TAT Protein for preventing or treating AIDS
a technology of tat protein and tat subtype, which is applied in the field of tat protein for preventing or treating aids, can solve the problems of low probability of providing therapeutic and preventive effects of tat vaccine using a b subtype tat, and patients who have antibodies against tat are unable to recognize tat variants from all hiv-1 subtypes, and achieve the effect of strengthening the original tat oyi sequence's immunogenicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Sera from Vietnamese EPS Patients can Recognize Tat Variants from the Five Main HIV-1 Subtypes including Tat Oyi
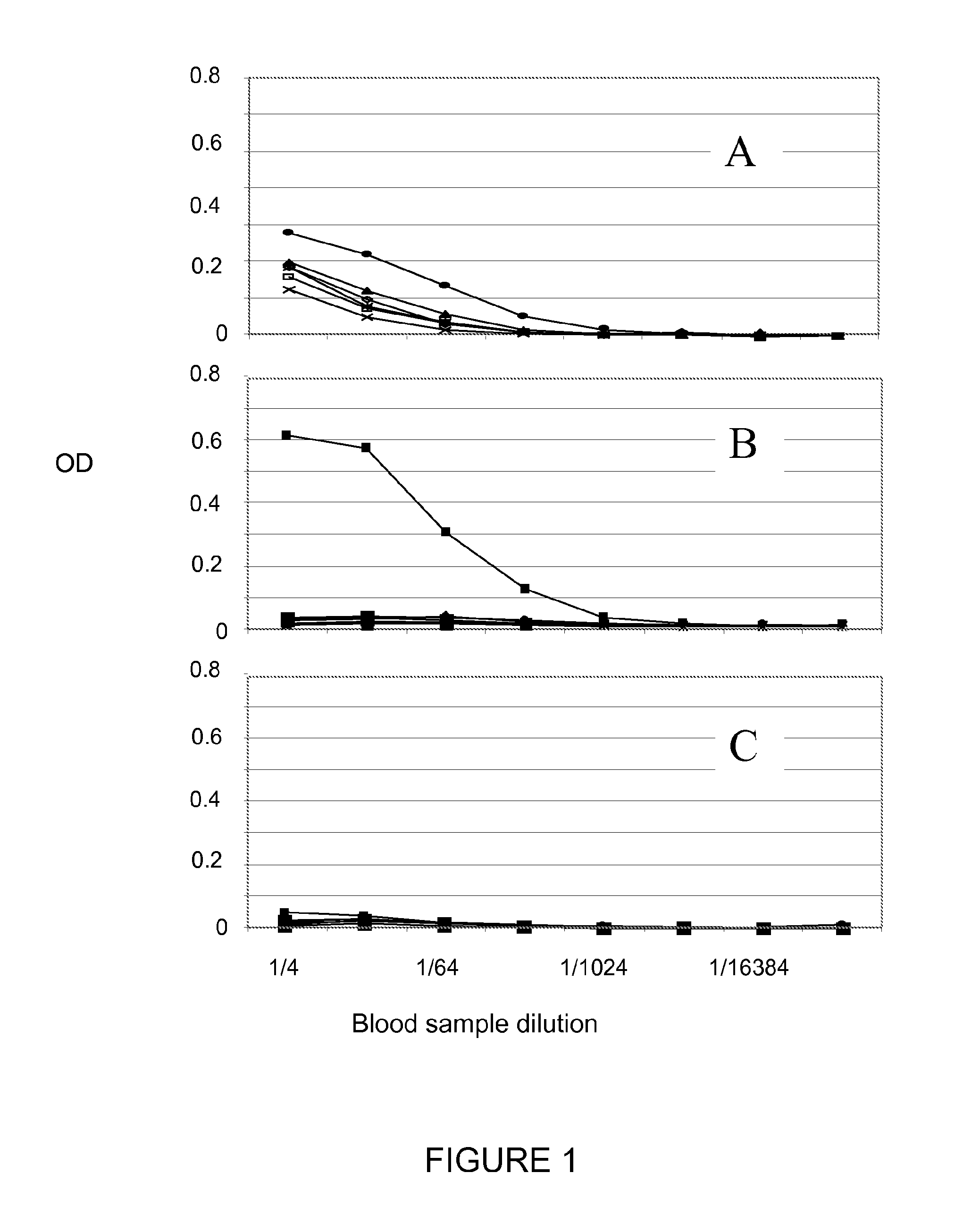
[0084]Anti-Tat IgG detected in EPS patients: We were able to detect Tat antibodies in a cohort of EPS patients in Vietnam. We carried out ELISA test with Tat variants representative of the five main HIV-1 subtypes including Tat Oyi on three cohorts, one was Vietnamese EPS patients (n=25), the second was French seropositive patients (n=100) and the third was French seronegative naive patients (n=20). Three types of serological pattern were observed in Elisa test (FIG. 1). The first one is characterized by the specific recognition (OD superior to 0.1) of all Tat variants and is observed only in the EPS cohort (n=25). FIG. 1A shows the recognition of six Tat variants obtained with a plasma from a Vietnamese EPS patient. The level of Tat antibodies is not the same regarding the six Tat variants and Tat from HIV-1 CM240 (Can et al., 1996) is best recognized for this patient. Th...
example 2
Synthesis, Purification and Characterization of Tat Oyi Cys 22
[0096]Tat OyiCys22 (SEQ ID NO:2) was assembled in solid-phase peptide synthesis. Before cleavage of the resin, 330 mg of crude material were obtained from a theoretical amount of 707 mg. The synthesis yield was 46.7% and is similar to the one observed with the synthesis Tat Oyi Ser 22.
