Method for producing a flat semi-finished product from a fiber composite material and flat semi-finished product
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
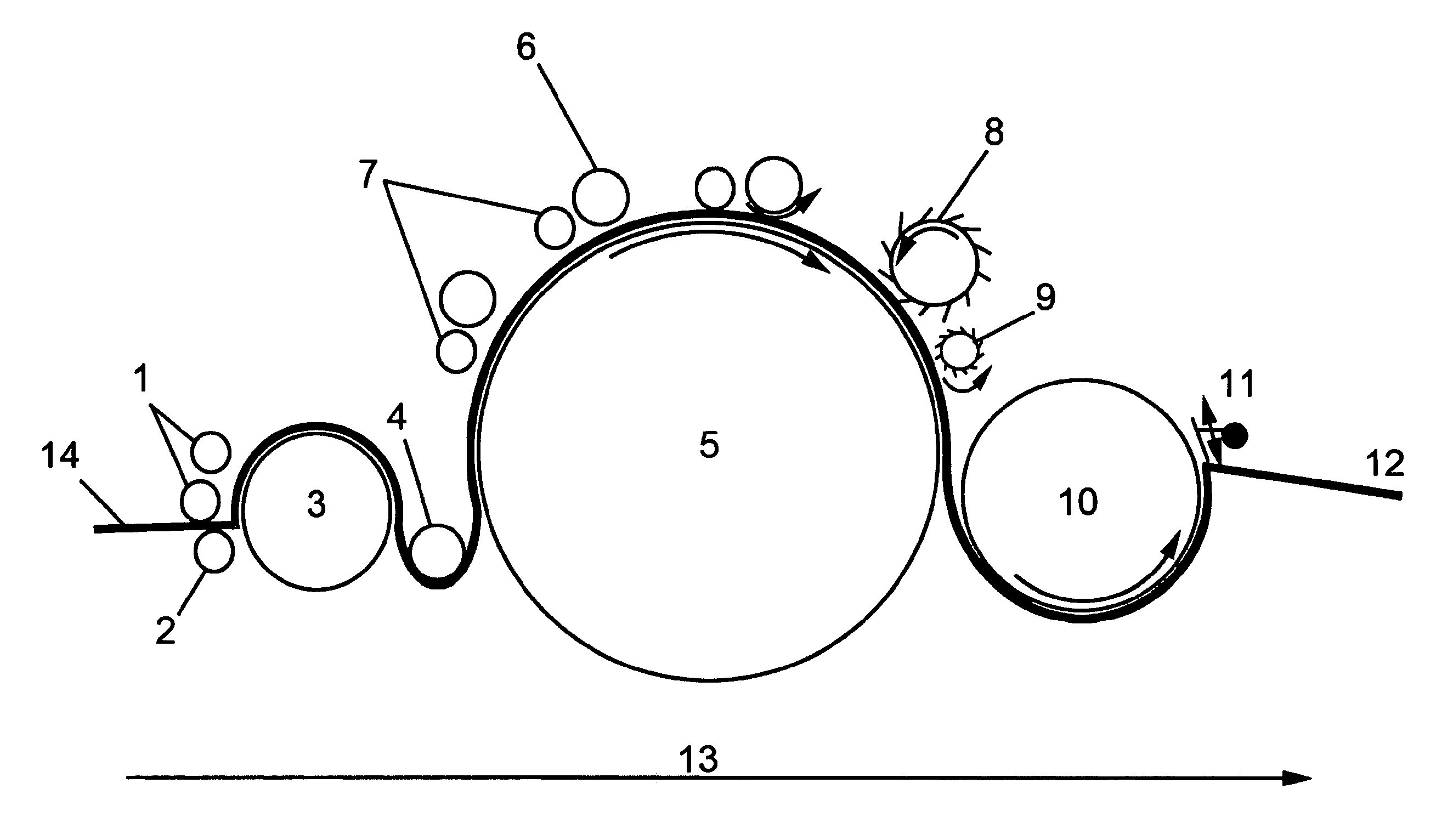
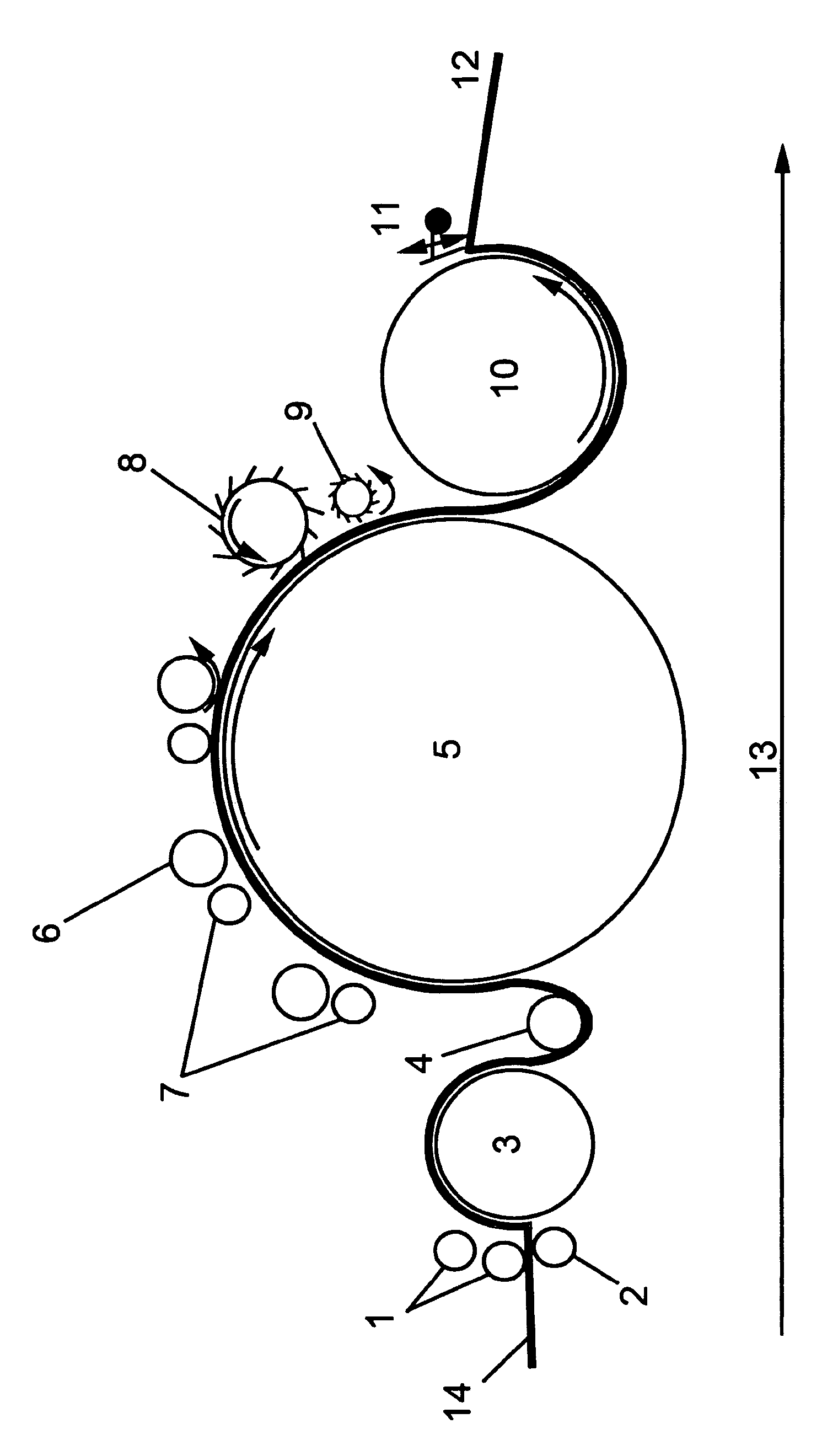
[0067]Referring now to the single FIGURE of the drawing in detail, there is shown at least one fiber layer 14 (at the left in the drawing) being fed into the carding system, passing initially over feed rollers 1, 2 onto a licker-in 3 rotating in the opposite direction from the intake rollers. A transfer roller 4 rotating in a direction opposite that of the licker-in 3 and the main drum 5 is arranged between the licker-in 3 and the main drum 5 (tambour) rotating in the same direction of rotation as the licker-in 3. Various workers 6 and turners 7 are arranged on the circumference of the main drum 5 in various circumferential positions. The object of these devices is to shred the incoming fiber layer 14 in the carding system down to individual fibers and then shape them back into a thin fiber web having a uniform weight and a defined weight per unit of area. A longitudinal fiber orientation is preferably the goal here.
[0068]Downstream from the main drum 5, a takeoff drum 10 rotating i...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com