Control apparatus for internal-combustion engine with variable valve mechanism
a control apparatus and internal combustion technology, applied in combustion engines, valve arrangements, machines/engines, etc., can solve the problems of increased actual in-cylinder compression ratio and more likely knocking, and achieve the effect of properly suppressing the torque change due to deterioration of combustion during the control mode selection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
System Configuration
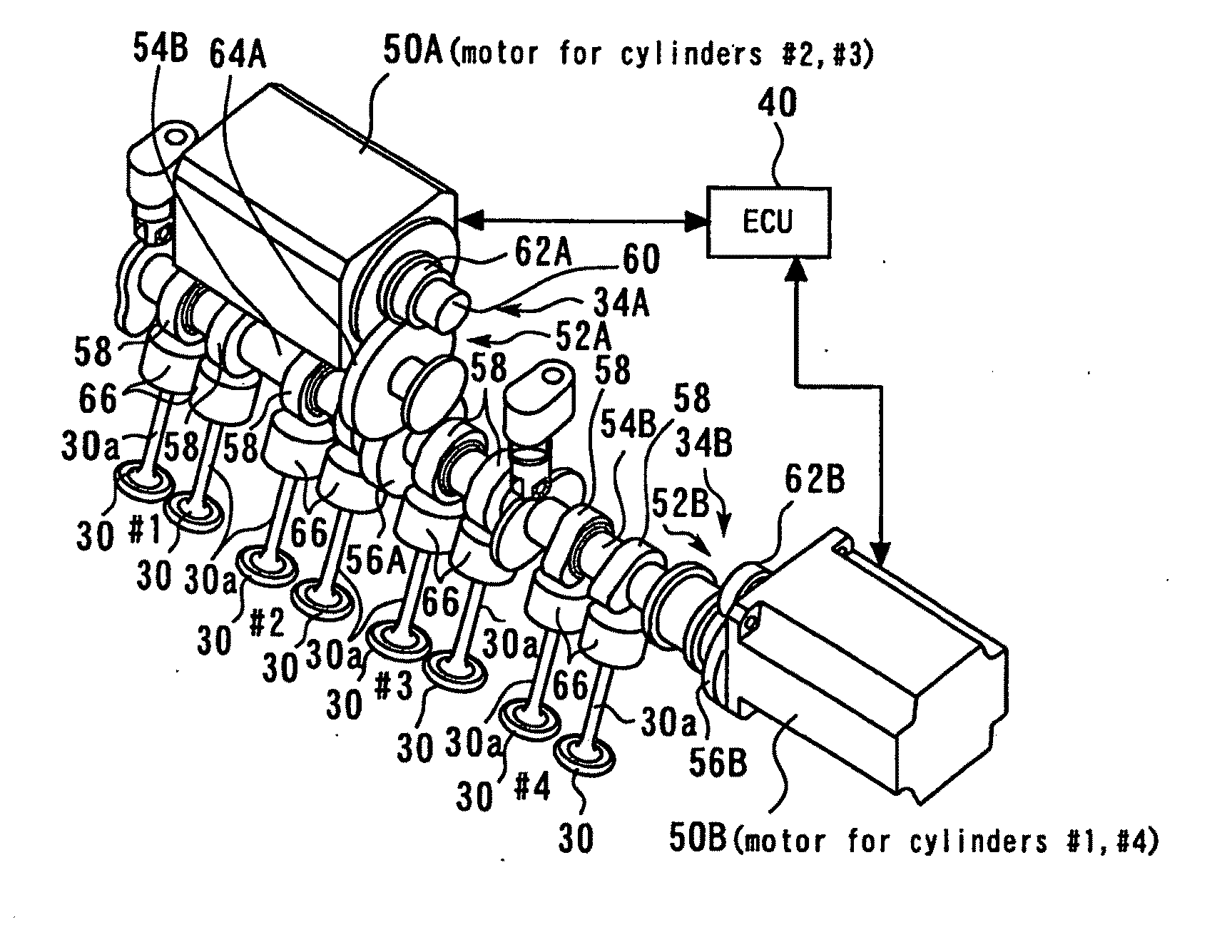
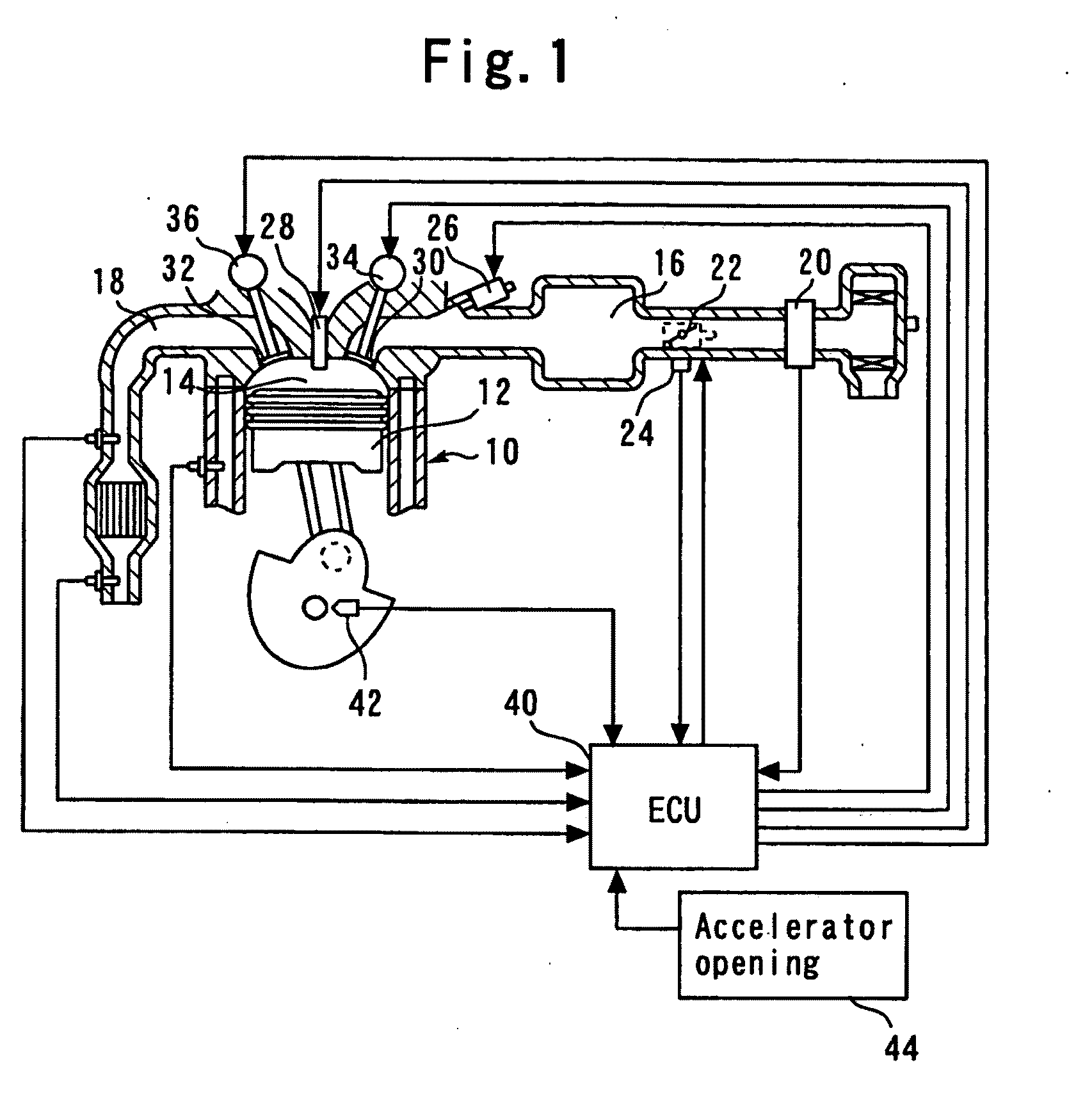
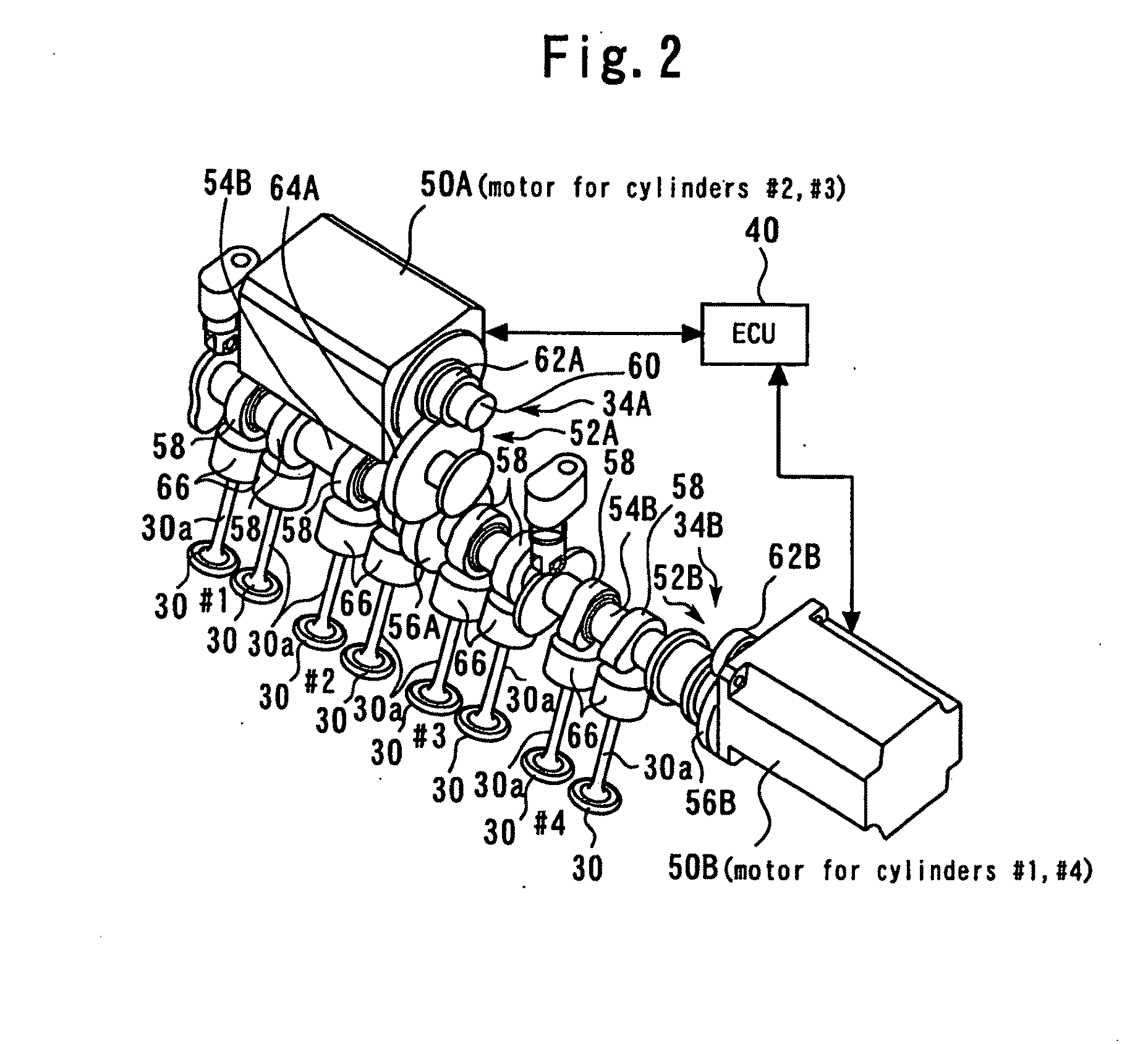
[0045]FIG. 1 is a diagram explaining a configuration of an internal-combustion engine 10 according to a first embodiment of the present invention. The system of the present embodiment includes the internal-combustion engine 10. Also, the present embodiment assumes an inline four-cylinder engine as the internal-combustion engine 10. Each of cylinders of the internal-combustion engine 10 contains a piston 12. Each of the cylinders of the internal-combustion engine 10 has a combustion chamber 14 formed atop the piston 12. An air intake passageway 16 and an exhaust passageway 18 are communicated with the combustion chamber 14.
