Tissue compression using surgical clips
a technology of tissue compression and surgical clips, applied in the field of tissue compression employing surgical clips, can solve the problems of difficult to achieve continuous lines, and achieve the effect of reducing the risk of tissue perforation by a clip and reducing the leakage of bodily fluids
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
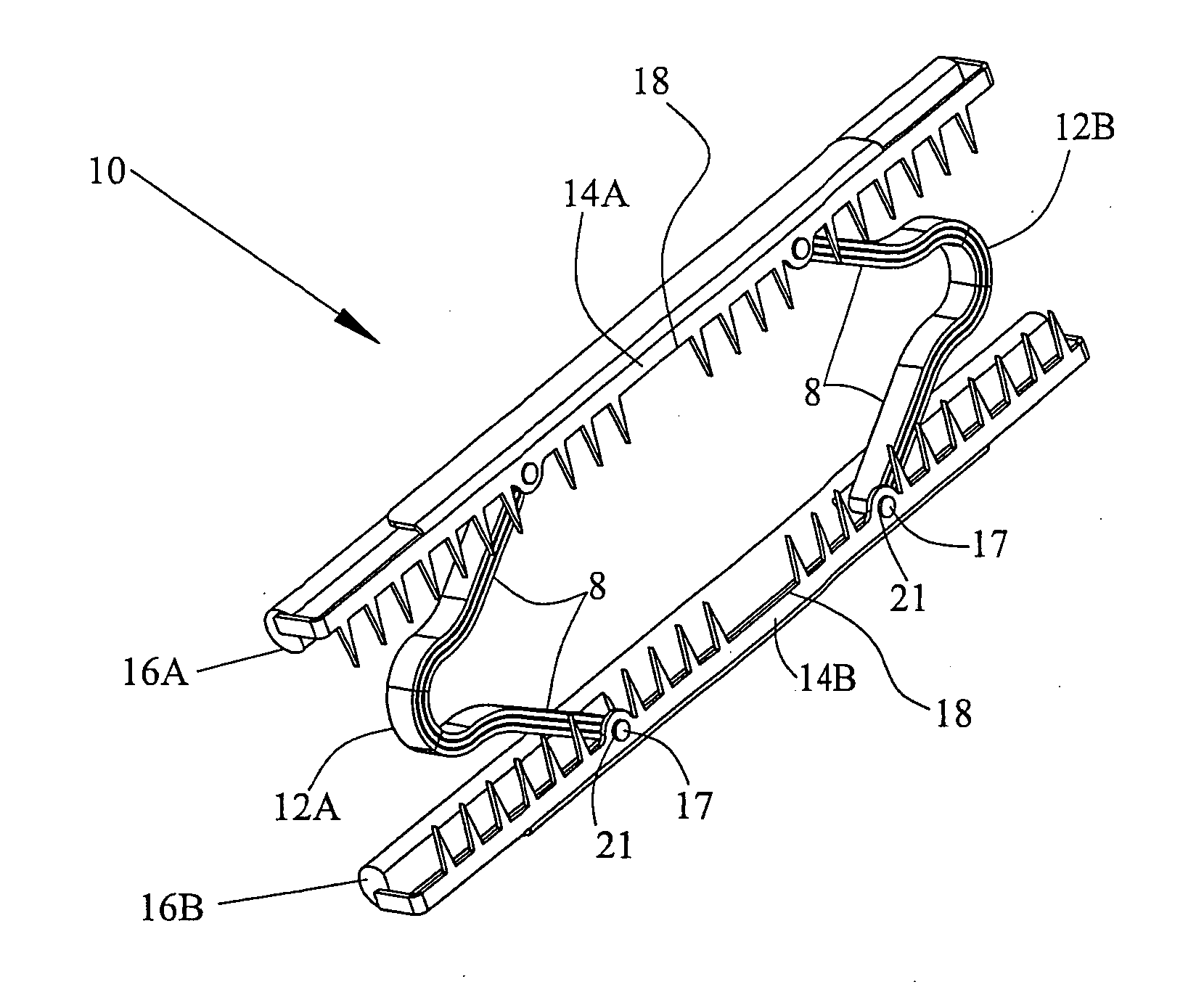
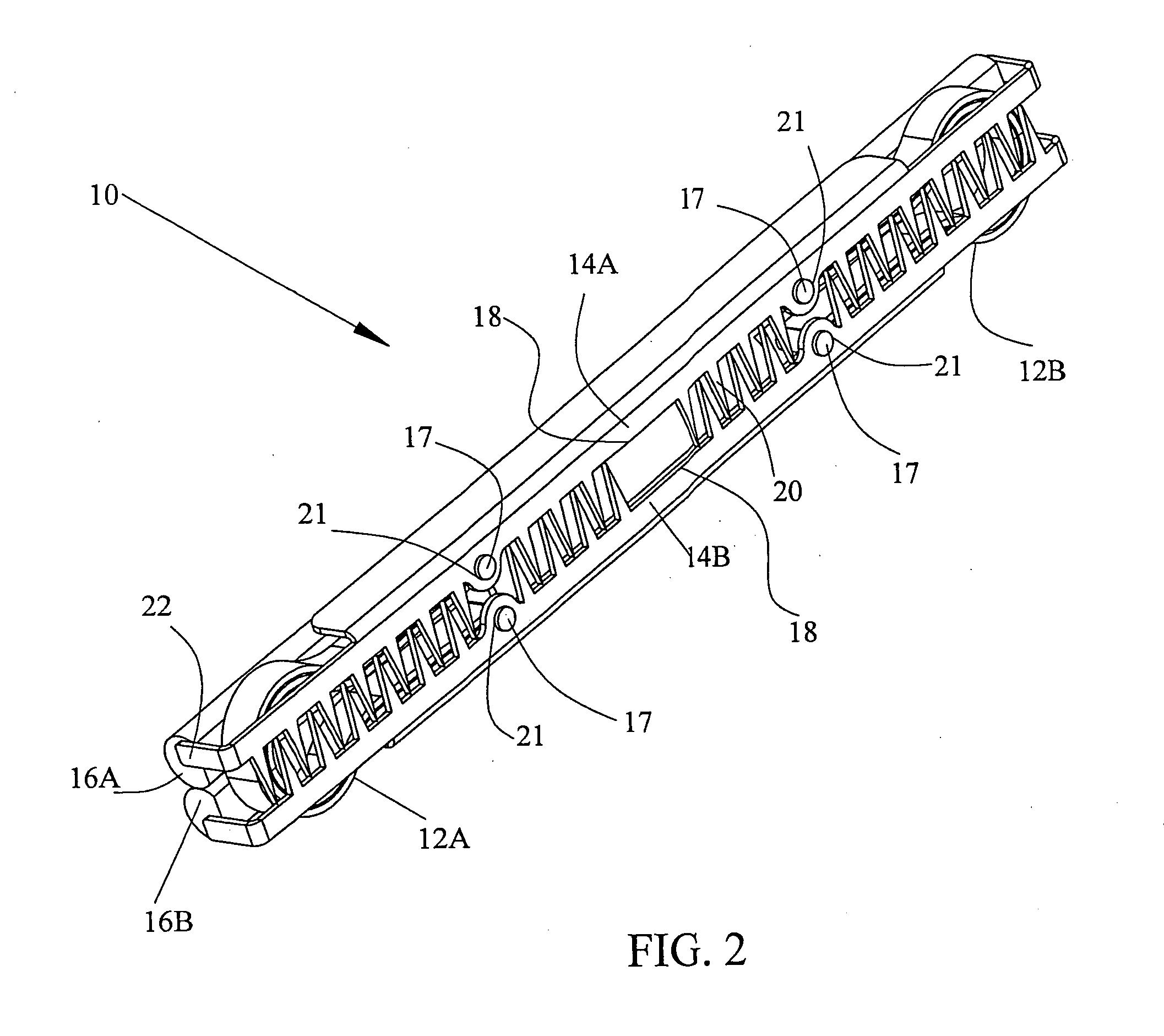
[0155]Reference is now made to FIGS. 2-3B where FIG. 2 presents a view of a non-unitary compression clip constructed according to the present invention. In FIG. 2 the clip is shown in its closed position. FIGS. 3A and 3B present a view of the compression clip shown in FIG. 2 in its open position.
[0156]Clip 10 is constructed of two shape-memory hinge springs 12A and 12B, also herein often denoted as force appliers. Typically, but without intending to be limiting, the shape-memory material is a Ni—Ti alloy. The operation of the clip relies on shape-memory effects exhibited by these materials. Springs 12A and 12B may be made of a single wire or flattened wire or strip or it may be constructed of two or more wires, flattened wires or strips connected together at their ends. Furthermore, in some embodiments, the springs may be constructed to have a coiled shape.
[0157]Clip 10 further includes two securing elements 14A and 14B, each of which has a series of teeth 20 for grasping tissue. Ea...
