Forming Multiple Deviated Wellbores
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
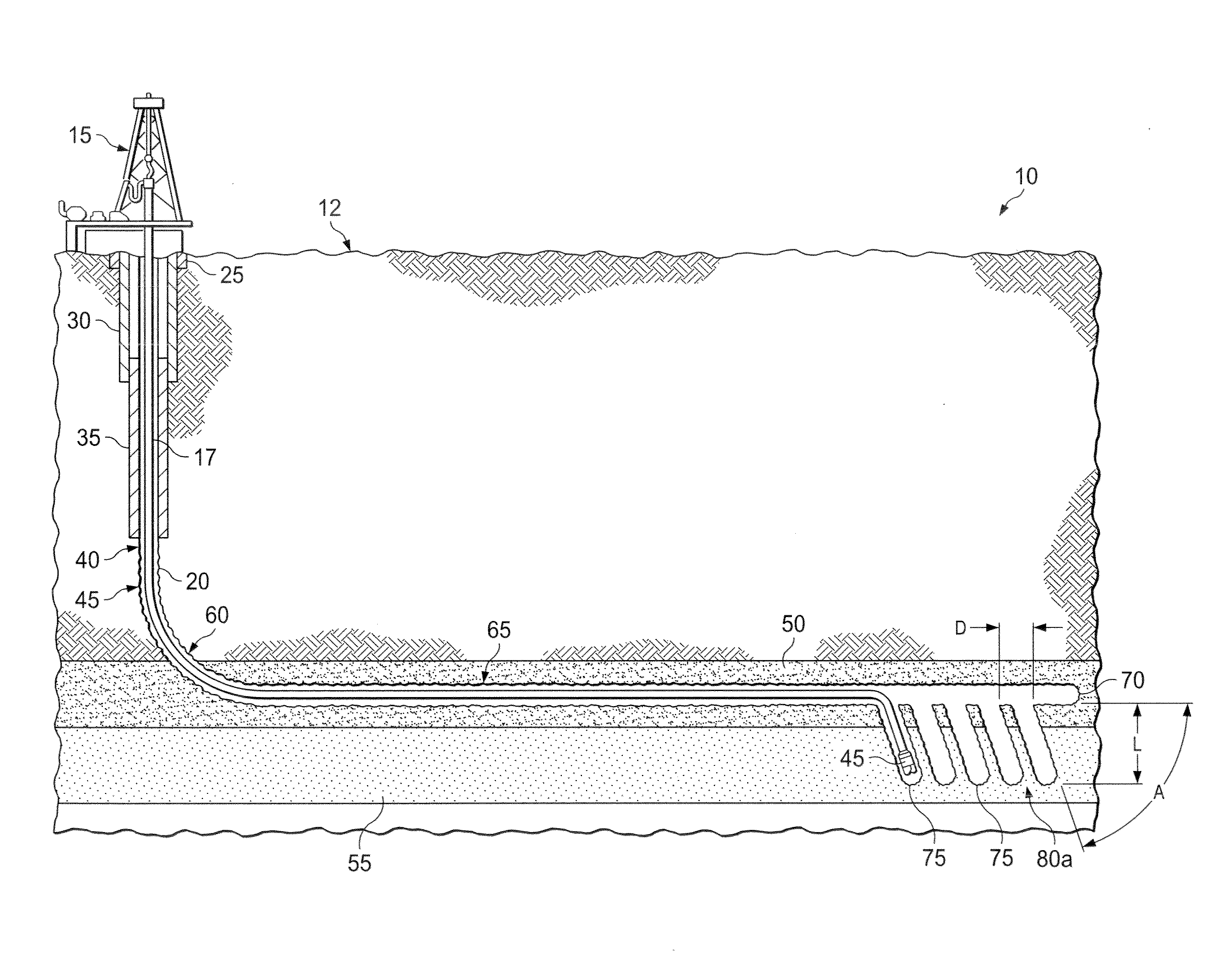
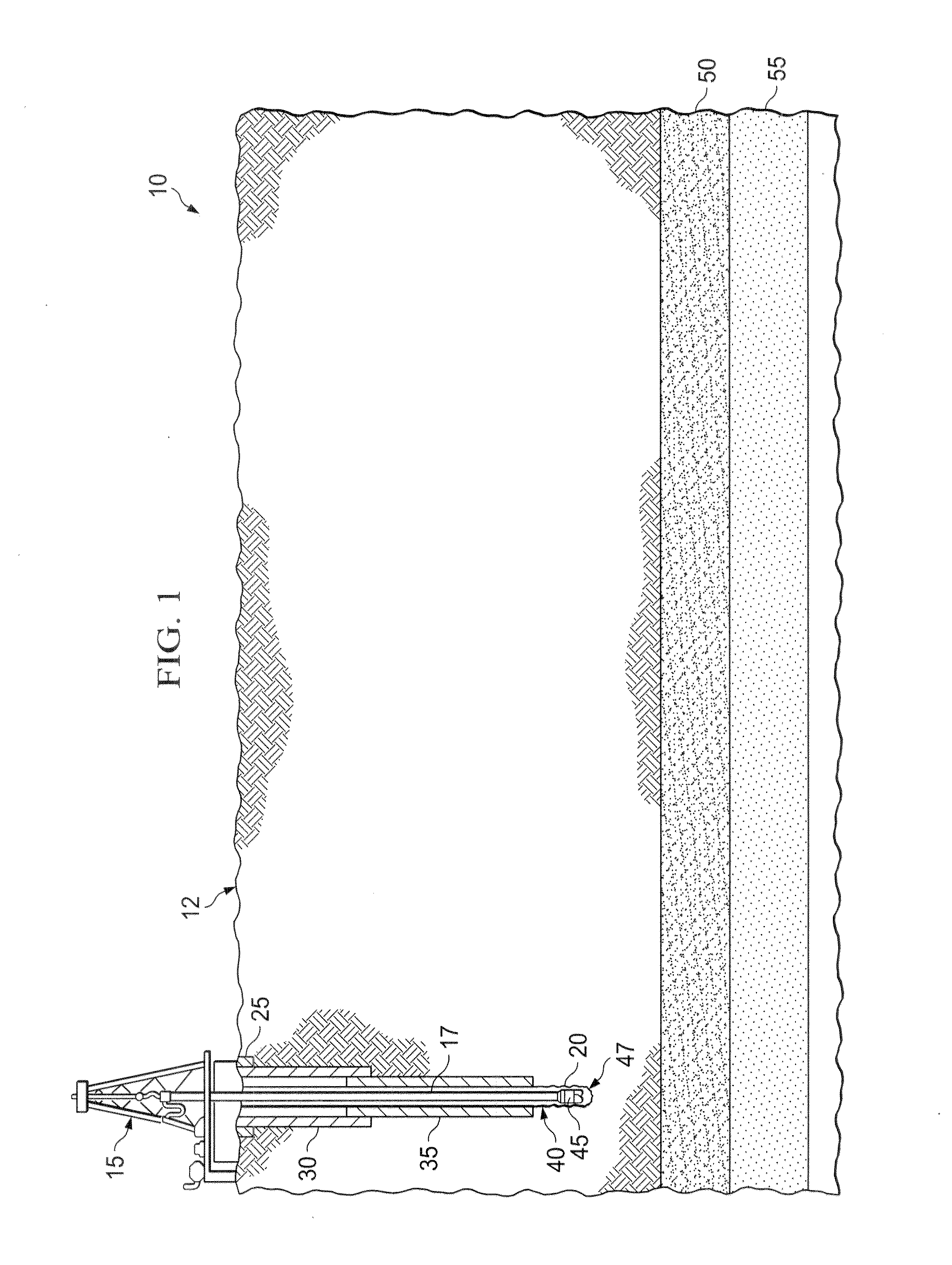
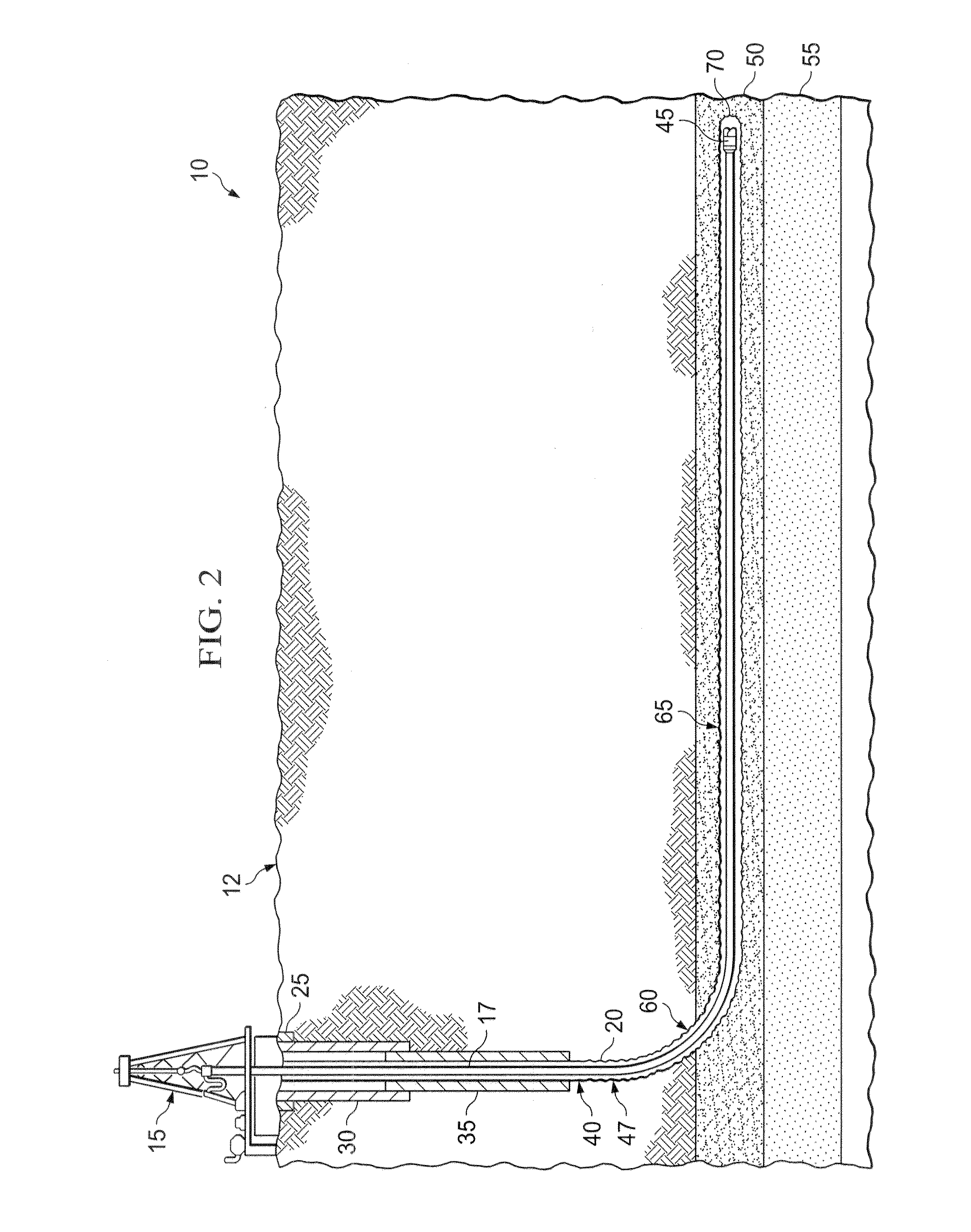
[0030]In some embodiments, a deviated wellbore system according to the present disclosure includes an articulated wellbore drilled from the surface to a target geological formation located above the target productive formation. The articulated wellbore may include a substantially vertical portion, a radiused portion, and a substantially horizontal portion landing in the target geological formation to be drilled horizontally. In some embodiments, the target geological formation is located adjacent a production formation containing one or more hydrocarbons, such as oil or gas. In some embodiments, the production formation may be a formation containing natural gas such as a shale formation, siltstone, sandstone matrix or limestone matrix. The deviated wellbore system may also include one or more deviated wellbores, or completion paths (e.g., production, fracture, stimulation paths), drilled from the substantially horizontal portion of the wellbore into the productive formation. Complet...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com