[0046]An air flow meter 20 is installed near the inlet of the air intake passageway 16 to output a signal representing the flow rate of the air taken into the air intake passageway 16. A throttle valve 22 is installed downstream of the air flow meter 20. The throttle valve 22 is an electronically controlled throttle valve that can control an ope...
second embodiment
[0086]A second embodiment of the present invention will now be described with reference to FIGS. 10 to 12.
[0087]The system according to the second embodiment is implemented by adopting the hardware configuration shown in FIG. 1 and allowing the ECU 40 to execute a routine shown in FIG. 12 instead of the routine shown in FIG. 9.
Feature Portions of the Second Embodiment
[0088]FIG. 10 is a diagram explaining the opening / closing timing of the intake valve 30 used as the second control mode in a second embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 10 shows an example in which, in addition to being opened at a position relatively advanced in angle with respect to the top dead center TDC of air intake, the intake valve 30 has its IVC timing fully retarded to such an extent that blowback of the intake air into the intake passage intentionally occurs to lower an actual compression ratio.
[0089]The IVC timing here of such an extent that the blowback of the intake air intentionally occurs refers to ...
third embodiment
[0109]A third embodiment of the present invention will now be described with reference to FIG. 13.
[0110]The system according to the third embodiment is implemented by adopting the hardware configuration shown in FIG. 1 and allowing the ECU 40 to execute a routine shown in FIG. 13 instead of the routine shown in FIG. 12.
Feature Portions of the Third Embodiment
[0111]The system of the present embodiment is characterized in a technique relating to the torque adjustments performed when the control mode is instantly changed between the IVC variable control and the intake valve closing retardation control (the torque adjustments are detailed in step 300 and the like). More specifically, the present embodiment adjusts a change range of throttle angle TA on the basis of the IVC timing and operating angle of the intake valve 30 existing after the control mode change.
[0112]When the intake valve closing retardation control that uses such opening / closing timing of the intake valve 30 as shown in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com