second embodiment
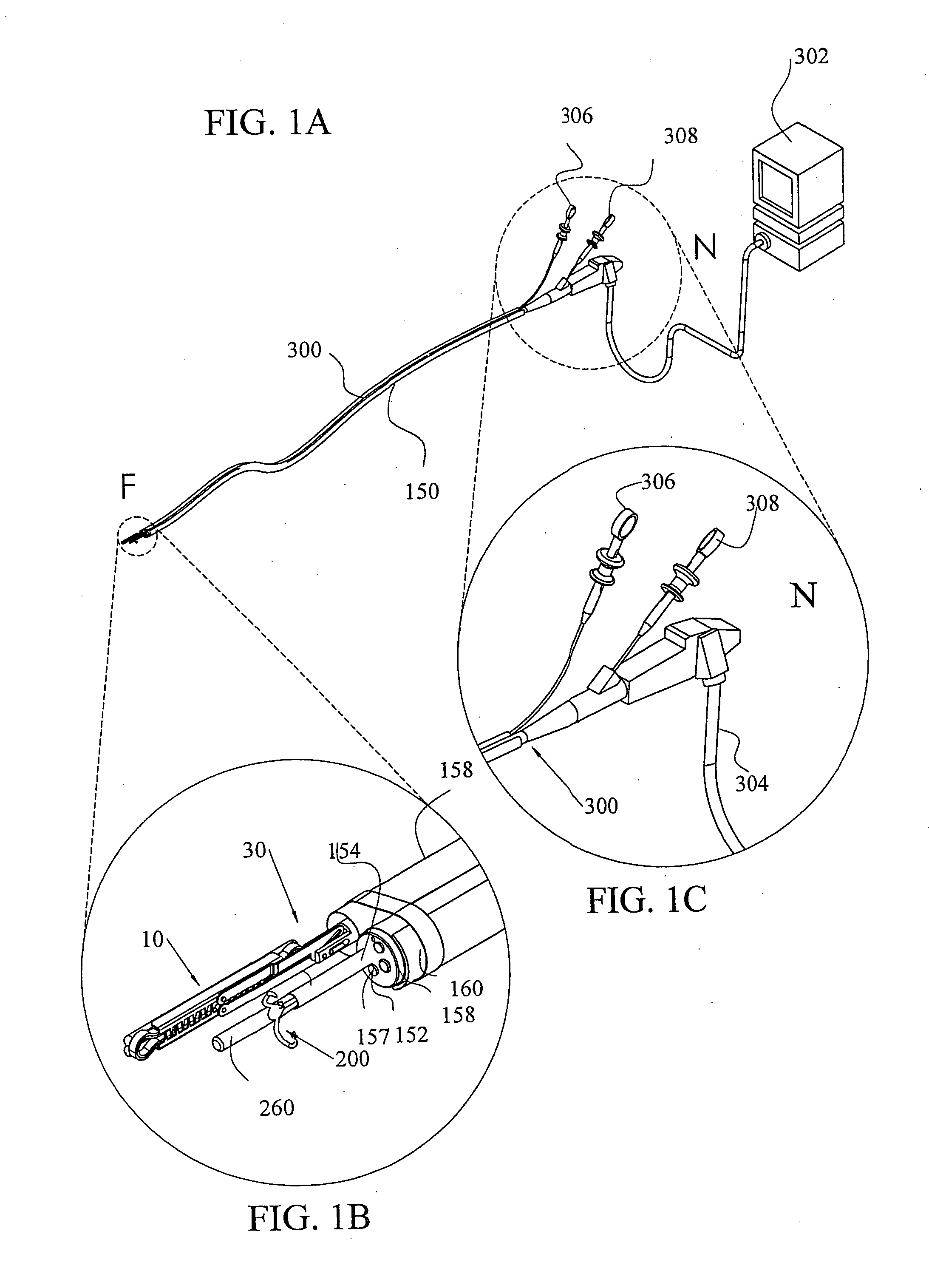
[0182]FIGS. 10-13, to which reference is now made, show various views of a clip applier constructed according to the present invention. The applier is intended for use with the surgical compression clip (slightly modified as discussed below) shown in and discussed in conjunction with FIGS. 2-3B. FIG. 10 shows the clip applier in its closed position, while FIG. 11 shows the applier in its open position.
[0183]Turning to FIG. 11 first, clip applier 50 includes insertion links 60A and 60B which are swing jointed by links 62A, 62B, 64A, 64B and central bar 66. An operating cable (not shown) is connected to the proximal end of central bar 66 and inserted into spring 52. The latter connection can be achieved by welding or any other connecting method or means known to those skilled in the art.
[0184]Insertion links 60A and 60B each have extensions (not shown) which are positioned on their distal end so that these extensions are insertable into cylindrical elements 58A and 58B. As shown in FI...
third embodiment
[0203]a compression clip constructed according to the present invention is shown in FIGS. 24A and 24B, to which reference is now made.
[0204]From FIG. 24A, which shows an exploded view of clip 610, it is readily apparent that many of the elements presented there have been encountered and described previously in conjunction with previously discussed embodiments of compression clips constructed according to the present invention. Accordingly, elements that are structurally and operationally similar to previously described elements will not be described again here. Essentially identical or equivalent elements to those found in clips 10 and 510 have been numbered as in clips 10 and 510 with the prefix 600.
[0205]Securing and compressing elements 614A, 614B and 616A, 616B, respectively, are essentially the same as in clip 510. Hinge springs 612A and 612B are unsymmetrical as in clip 510. Again, there is a bi-directional connector 617 on the shorter legs 609A and 609B of hinge springs 612A ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com