Permanent Magnet Machine with Offset Pole Spacing
a permanent magnet machine and offset pole technology, applied in battery/cell propulsion, engine-driven generator propulsion, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve the problems of adversely affecting the operation efficiency of the motor, and achieve the effect of reducing the amplitude of the total ripple of the machin
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
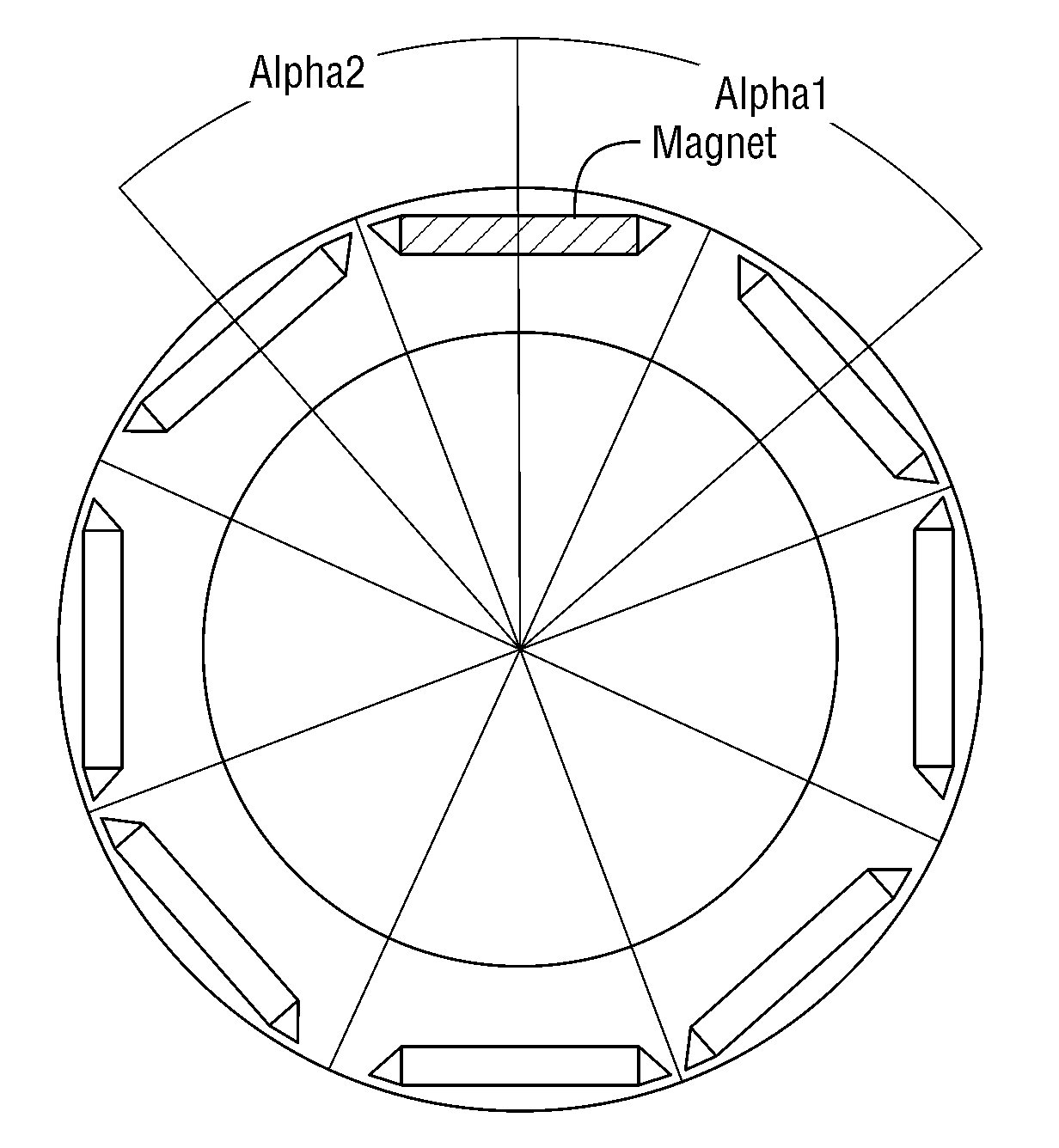
[0058]the invention is shown in FIG. 5, where a rotor lamination has poles that are radially skewed. The skewing is realized within each lamination itself by offsetting the magnetic axis of a motor pole with respect to an adjacent pole.
