Battery pack, and battery system
a battery system and battery pack technology, applied in the manufacture of secondary batteries, electrochemical generators, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve the problems of secondary batteries becoming unsafe states, unnecessary power loss increases, and expected life shortened, so as to reduce unnecessary power loss, and reduce the variation in the state of charge
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
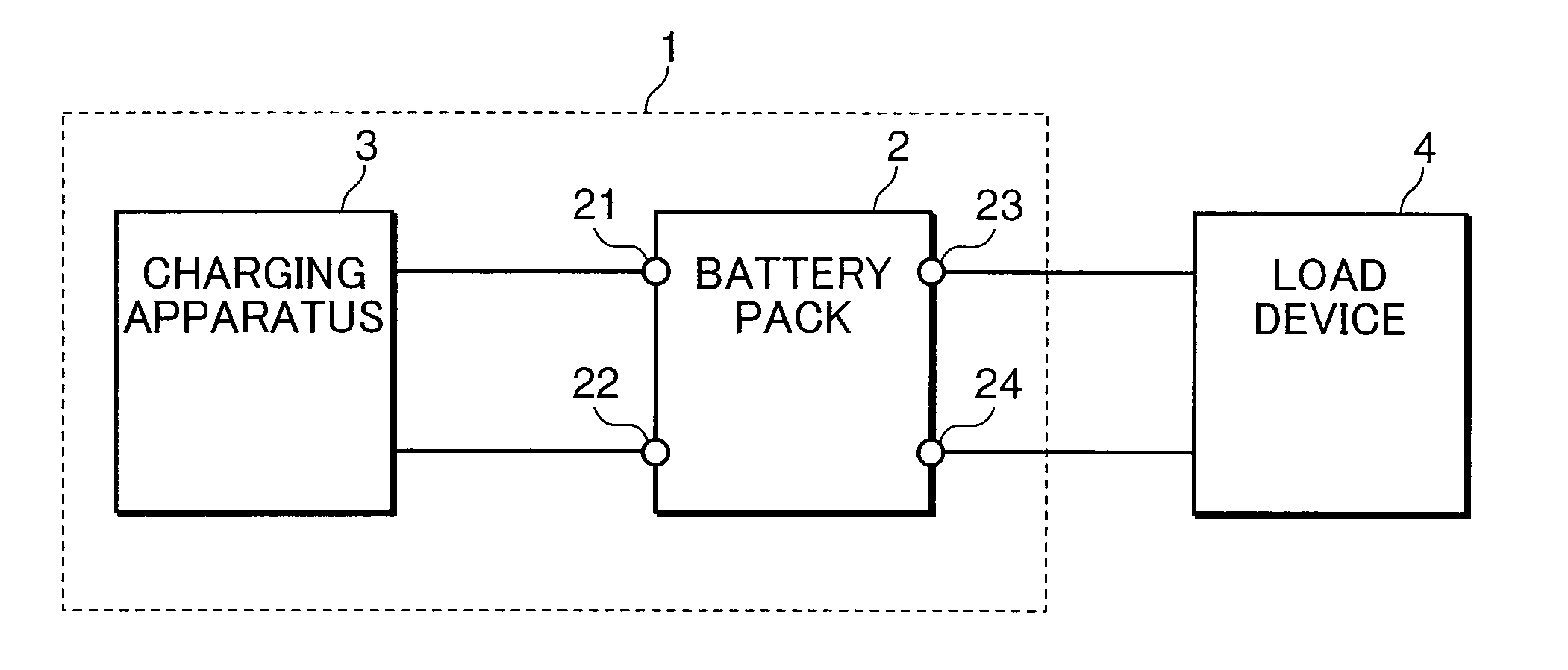
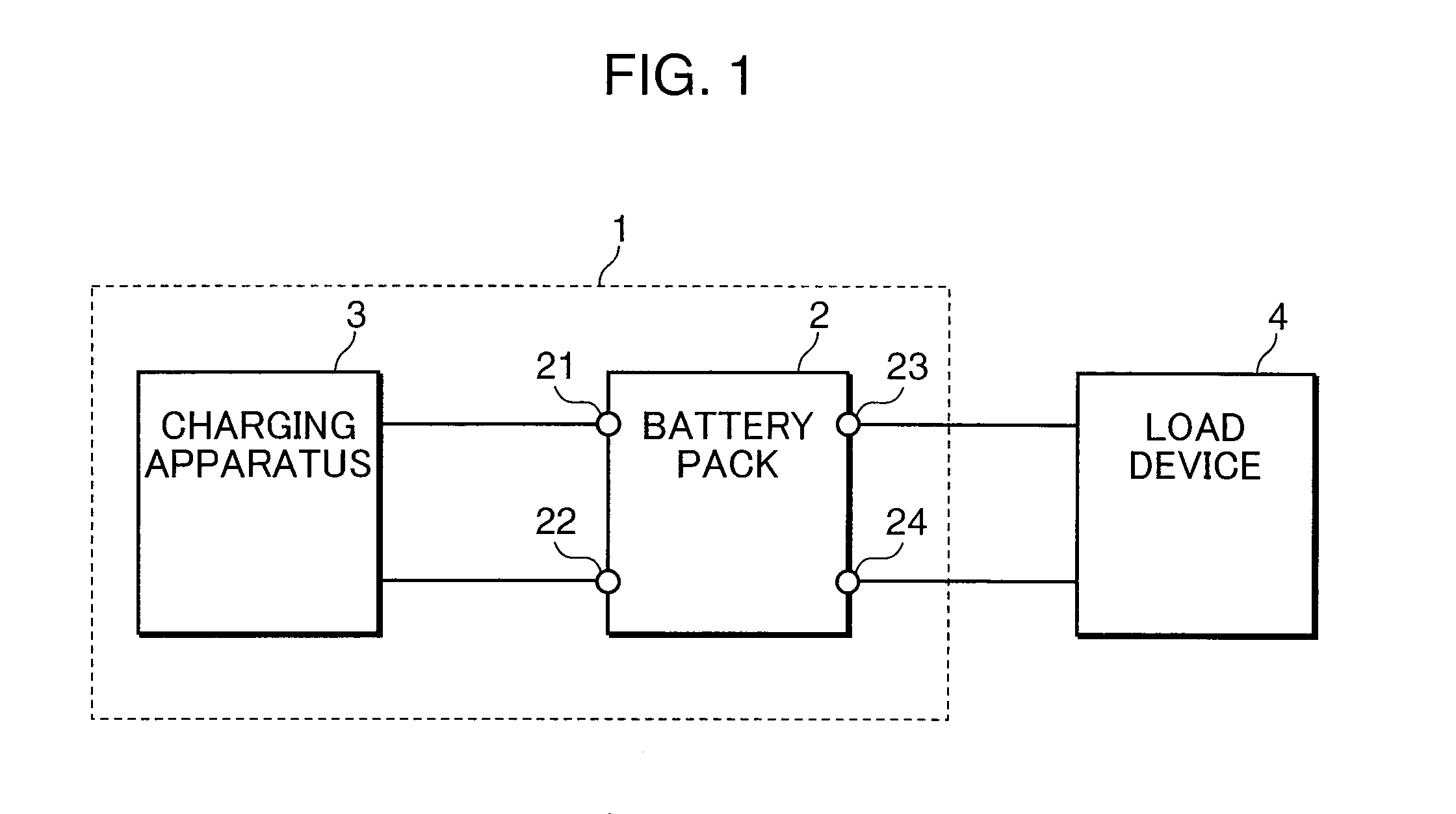
[0015]An embodiment of the present invention is now explained with reference to the attached drawings. Incidentally, configurations that are given the same reference numeral in the respective drawings mean that they are of the same configuration, and the explanation thereof is omitted. FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing an example of the configuration of the battery system according to an embodiment of the present invention. The battery system 1 shown in FIG. 1 comprises a battery pack 2, and a charging apparatus 3 (charging current supply unit).
