Secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine (SPARC) as chemotherapeutic sensitizers
a chemotherapeutic and sensitizing technology, applied in the field of cancer therapy sensitizing compositions and methods, can solve the problems of high cancer mortality rate, impede tumor regression and cure, and complex mechanisms involved in the mechanism of therapeutic resistan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
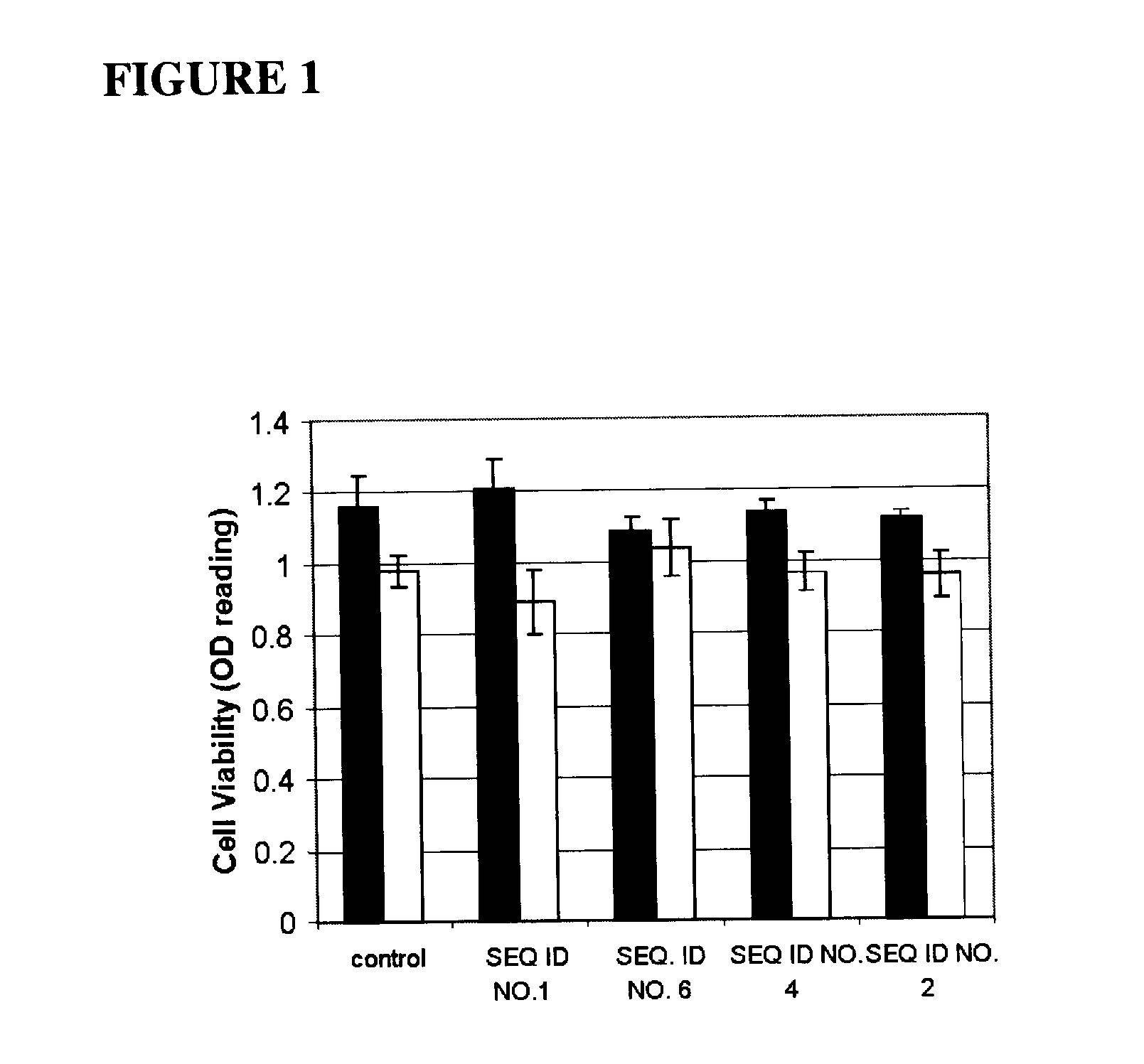
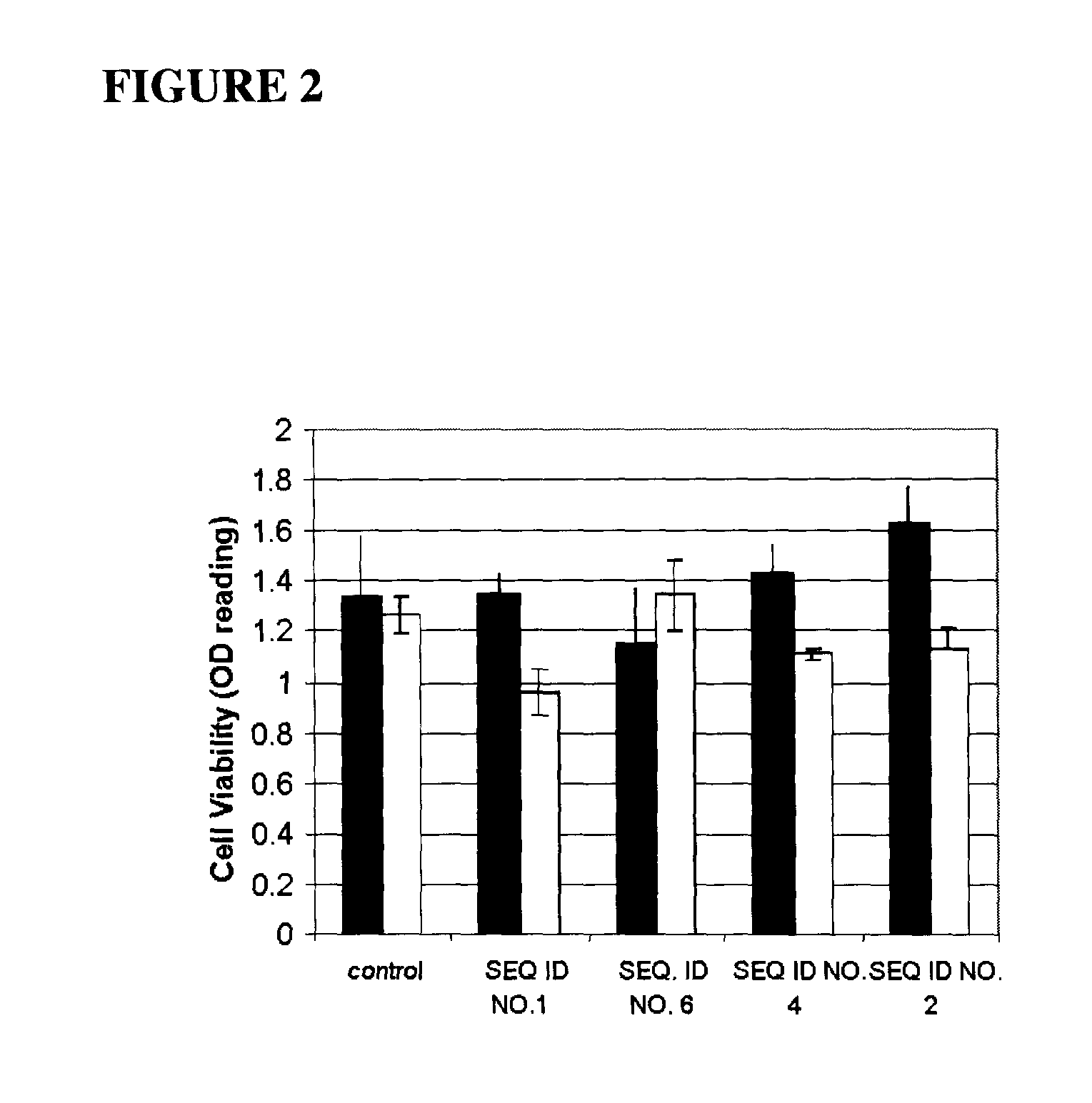
[0140]Sensitive (MIP101—FIG. 1) and multi-drug resistant (MIP / CPT—FIG. 2) cells were transiently transfected and assayed for survival upon exposure to irinotecan (CPT). Cell viability was quantified by an MTS assay. Transfection of both SEQ ID NO: 2 and SEQ ID NO: 4 had a similar effect by decreasing cell viability in the resistant MIP / CPT cells compared to that of the full length SPARC vector. Resistant MIP / CPT cells transfected with control (empty vector) remained viable despite exposure to 500 uM CPT-11.
example 2
Use of SPARC Peptide Chemosensitizers In Vitro
[0141]This example demonstrates the utility of the inventive SPARC peptide chemosensitizers in an in vitro model system.