[0097]Resin and protecting groups were cleaved from the protein content with acid trifluroacetic. The protein content was first purified by a precipitation with tertio buthyl Ether (TBE) to remove the free protecting groups that are soluble in TBE. The pullet was dried and re-suspended in a 0.1% TFA water buffer and then the resin was remove by filtration (0.22 μm). The resin-free protein content (approximately 240 mg) was freeze dried and re-suspended in 0.1% TFA water buffer at concentration up to 20 mg / ml in four fractions of approximately 60 mg called F1, F2, F3 and F4. Each fraction containing around 15 OD units.
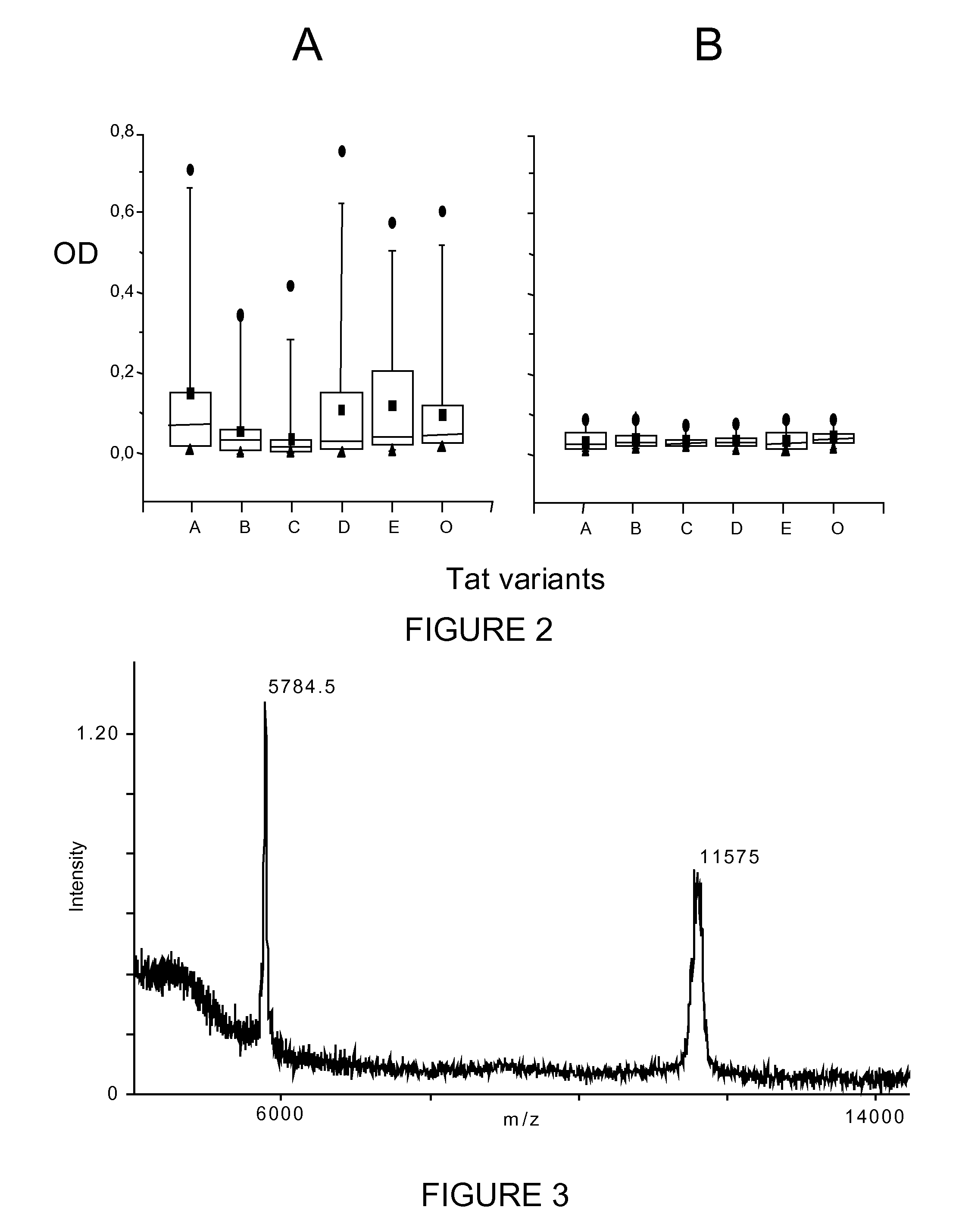
[0098]Purification was c...
example 3
Immunization with Tat Oyi Cys 22
[0106]Immunization of Mice was carried out with Tat Oyi Cys 22 (SEQ ID NO:2). No toxicity was observed on mice with Tat Oyi Cys 22 concentration that is 1000 fold higher compared to what is planned for clinical trials (data not shown).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| path length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| path length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com