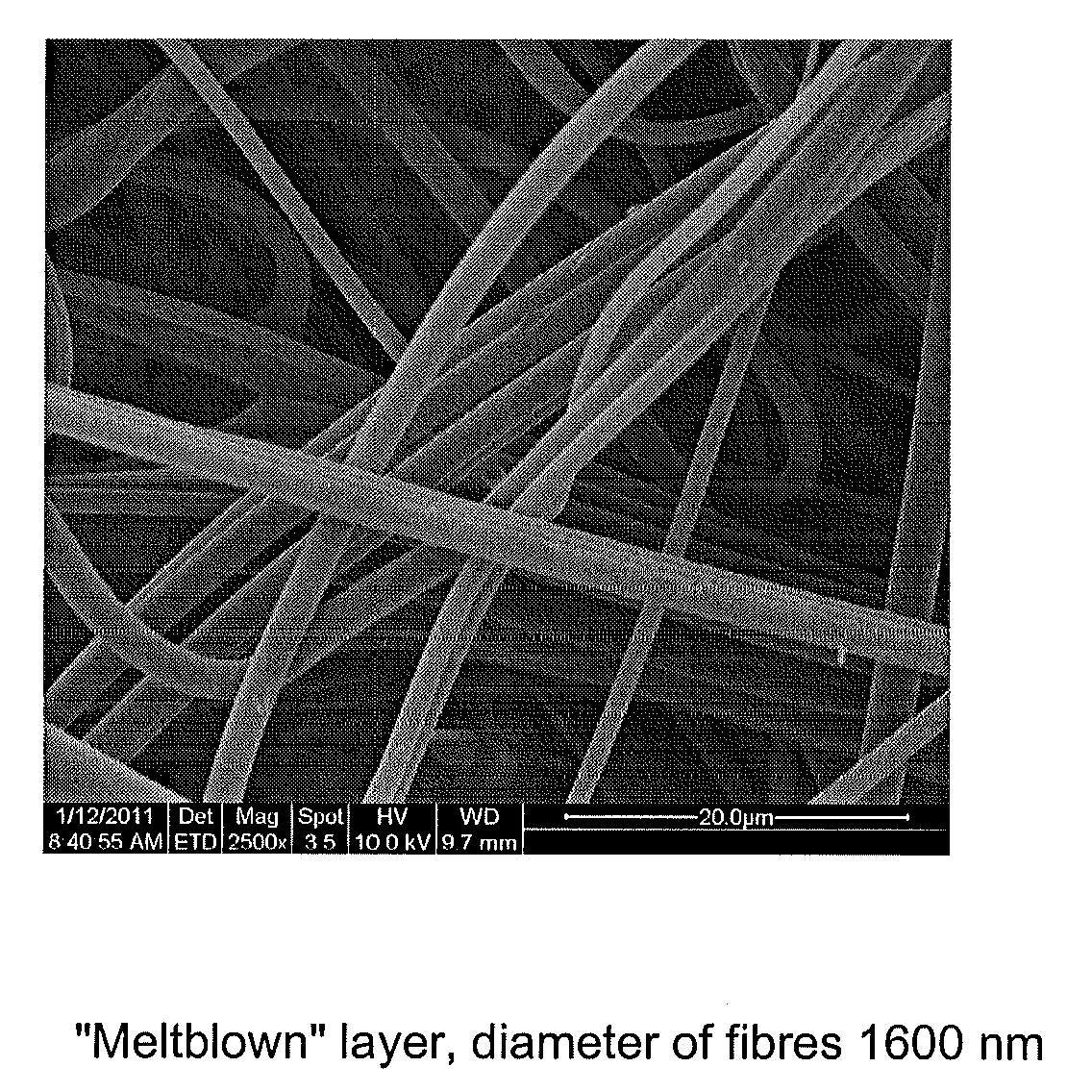
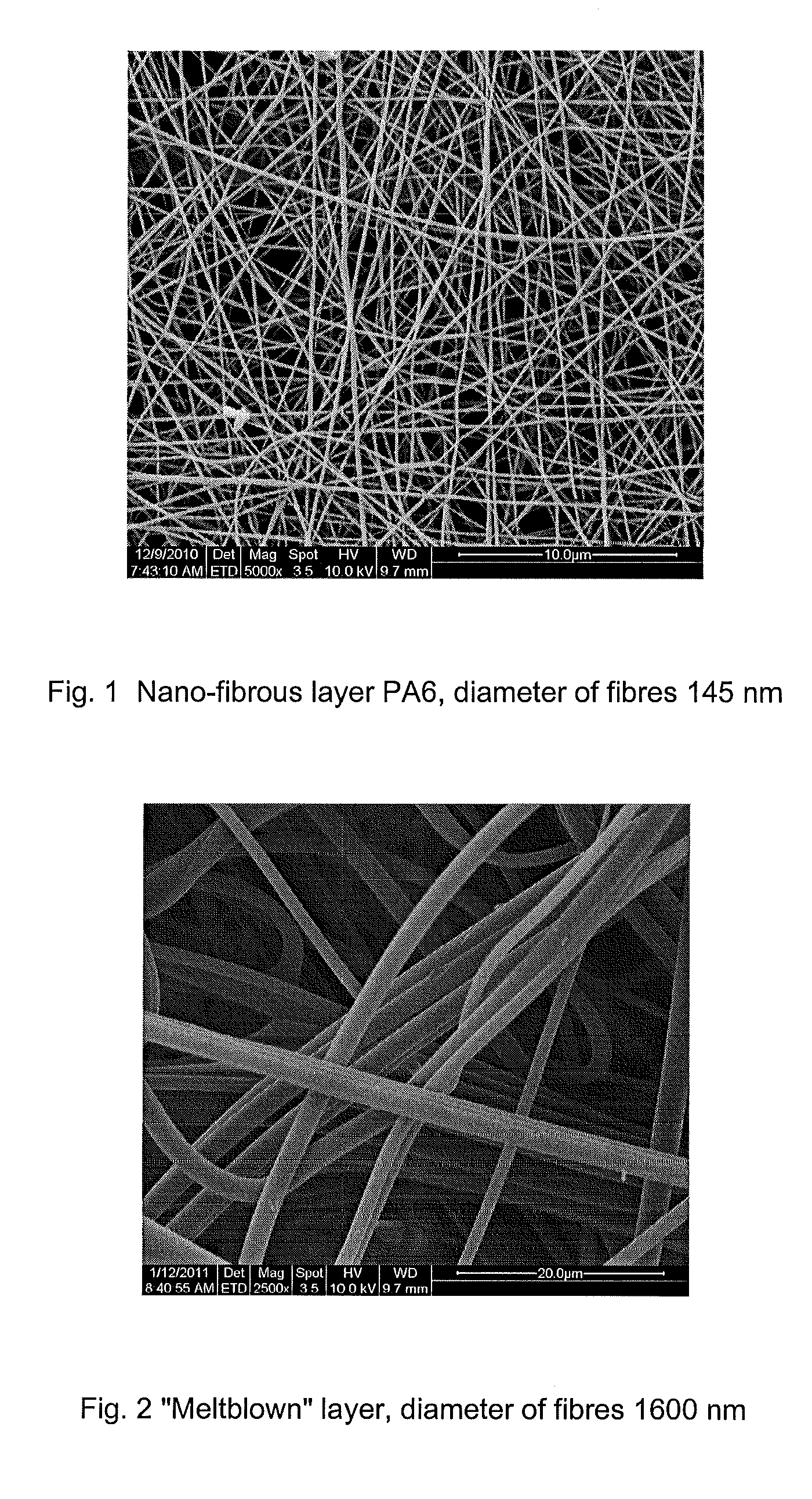
Barrier fabric
a textile fabric and fabric technology, applied in the field of barrier textile fabrics, can solve the problems of high material cost, inability to ensure maximum protection, and impairment of user comfort, and achieve the effect of low overall areal weight and low demand for materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0045]Sandwich: unwoven fabric of “spunbond” type—nano-fibrous layer—unwoven fabric of “spunbond” type. “Sunbond” areal weight (substrate and covering layer) 10 to 50 g / m2, nano-fibrous layer from hydrophobic polymer (PVDF, PUR, PP, etc.) areal weight of the nano-fibrous layer 0.05 to 0.2 g / m2, fibre diameters 150 to 170 nm, adhesion between the individual layers is provided by adhesives or by lamination, or by combination of both methods, respectively. An optimum combination as regards the usage characteristics and the production costs: “spunbond” substrate 20 g / m2, nano-fibrous layer PVDF 0.1 g / m2 with thickness 170 nm, “spunbond” covering layer 15 g / m2).
[0046]Also another unwoven type of textile may be used as the substrate or the covering layer, e.g. “meltblown” or “spunbond / meltblown”. The nano-fibrous layer may contain antimicrobial substances (silver in nano-crystallic or micro-crystallic form, chlorhexidine, quaternary salts, etc.).
example 2
[0047]Sandwich composition: unwoven fabric of “spunbond” type—1st nano-fibrous layer—2nd nano-fibrous layer—unwoven fabric of “spunbond” type, “spunbond” areal weight (substrate and the covering layer) 10 to 50 g / m2, 1st nano-fibrous layer from hydrophobic polymer (PVDF, PUR, etc.) areal weight 0.02 to 0.1 g / m2 and fibre diameters 150 to 