Nanotube Film Electrode and an Electroactive Device Fabricated with the Nanotube Film Electrode and Methods for Making Same
a technology of nanotube film and electrode, which is applied in the field of electroactive polymeric devices and compliant electrodes, can solve the problems of low conductivity, inability to be used in applications which require high thermal stability, and the actual strain output of electric field-induced devices with metal electrodes is always smaller than, so as to achieve good thermal stability and high conductivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0016]Shown in the drawings and described herein in detail are advantageous embodiments of the present invention. It should be understood that the present invention is susceptible of embodiments in many different forms and thus the present disclosure is to be considered as an exemplification of the principles of the invention and is not intended to limit the broad aspect of the invention to the embodiments described and illustrated herein.
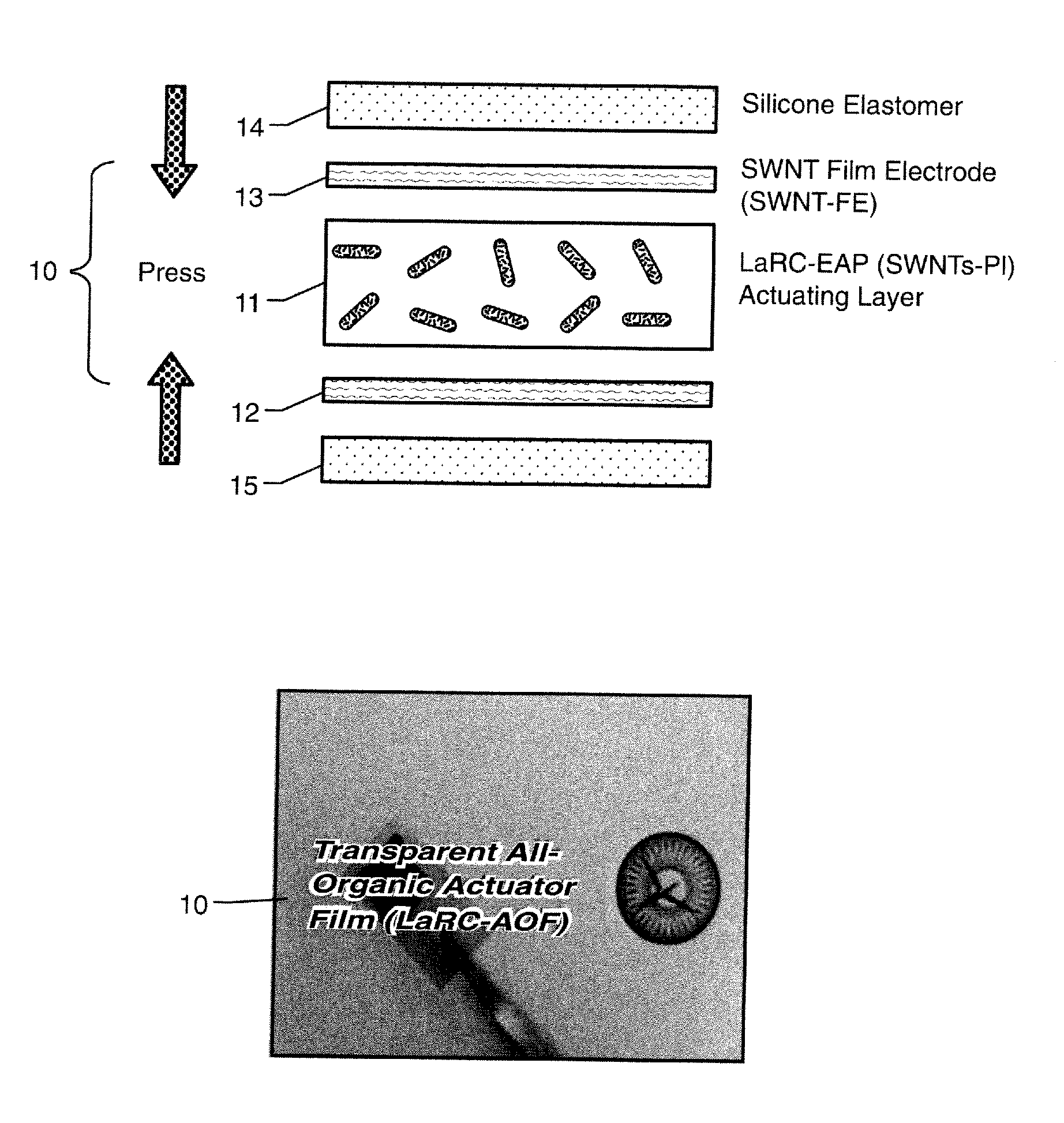
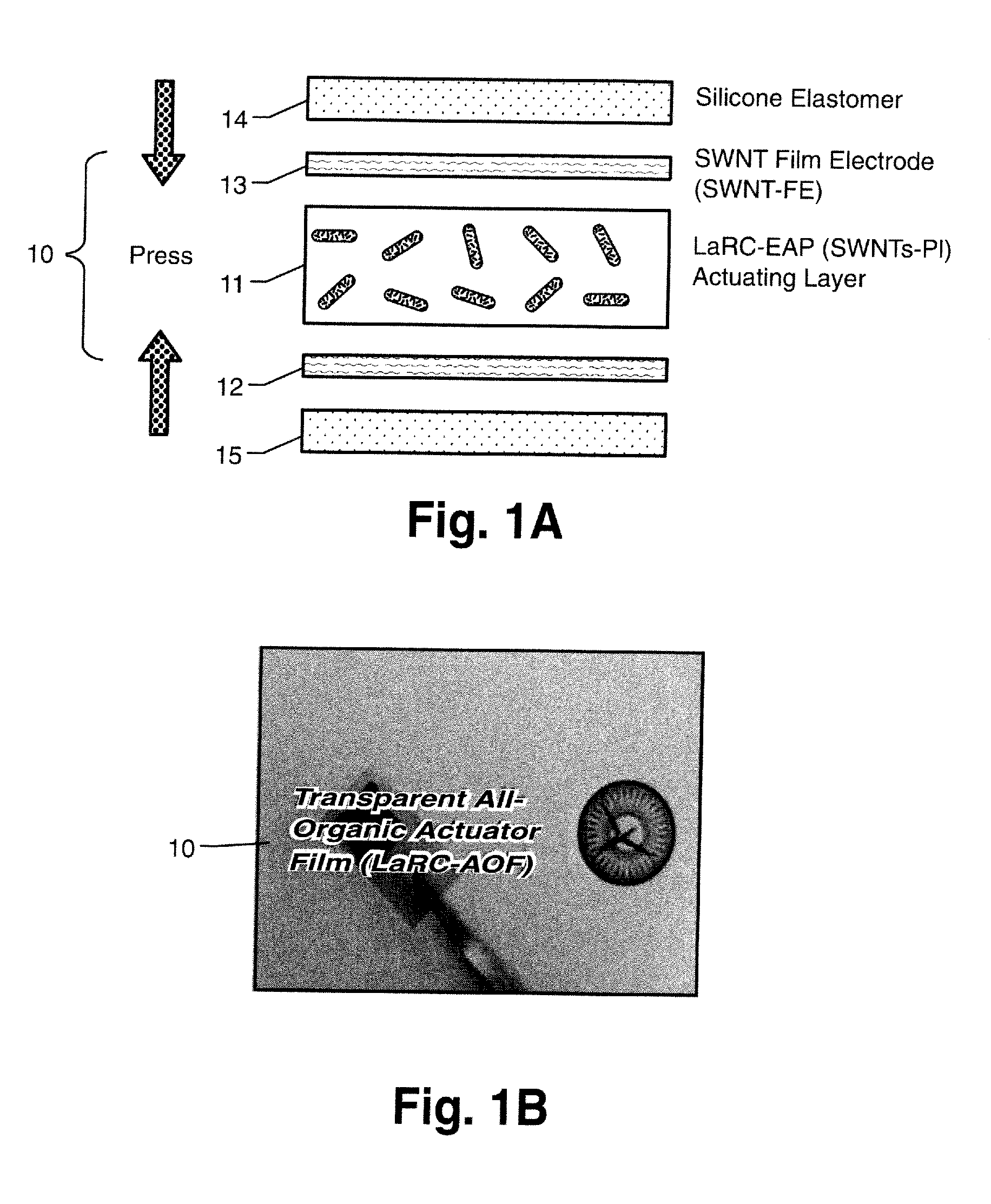
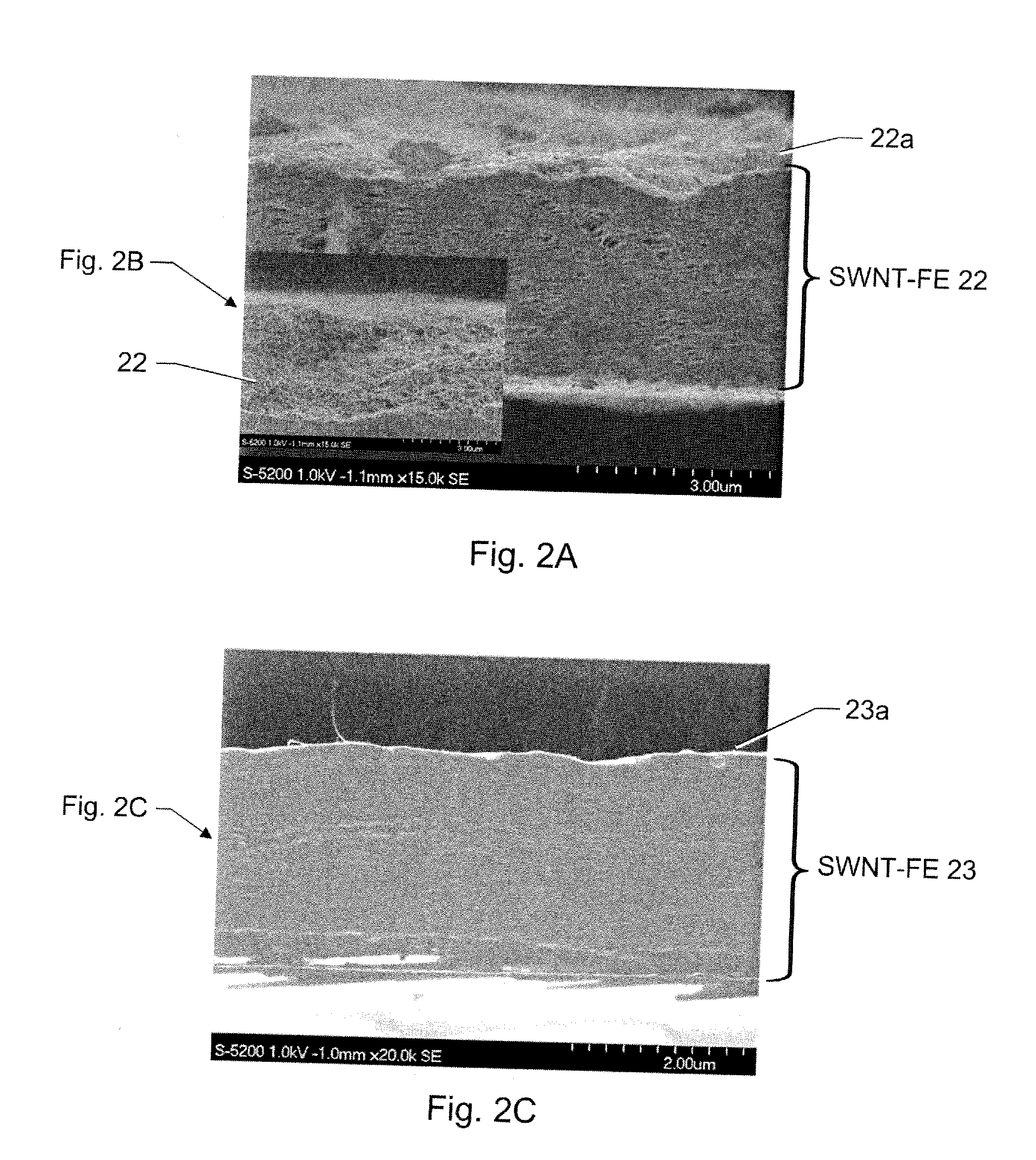
[0017]Referring now to the drawings, FIG. 1A is a diagram depicting the preparation of an all-organic electroactive device system in accordance with at least one embodiment of the present invention (such as the device 10 shown in FIG. 1B). A SWCNT film can be prepared by a method similar to the method set forth in A. G. Rinzler and Z. Chen, U.S. Patent Application Publication 20040197546 (Oct. 7, 2004), the entire contents of which are hereby incorporated by reference. However, in accordance with the present invention, unlike U.S. Application Publi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com