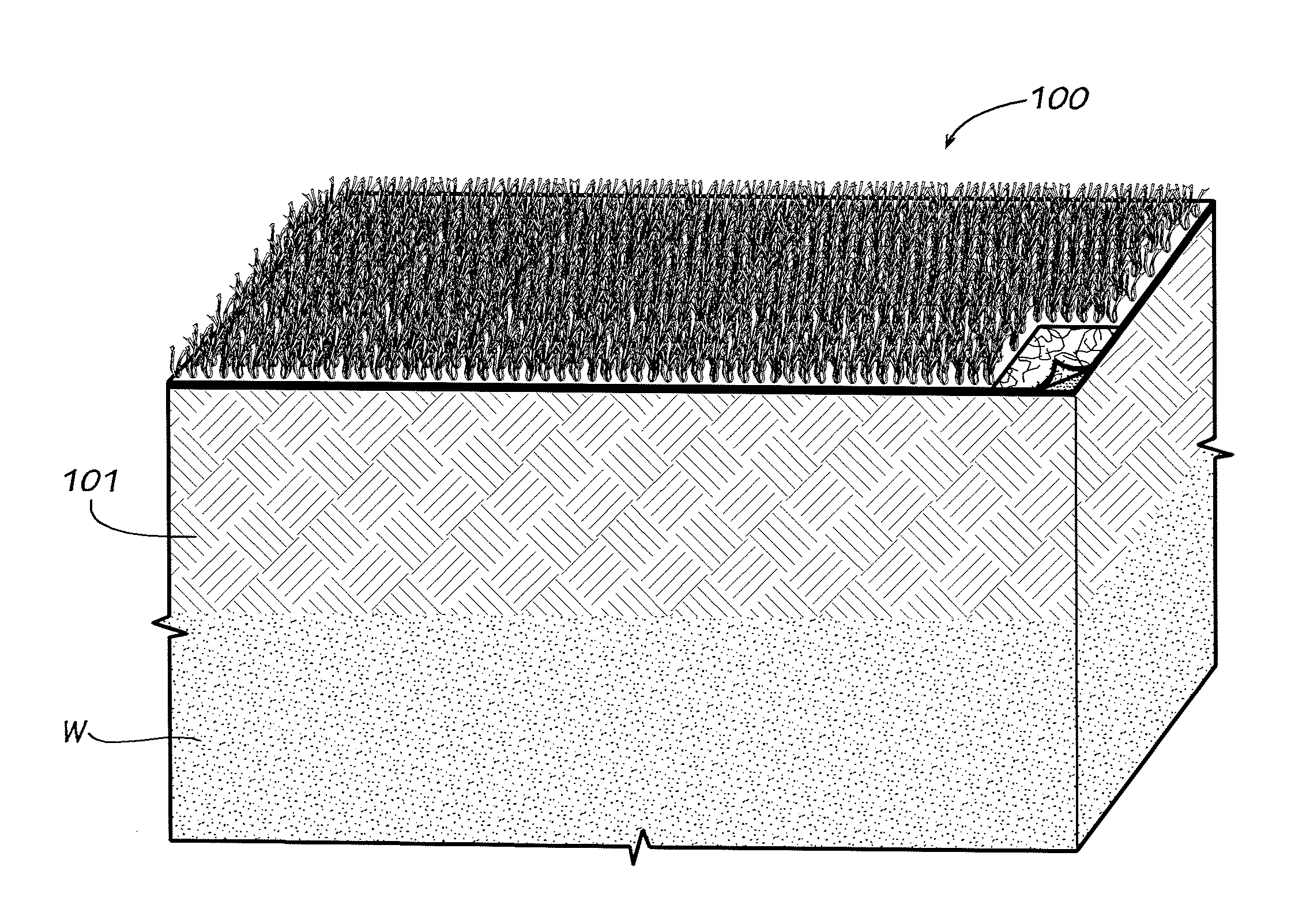
Wind-resistant environmental synthetic cover
a synthetic cover and wind-resistant technology, applied in the field of wind-resistant environmental synthetic cover, can solve the problems of large construction cost, difficult maintenance, easy eroded soil layer, etc., and achieve the effects of increasing the friction resistance, extending the longevity of the geomembrane component, and increasing the distan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
