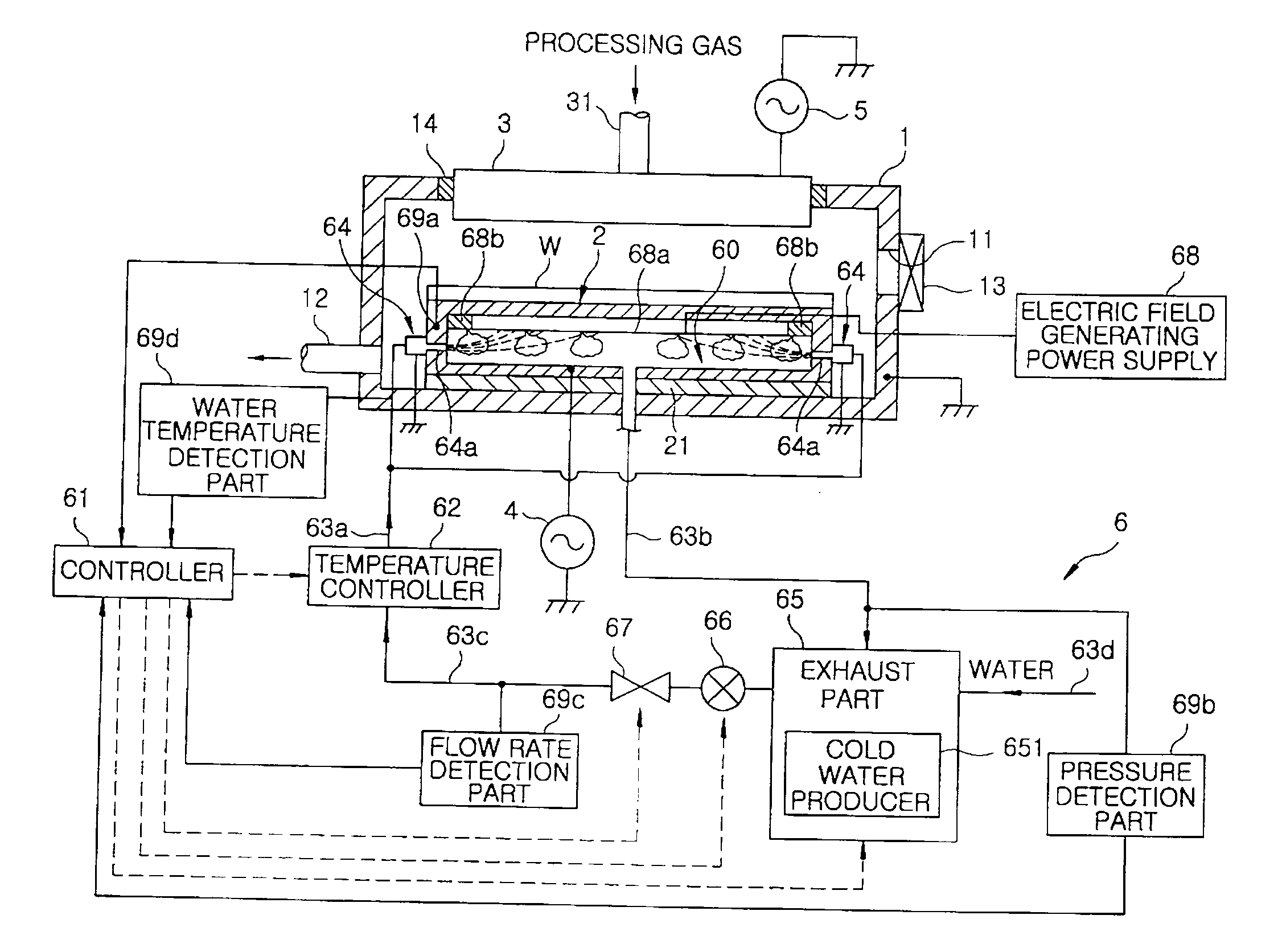
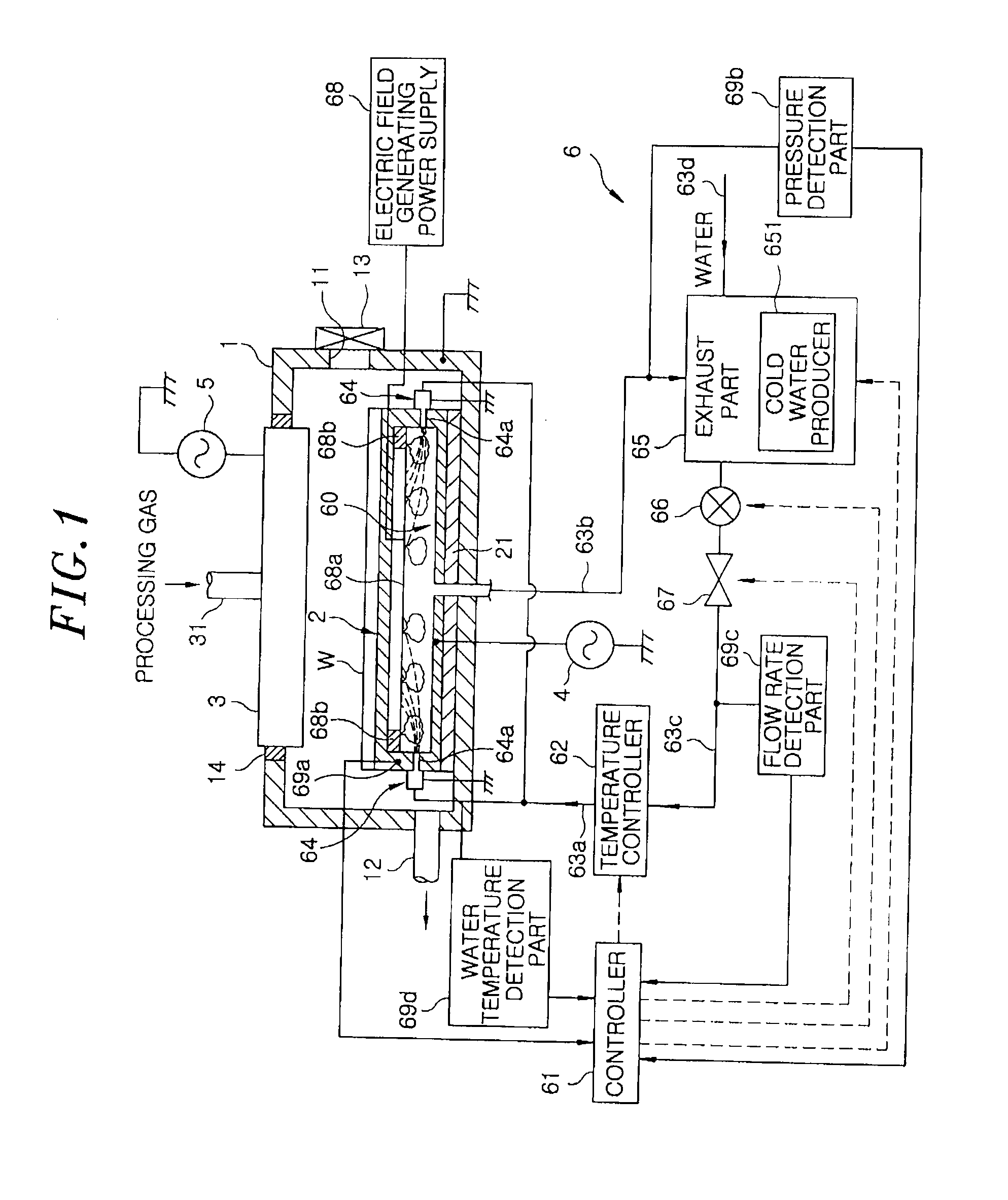
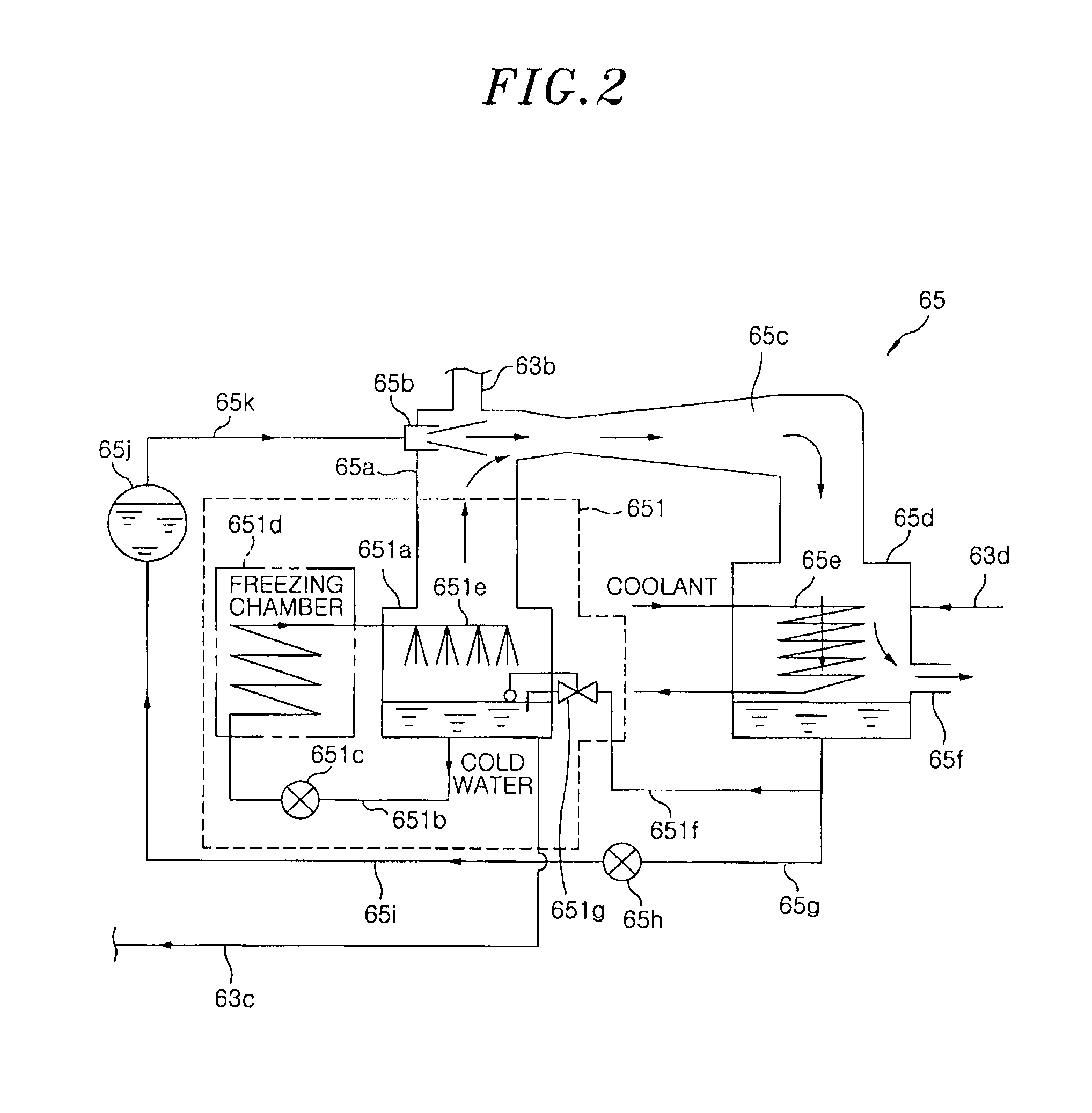
Cooling unit, processing chamber, part in the processing chamber, and cooling method
a cooling unit and processing chamber technology, applied in the field of cooling units, can solve the problems of difficult uniform cooling of semiconductor wafers, poor temperature control responsiveness, and unnecessarily heating of semiconductor wafers or the wall of processing chambers, and achieve the effect of reducing the amount of heat medium and high efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
modification example 1
[0078]FIG. 5 schematically shows a configuration of a semiconductor manufacturing apparatus including a cooling unit 106 in accordance with Modification Example 1. The semiconductor manufacturing apparatus and the cooling unit 106 in accordance with Modification Example 1 have the same configurations as those of the above-described embodiment, and further include a voltage application part 164b to apply a voltage to the spraying part 64. The voltage application part 164b is a DC power supply for electrically charging the water sprayed from the spraying part 64. In a case where the electric field