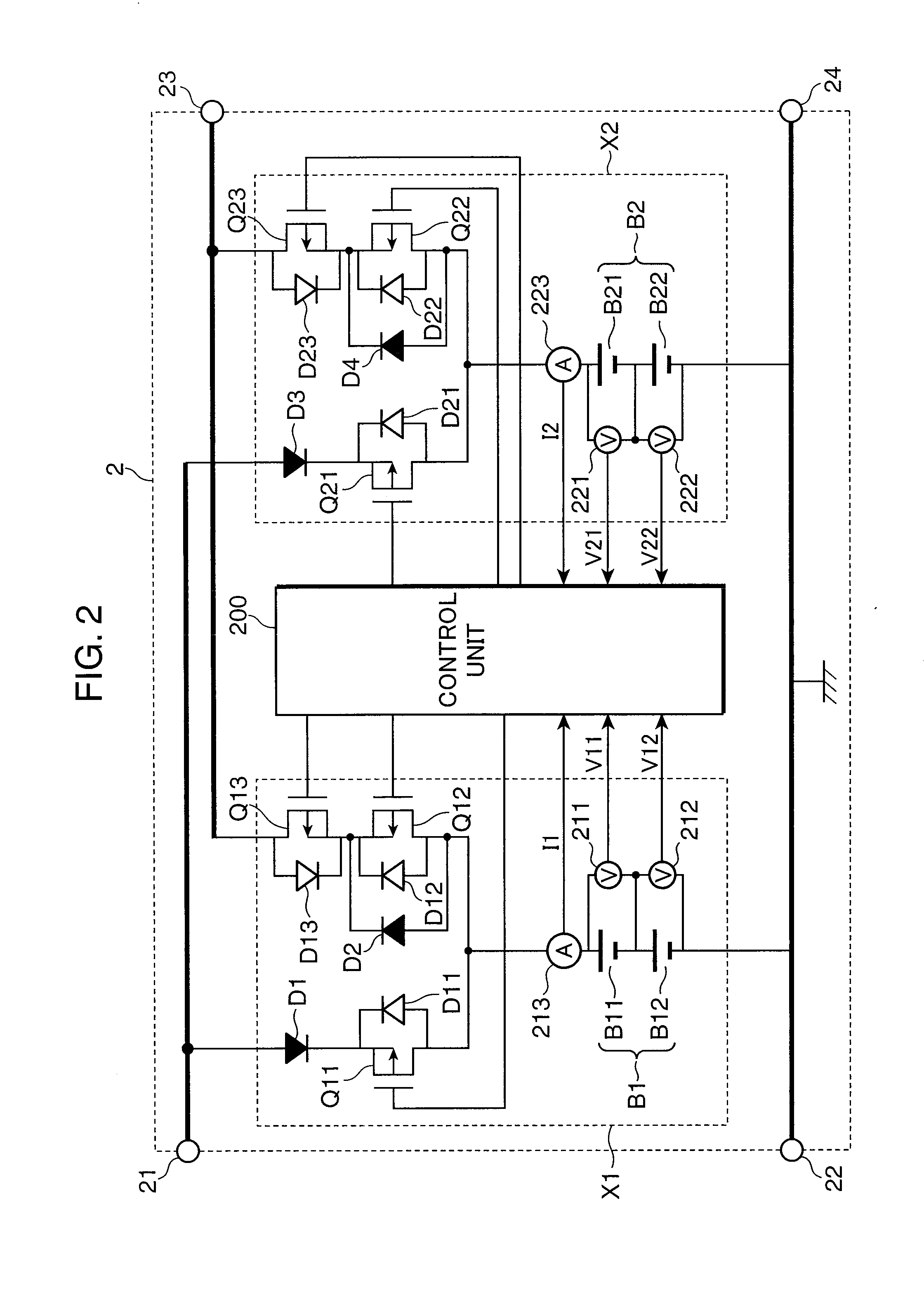
[0016]The charging apparatus 3 is a power circuit for outputting a charging current for charging the battery pack 2. The battery pack 2 comprises connecting terminals 21, 22, 23, 24. The connecting terminals 21, 22 are charge terminals for receiving the charging current output from the charging apparatus 3, and are connected to the charging apparatus 3. The connecting terminals 23, 24 are discharge terminals for supplying the discharging curr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com