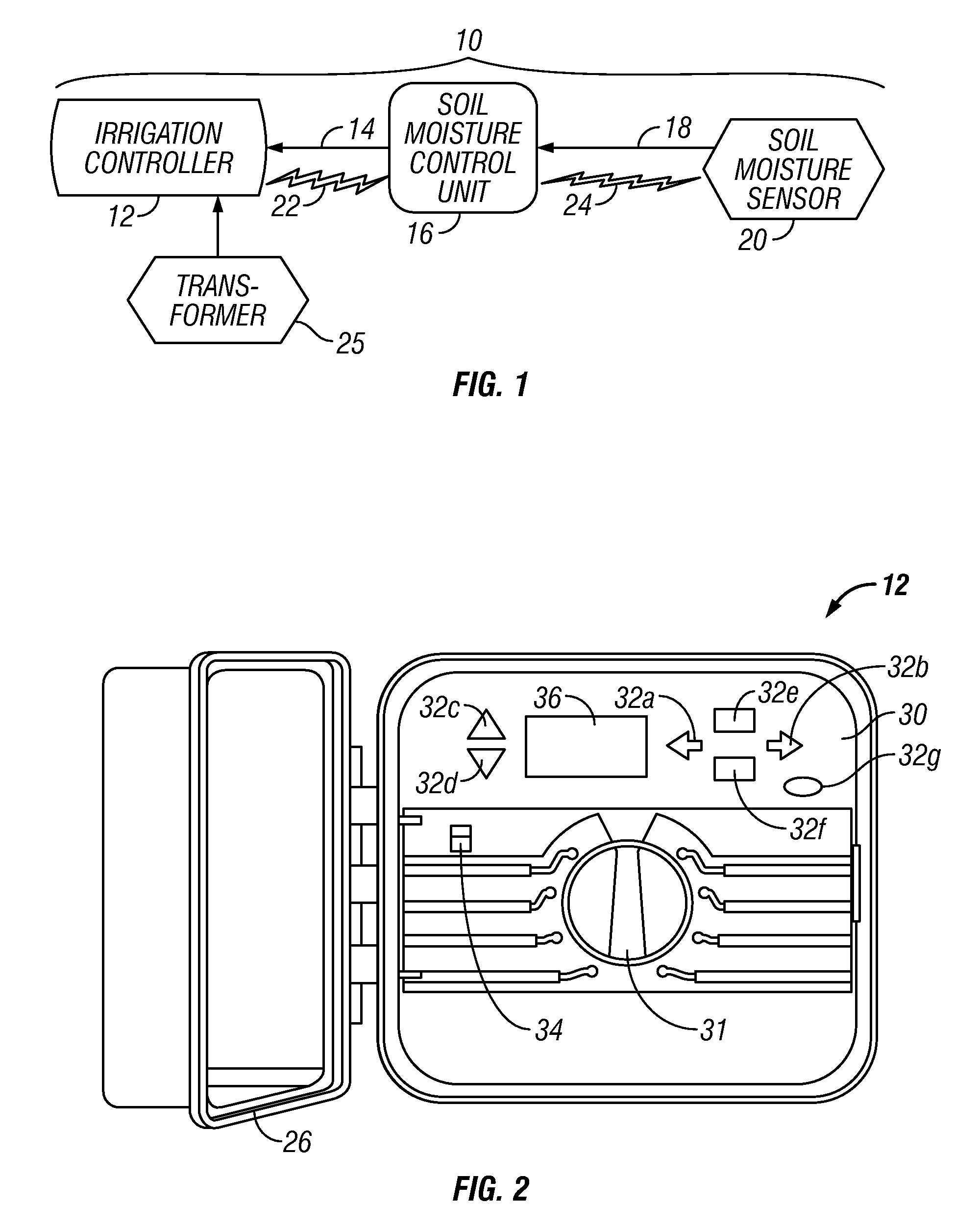
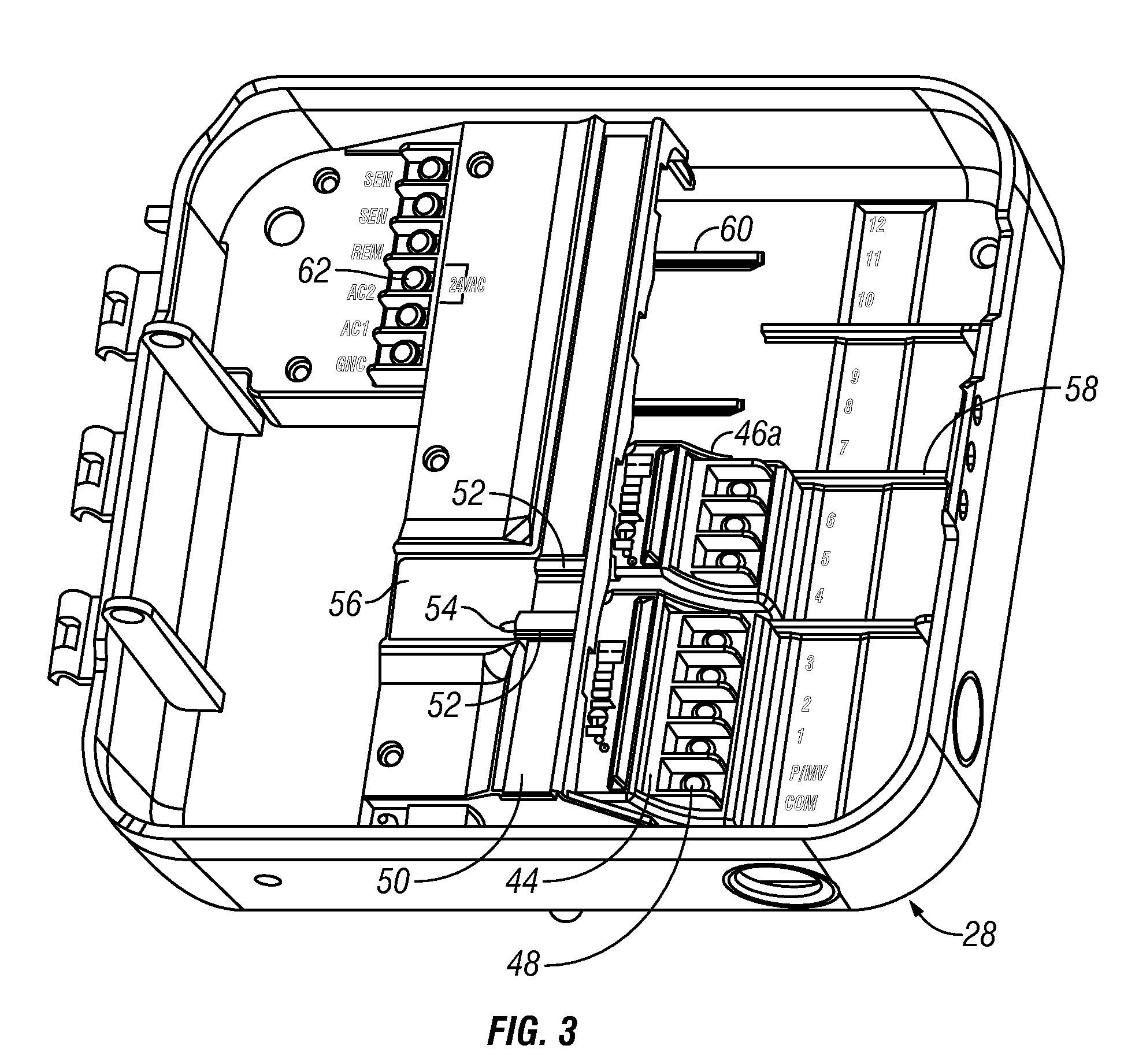
[0024]The entire disclosures of the following U.S. patents and U.S. patent applications are hereby incorporated by reference: U.S. Pat. No. 5,097,861 granted Mar. 24, 1992 of Hopkins et al. entitled IRRIGATION METHOD AND CONTROL SYSTEM; U.S. Pat. No. 5,444,611 granted Aug. 22, 1995 of Peter J. Woytowitz, et al. entitled LAWN AND GARDEN IRRIGATION CONTROLLER; U.S. Pat. No. 5,829,678 granted Nov. 3, 1998 of Richard E. Hunter et al. entitled SELF-CLEANING IRRIGATION REGULATOR VALVE APPARATUS; U.S. Pat. No. 6,088,621 granted Jul. 11, 2000 also of Peter J. Woytowitz et al. entitled PORTABLE APPARATUS FOR RAPID REPROGRAMMING OF IRRIGATION CONTROLLERS; U.S. Pat. No. 6,721,630 granted Apr. 13, 2004 also of Peter J. Woytowitz entitled EXPANDABLE IRRIGATION CONTROLLER WITH OPTIONAL HIGH-DENSITY STATION MODULE; U.S. Pat. No. 6,842,667 granted Jan. 11, 2005 of Beutler et al. entitled POSITIVE STATION MODULE LOCKING MECHANISM FOR EXPANDABLE IRRIGATION CONTROLLER; U.S. patent application Ser. No....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com