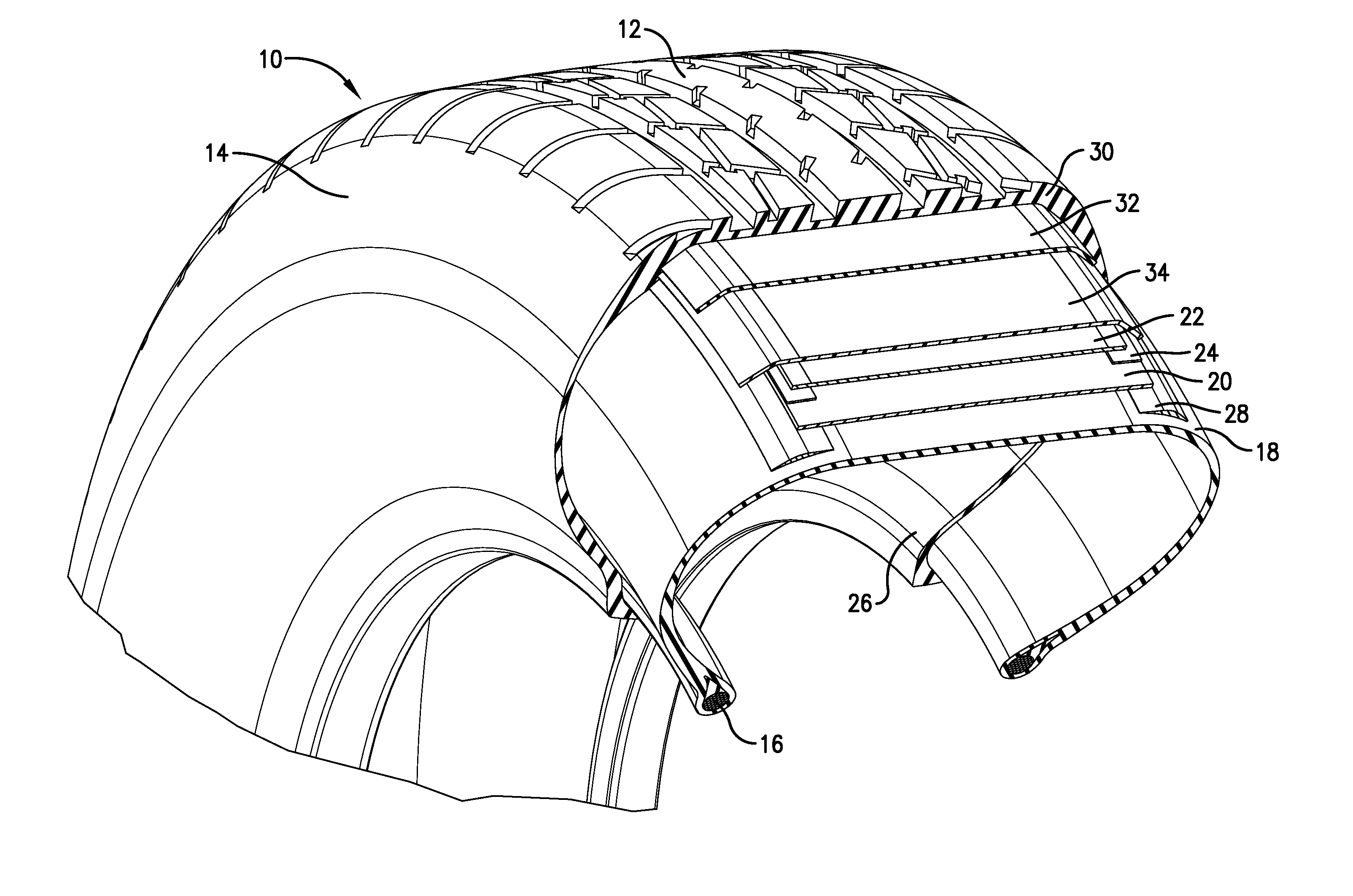
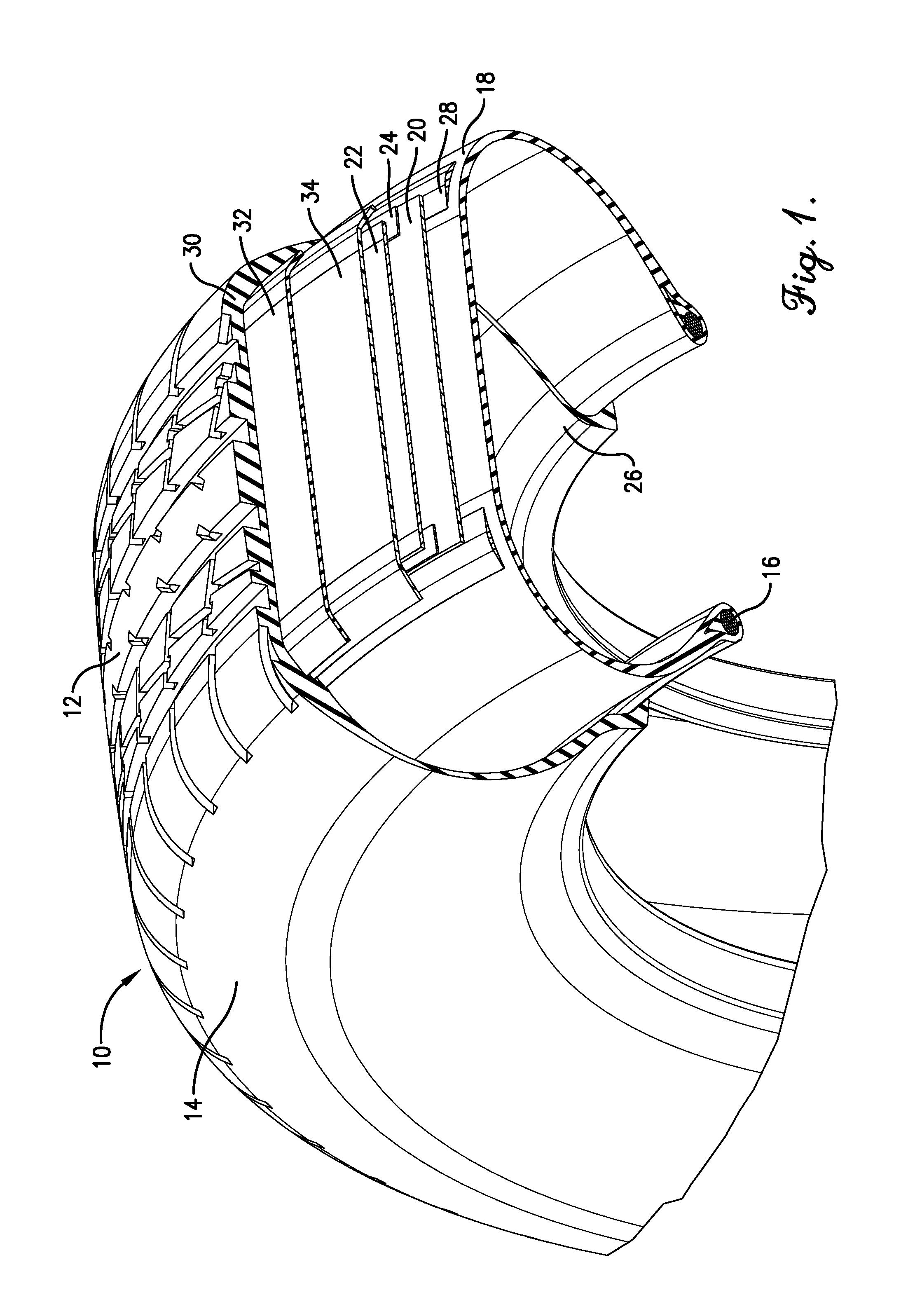
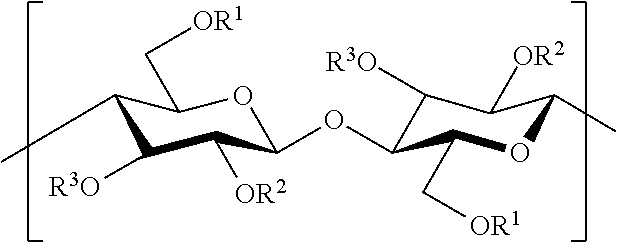
Cellulose esters in pneumatic tires
a technology of cellulose ester and pneumatic tires, which is applied in the direction of coatings, etc., can solve the problems of difficult processing and limited application of many conventional high-filling elastomeric compositions in tires
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0134]Elastomeric compositions containing varying amounts of cellulose ester were compared to elastomeric compositions not containing any cellulose ester. The elastomeric compositions were produced according to the formulations and parameters in TABLE 1. Examples 1 and 2 contained varying amounts of cellulose ester, while no cellulose ester was added to Comparative Examples 1 and 2.