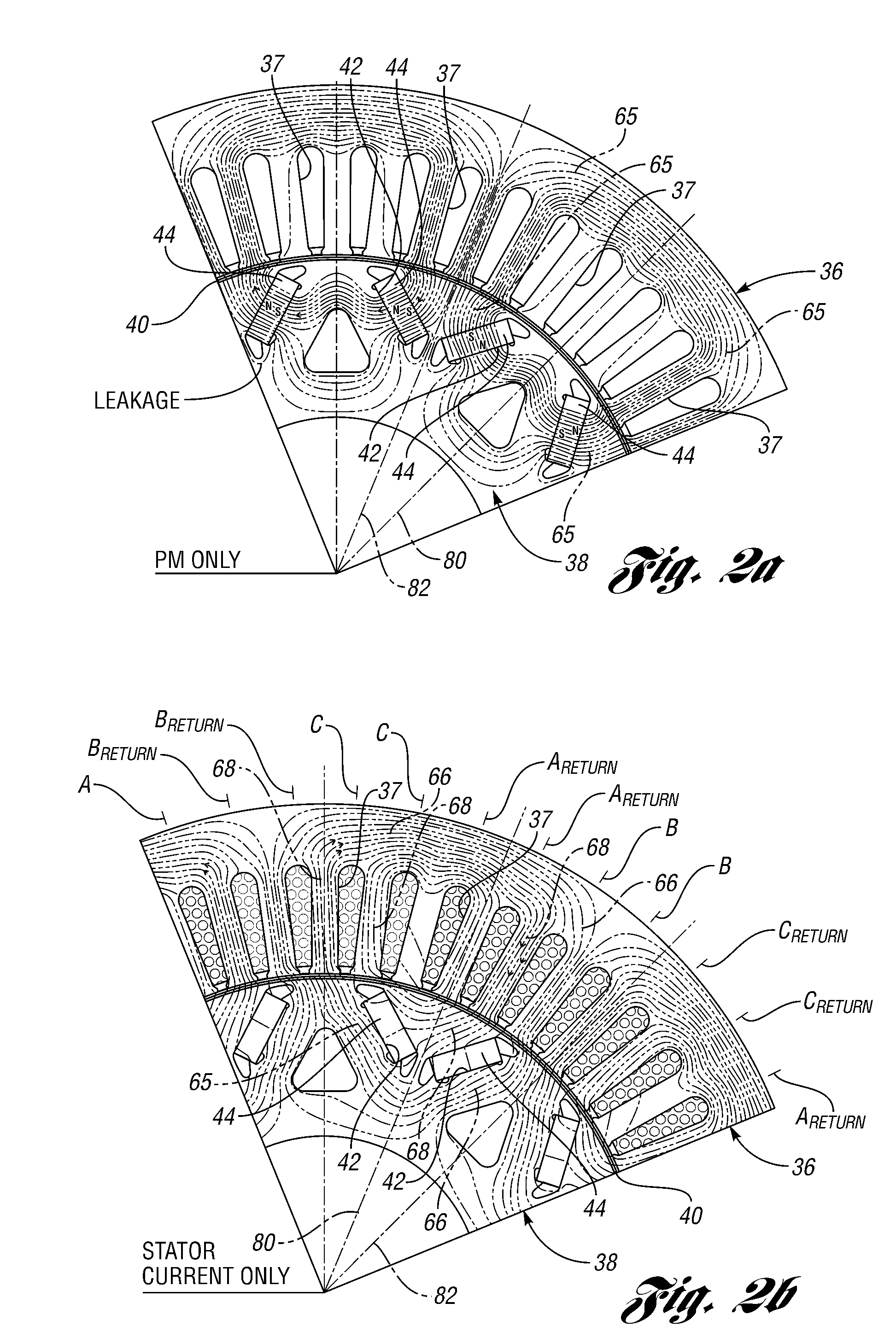
[0059]Manufacture of the rotor is simplified by the absence of several steps usually needed to create multiple, axially-stacked rotor sections. This manufacturing method is especially valuable in the case of an integrated starter-generator type motor, where the stacked length of the sections is normally short and the known skewing method described with reference to FIG. 3 is not feasible. The embodiment of the invention, however, is not limited to short stack motors and generators, but it can be applied to any permanent magnet machine. It can exceed the performance of an electric machine with known skewing and it may be made using simpler manufacturing processes. The performance improvement is due to a further reduction of the torque ripple previously...