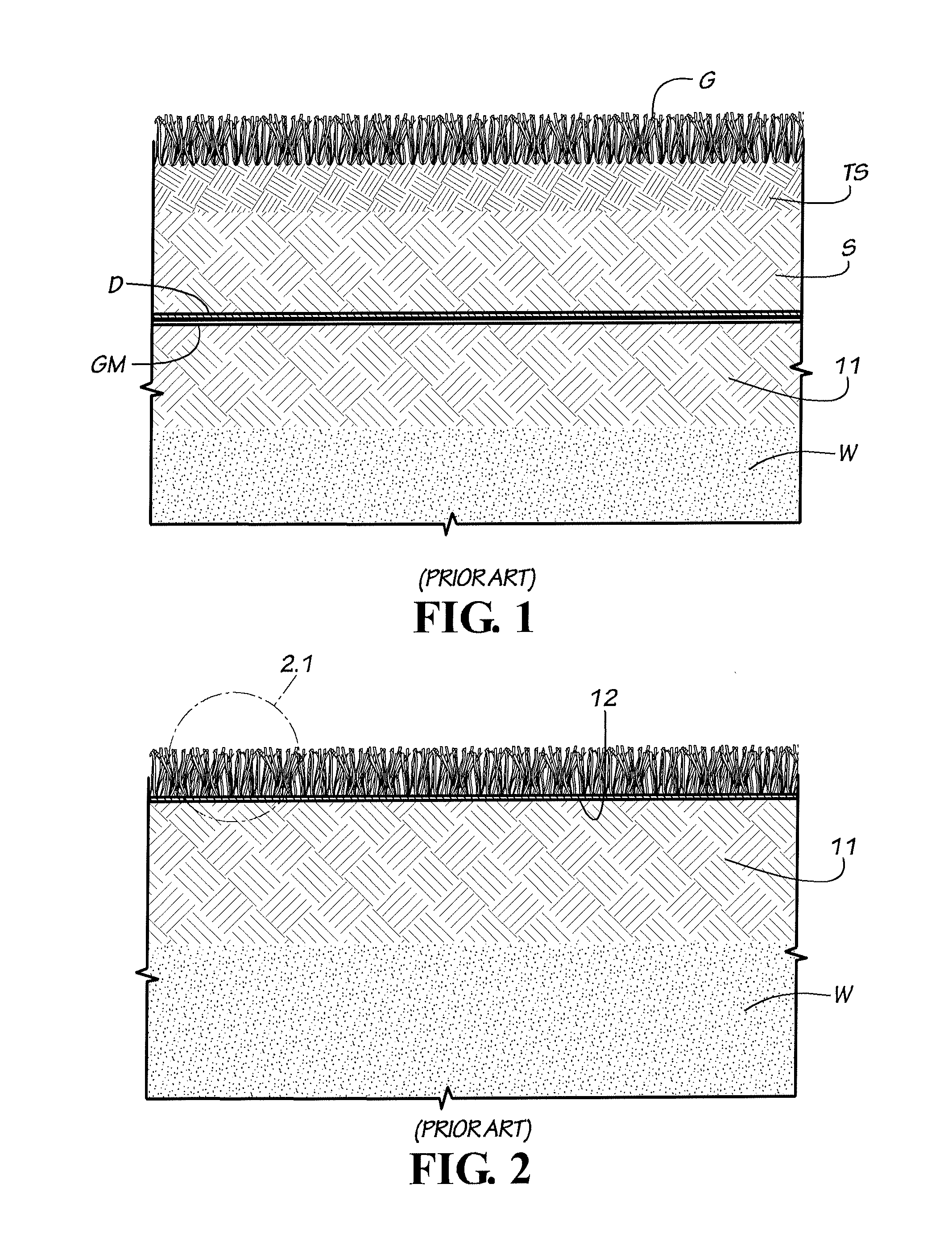
[0021]FIG. 1 depicts a cross sectional view of a typical cover system as described in current United States Environmental Protection Agency federal regulations and as used in the covers for landfills and mines. In this case the two feet of soil is used to cover the geomembrane against wind uplift.
[0022]FIG. 2 depicts a prior art cover where the geomembrane is exposed to the environment. The system requires extensive anchoring in order to resist wind uplift forces.
