Human Oncostatin M Antibodies and Methods of Use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Reagents and Assays
[0105]In order to select and characterize OSM-binding antibodies, constructs of human and Cyno OSM were generated for mammalian cell expression. Human OSM (NP—065391 encoded by NM—020530) is a 252 amino acid precursor processed into a full-length secreted protein of 227 amino acids (SEQ ID NO: 11), which is a proprotein further processed into the more fully active mature form, amino acids, 1-184. Human OSM cDNA was ordered from OriGene (Cat. No. SC121421) and the ORF of human OSM from the OriGene clone was amplified by PCR and a signal peptide (murine IgG1) was introduced along with a hexa-His tag for protein purification and an AviTag (SEQ ID NO: 56) for site-directed protein biotinylation. The latter was chosen to avoid random chemical biotinylation of lysine residues present in the vicinity of OSM intereaction with receptors.
[0106]Cynomolgous monkey OSM was cloned from cyno PBMC's RNA using Superscript III first strand synthesis system (InVitrogen) to obtain th...
example 2
Selection Of OSM Binding Fabs
[0128]The de novo Fab-pIX libraries have been described Shi et al. J Mol Biol 397:385-396, 2010; WO09085462A1; U.S. Ser. No. 12 / 546,850; and herein above are designated 169, 323 and 551 which references the heavy-chain human germline framework being used: IGHV1-69 (SEQ ID NO: 1), IGHV3-23 (SEQ ID NO: 2), or IGHVS-51(SEQ ID NO: 3) in IMGT nomenclature. The three heavy-chain library frameworks are combined with four light-chain library VLkappa frameworks: A27 (IGKV3-20*01 (SEQ ID NO: 5)), B3 (IGKV4-1*01 (SEQ ID NO: 6)), L6 (IGKV3-11*01 (SEQ ID NO: 7)), and 012 (IGKV1-39*01 (SEQ ID NO: 8)). In the libraries, the Fabs V-regions are completed by the addition of a J-region (FR4) comprising SEQ ID NO: 4 in the heavy chains and SEQ ID NO: 10 in the light chains. The heavy chain CDR3 is of variable length from 7-14 residues. Examples of the complete V-regions for each library are shown in FIG. 1 and numbered and CDR regions shown according to Kabat.
[0129]The init...
example 3
Characterization of OSM Binding Mabs
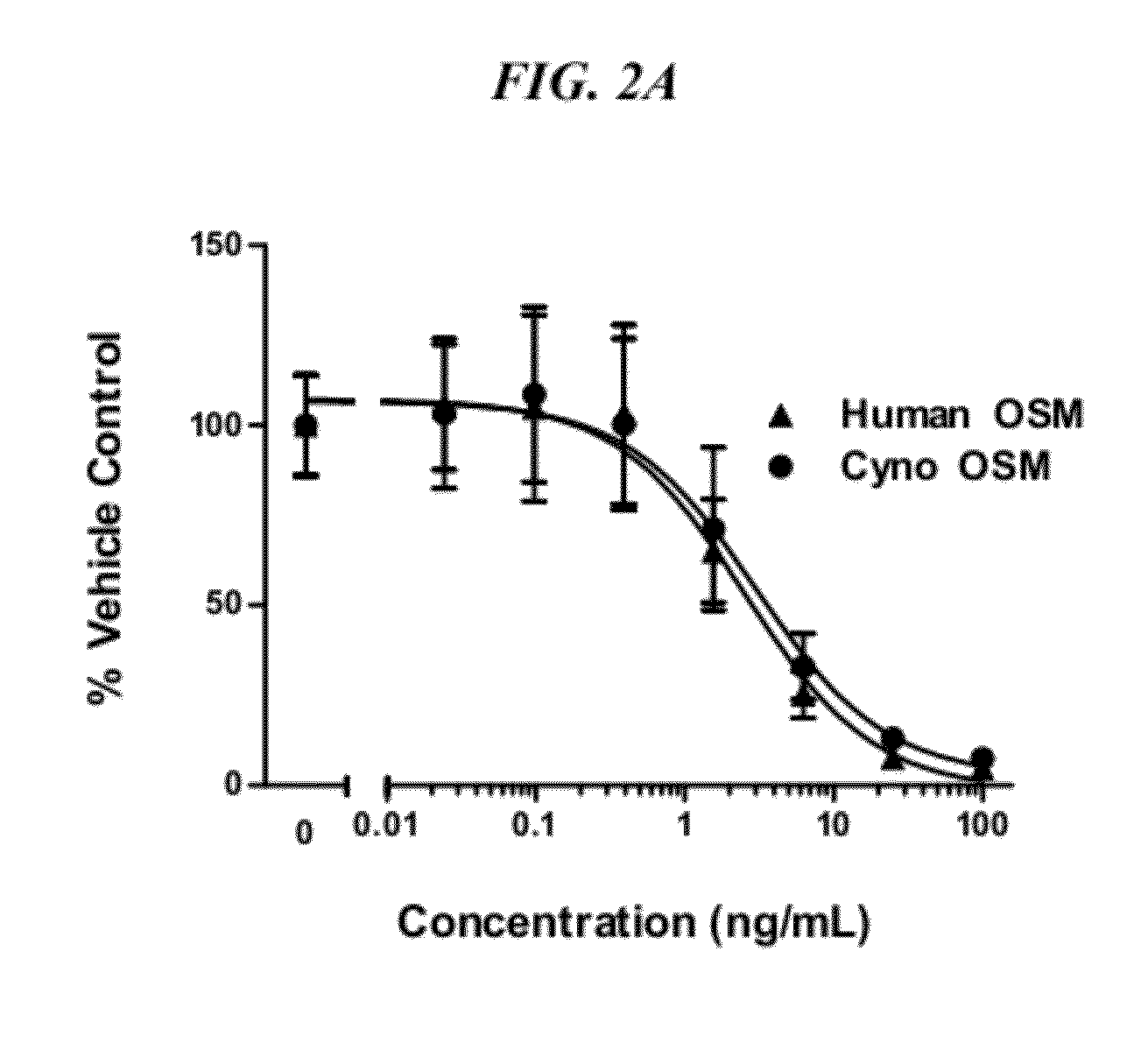
[0132]The four-helix bundle architecture OSM is characterized by four α helical segments designated A, B, C and D linked by relatively unstructured loops. OSM interacts with gp130 via an surface located in helices A and C (Site II) which was determined to include contact by amino acid residues Q16, Q20, G120, N123, N124 of SEQ ID NO: 1 (Deller et al. Structure 8(8): 863-874, 2000; Liu et al. Int. J. Mol. Med. 23: 161-172, 2009). The surface responsible for OSM interaction with OSMRβ and LIFRα (Site III) is believed to be largely defined by residues located in helix D (Deller et al. ibid).