third embodiment
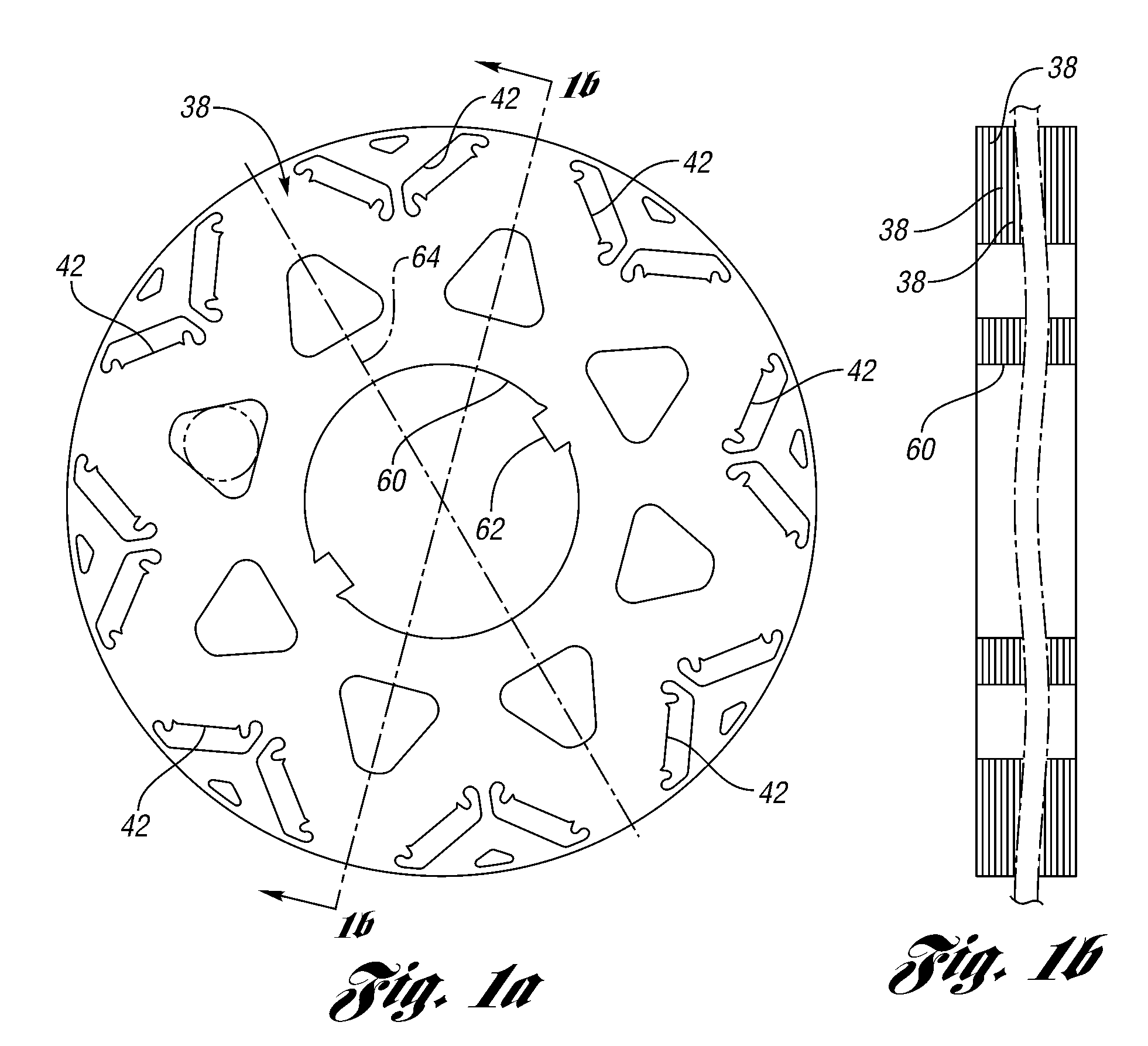
[0071]the invention makes it possible to form the laminations of multiple axial sections in a manufacturing process using a single rotor lamination stamping die in order to avoid multiple lamination types in the same rotor.
[0072]FIG. 14 shows a known skewing arrangement for a permanent magnet motor using a single lamination type where the first section of the rotor is assembled by stacking half of the rotor laminations and inserting the magnets in their magnet openings. The laminations have a key slot 124, where key slot axis 130 is rotated with respect to the nearest pole axis 126 by a certain angle. To create the second section of the rotor, the rest of the laminations are flipped around axis 130, as shown in FIGS. 14 and 15. Because of the flip, the pole axis shown at 126 in FIG. 14 becomes pole axis 128 in FIG. 15 and is rotated by Gamma with respect to axis 130 in the counter-clockwise direction. The optimum angle would be determined based on the harmonic content of the air gap...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com