TABLE 1ComparativeComparativeIngredientComponentExample 1Example 2Example 1Example 2STAGE 1BUNA VSLS-SBR89.3889.3889.3889.385025-2 HMextended with37.5 phr TDAEBUNA CB 22PBD Rubber35353535ULTRASILSilica656565657000 GRN234Carbon black15151515Si 266Coupling agent5.085.085.085.08SUNDEX 790Aromatic oil———8.75Stearic acidCure Activator1.51.51.51.5Product ofMB1210.96210.96210.96219.71Stage 1STAGE 2Product ofMB1210.96210.96210.96219.71Stage 1CAB-551-0.01Cellulose Ester715——Si 69Coupling agent0.5461.17——Zinc oxideCure activator1.91.91.91.9OKERIN WAXMicrocrystalline1.51.51.51.57240waxSANTOFLEXAntioxidant22226PPDPro...
example 2
[0138]Various performance properties of the elastomeric compositions produced in Example 1 were tested.
[0139]The break stress and break strain were measured as per ASTM D412 using a Die C for specimen preparation. The specimen had a width of 1 inch and a length of 4.5 inches. The speed of testing was 20 inches / min and the gauge length was 63.5 mm (2.5 inch). The samples were conditioned in the lab for 40 hours at 50%+ / −5% humidity and at 72° F. (22° C.).
[0140]The Mooney Viscosities were measured at 100° C. according to ASTM D 1646.
[0141]The Phillips Dispersion Rating was calculated by cutting the samples with a razor blade and subsequently taking pictures at 30× magnification with an Olympus SZ60 Zoom Stereo Microscope interfaced with a PAXCAM ARC digital camera and a Hewlett Packard 4600 color printer. The pictures of the samples were then compared to a Phillips standard dispersion rating chart having standards ranging from 1 (bad) to 10 (excellent).
[0142]The Dynamic Mechanical Ana...
example 3
[0146]In this example, elastomeric compositions were produced using the masterbatch process. A number of different cellulose ester concentrates were prepared and subsequently combined with elastomers to produce the elastomeric compositions.
[0147]In the first stage of the masterbatch process, cellulose esters were bag blended with styrenic block copolymer materials and then fed using a simple volumetric feeder into the chilled feed throat of a Leitstritz twin screw extruder to make cellulose ester concentrates (i.e., masterbatches). The various properties of the cellulose esters and styrenic block copolymer materials utilized in this first stage are depicted in TABLES 4 and 5. All of the recited cellulose esters in TABLE 4 are from Eastman Chemical Company, Kingsport, Tenn. All of the styrenic block copolymers in TABLE 5 are from Kraton Polymers, Houston, Tex. The Leistritz extruder is an 18 mm diameter counter-rotating extruder having an L / D of 38:1. Material was typically extruded ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| weight percent | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com