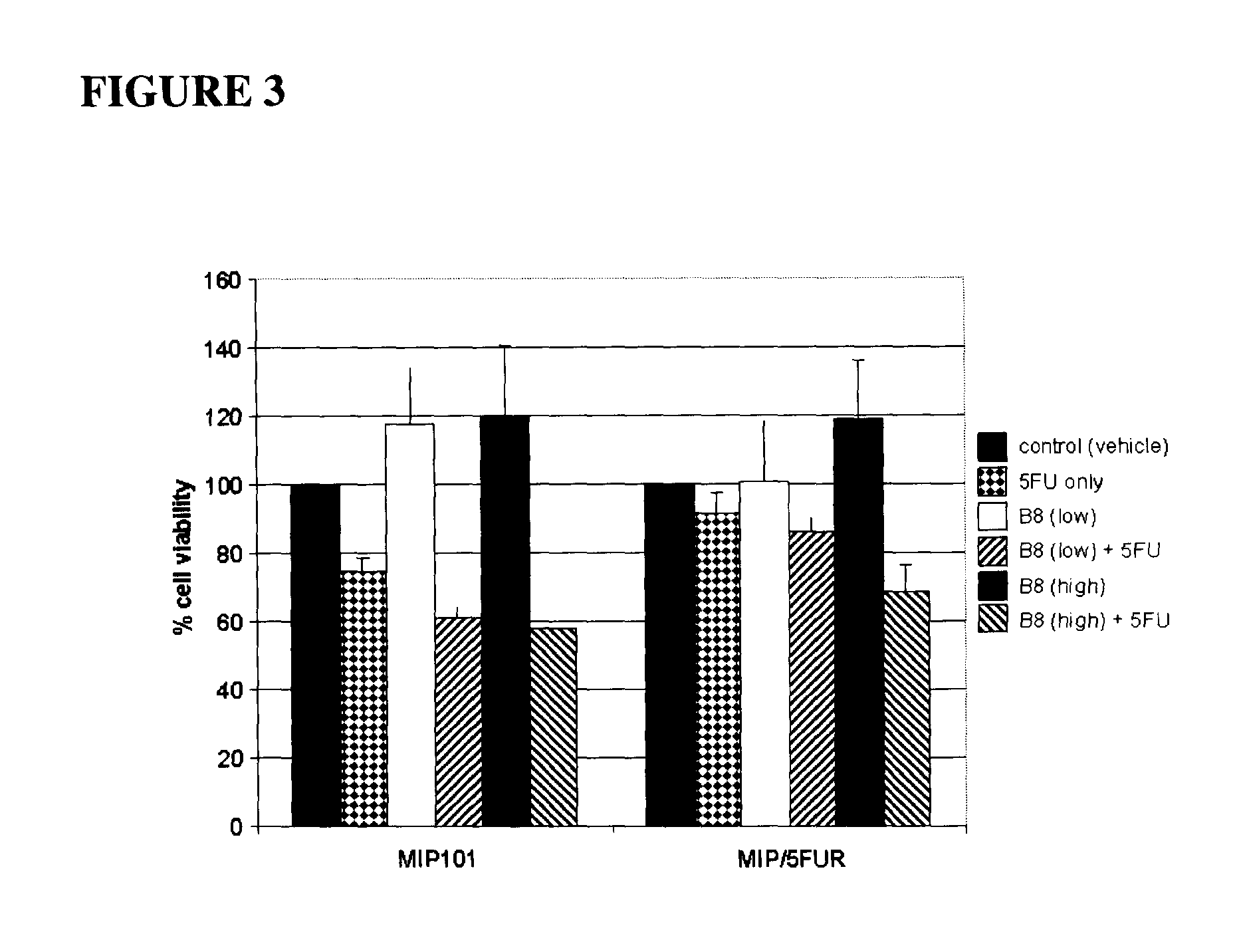
[0142]Shorter peptides corresponding to various regions of either the N-terminal acidic region or the follistatin domain were synthesized to further narrow the peptide sequences demonstrating chemosensitizing activity. MIP101 sensitive or resistant to 5-FU (MIP / 5FU) cells were exposed to the B14 peptide (SEQ ID NO. 9) as described. In both resistant and sensitive cells, the peptide alone, at either of the concentrations tested did not significantly affect viability (FIG. 4). As expected the resistant cells exhibited greater viability in the presence of 5-FU alone—with the addition of the B 14 peptide at 96 or 200 μg / ml, cell viability decreased compared to 5-FU alone, indicating that the presence of the peptide increases the sensitivity of the resistant cells to the chemotherapeutic agent.
[0143]A similar trend is observ...
example 3
Use of SPARC Peptide Chemosensitizers in Vivo
[0145]This example demonstrates A utility of the inventive SPARC peptide chemosensitizers in a tumor xenograft model system.
[0146]Tumor xenograft animal models were used to assess the effect of overexpressing different SPARC fragments on tumor progression in vivo. MIP 101 cells with stable transfection and expression of SPARC (MIP / SP) or different biological fragments representing the N-terminus (MIP / NT), follistatin (MIP / FS) and extracellular (MIP / EC) domains of SPARC were used for the tumor xenograft model. NIH nude mice (6 weeks old, Taconic Laboratories, Germantown, N.Y.) were implanted with 1×106 cells at the left flank. Treatment regimens were initiated once the average tumor size reached 75-100 mm3 in volume. Tumors were measured using a hand-held caliper (Fisher Scientific International, Inc. Hampton, N.H.) with concurrent body weight measurements until the completion of the study. Chemotherapy was provided using a 3-week cycle re...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com