directed from the inside of the decompression chamber 60 toward the top surface portion of the decompression chamber 60 is generated by the electric field generating power supply 68, a positive potential is applied to the spraying part 64. In a case where the electric field directed from the top surface portion of the decompression chamber 60 toward the inside of the decompression chamber 60...
modification example 2
[0080]FIG. 6 schematically shows a configuration of a semiconductor manufacturing apparatus including a cooling unit 206 in accordance with Modification Example 2. The semiconductor manufacturing apparatus and the cooling unit 206 in accordance with Modification Example 2 have the same configurations as those of the above-described embodiment, and are different from those of the above embodiment in that a decompression chamber 260 and a spraying part 264 are further provided in the wall of a processing chamber (target object to be cooled) 201, so that a desired location of the inner wall of the processing chamber 201 is cooled. The desired location of the inner wall of the processing chamber 201 may be a part of the inner wall, or the whole inner wall. The difference will be mainly described below.
[0081]The processing chamber 201 of the semiconductor manufacturing apparatus in accordance with Modification Example 2 has the decompression chamber 260 formed in the wall thereof to cool...
modification example 3
[0087]FIG. 7 schematically shows a configuration of a semiconductor manufacturing apparatus including a cooling unit 306 in accordance with Modification Example 3. The cooling unit 306 in accordance with Modification Example 3 has a first and a second decompression chamber 360 and 370 for cooling the mounting table 2 as a target object to be cooled and a processing chamber (target object to be cooled) 301, respectively, wherein the first decompression chamber 360 is provided at an external of the mounting table 2 and the second decompression chamber 370 is provided at an external of the processing chamber 301.
[0088]The first decompression chamber 360 is formed in a hollow cylindrical shape, and fixed onto an approximately central bottom portion of the processing chamber 301. The mounting table 2 is fixed on the top of the first decompression chamber 360 through the disc-shaped insulator 21. The first decompression chamber 360 has the same configuration as the decompression chamber 6...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com