170 nm, 2nd nano-fibrous layer from hydrophilic polymer (PA, PVA, etc.) areal weight 0.02 to OA g / m2 and fibre diameters 50 to 250 nm. Adhesion between the individual layers is provided by depositing of adhesives to the substrate before imbedding the fibrous material, or by lamination of the sandwich, or by combination of both methods, respectively. An optimum combination as regards the usage characteristics and the production costs: “spunbond” substrate 20 g / m2, 1st nano-fibrous layer PVDF 0.1 g / m2, 2nd nano-fibrous layer PA6 0.05 g / m2, covering layer “spunbond” SB 15 g / m2.
[0048]The 1st and 2nd nano-fibrous layers differ from each other by the used...
example 3
[0050]Sandwich: unwoven fabric of “spunbond” type—nano-fibrous layer—unwoven fabric of “spunbond” type. The “spunbond” areal weight (substrate with covering layer) 15 to 50 g / m2, nano-fibrous layer from a hydrophilic or hydrophobic polymer (PA, PAN, PVDF, PET, PP, etc.) areal weight 0.05 to 0.3 g / m2, fibre diameters 100 to 500 nm, ideally 100 nm. Adhesion between the individual layers is provided by depositing of adhesives to the substrate before imbedding the fibrous material, or by lamination of the sandwich, or by combination of both methods, respectively. An optimum combination as regards the usage characteristics and the production costs: “spunbond” substrate 20 g / m2, nano-fibrous layer PA6 0.1 g / m2, “spunbond” covering layer / layers 20 g / m2).
[0051]The nano-fibrous layer may contain acaricides (phenylmethyl benzoate, sulphide).
[0052]The substrate or the protective layer, or both layers are textiles, areal weight 50 to 150 g / m2, adhesion between the individual layers is provided ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com