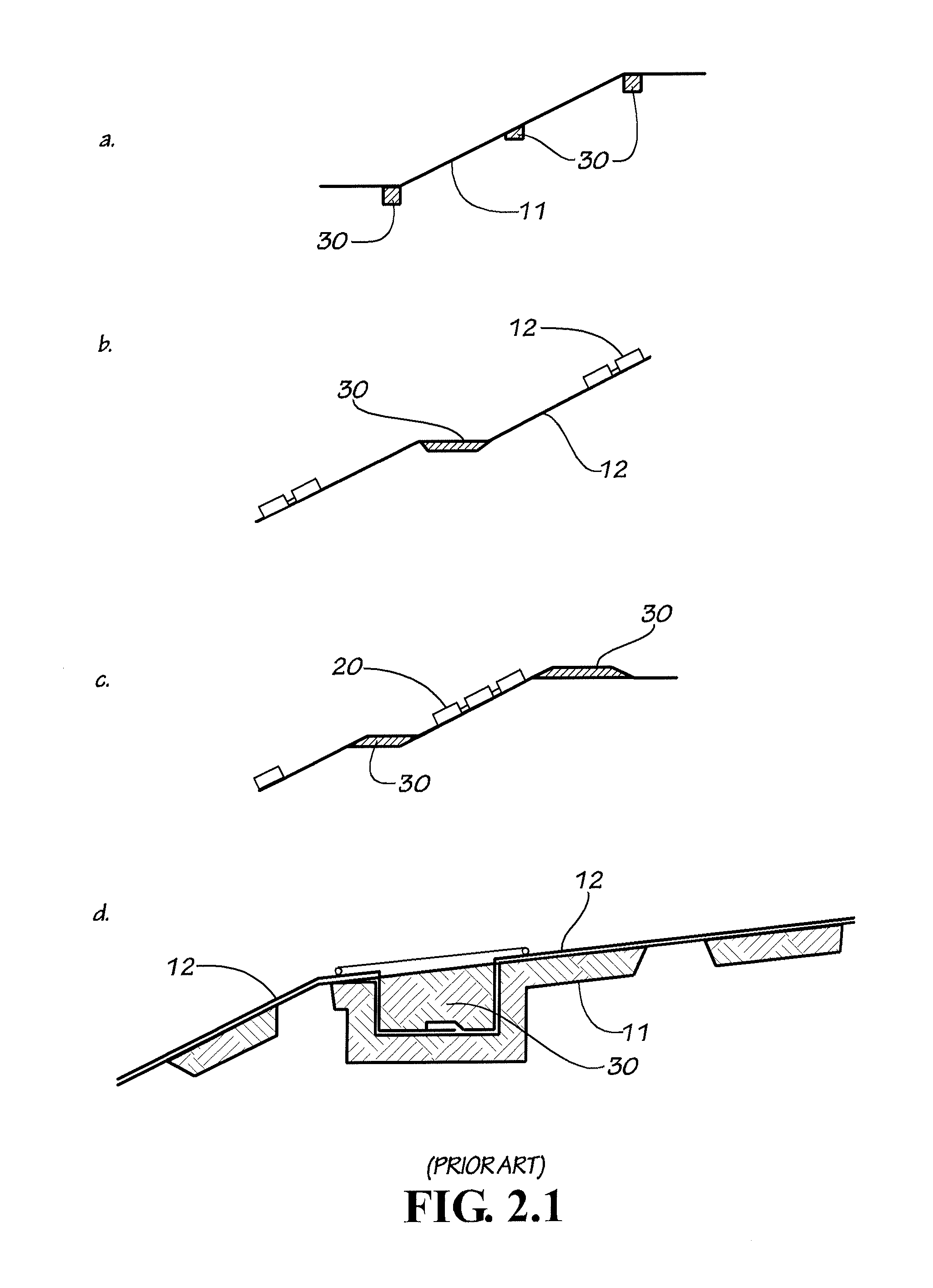
[0023]FIG. 2.1 depicts prior art covers of exposed geomembrane arrangements and in general shows a cross sectional view of anchor trenches (30) used along the slope of an exposed geomembrane cover to secure it in place in the face of wind which would otherwise tend to lift the cover. The figure shows the geomembrane / raincoat cover (12), and the use of tires (20) tied with ropes as additional ballasting system of the exposed geomembrane (12). This type of prior art anchoring required to resist uplift is very expensive and it...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com