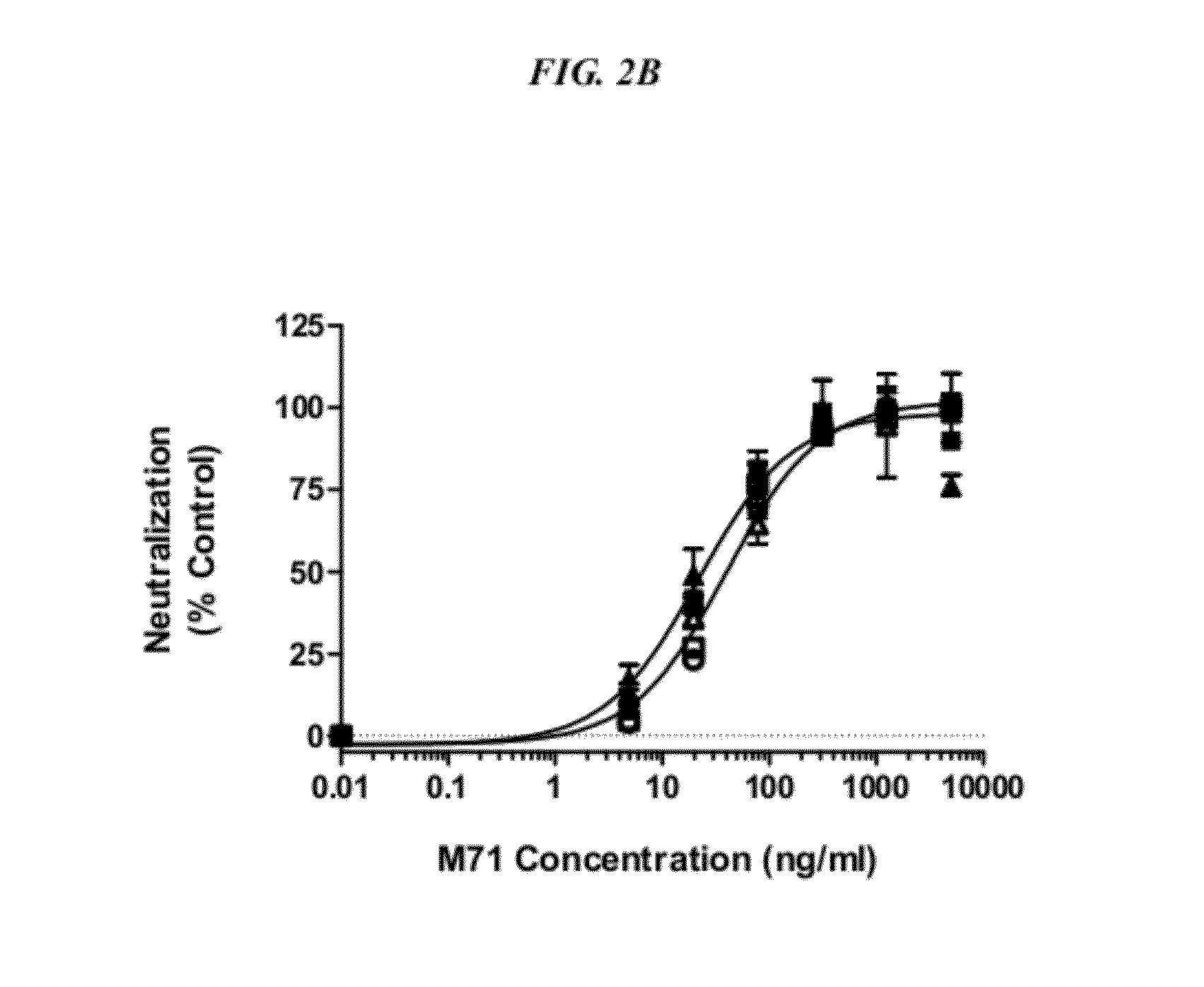
[0133]It was the objective to select high affinity binders to OSM capable of preventing OSM driven gp130 signaling either through the prevention of OSM binding to gp130 (Site II or B-blocker) or prevention of OSM bound gp130 recruitment of the LIFRα or OSMRb (Site III or R-blocker).
[0134]Of the 30 initially selected OSM-binding Fabs, 29 were cloned into vectors fo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com