Method of Providing Disease-Specific Binding Molecules and Targets
a technology of specific binding molecules and targets, applied in the direction of peptides, drug compositions, fused cells, etc., can solve the problems of inconvenient production of antibodies with characteristics, insufficient specificity of antibodies, and hampered therapeutic utility of murine based antibodies in human patients
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Detection of Human Antibodies Against Abnormal Structures Prevalent in Human Brain Diseases
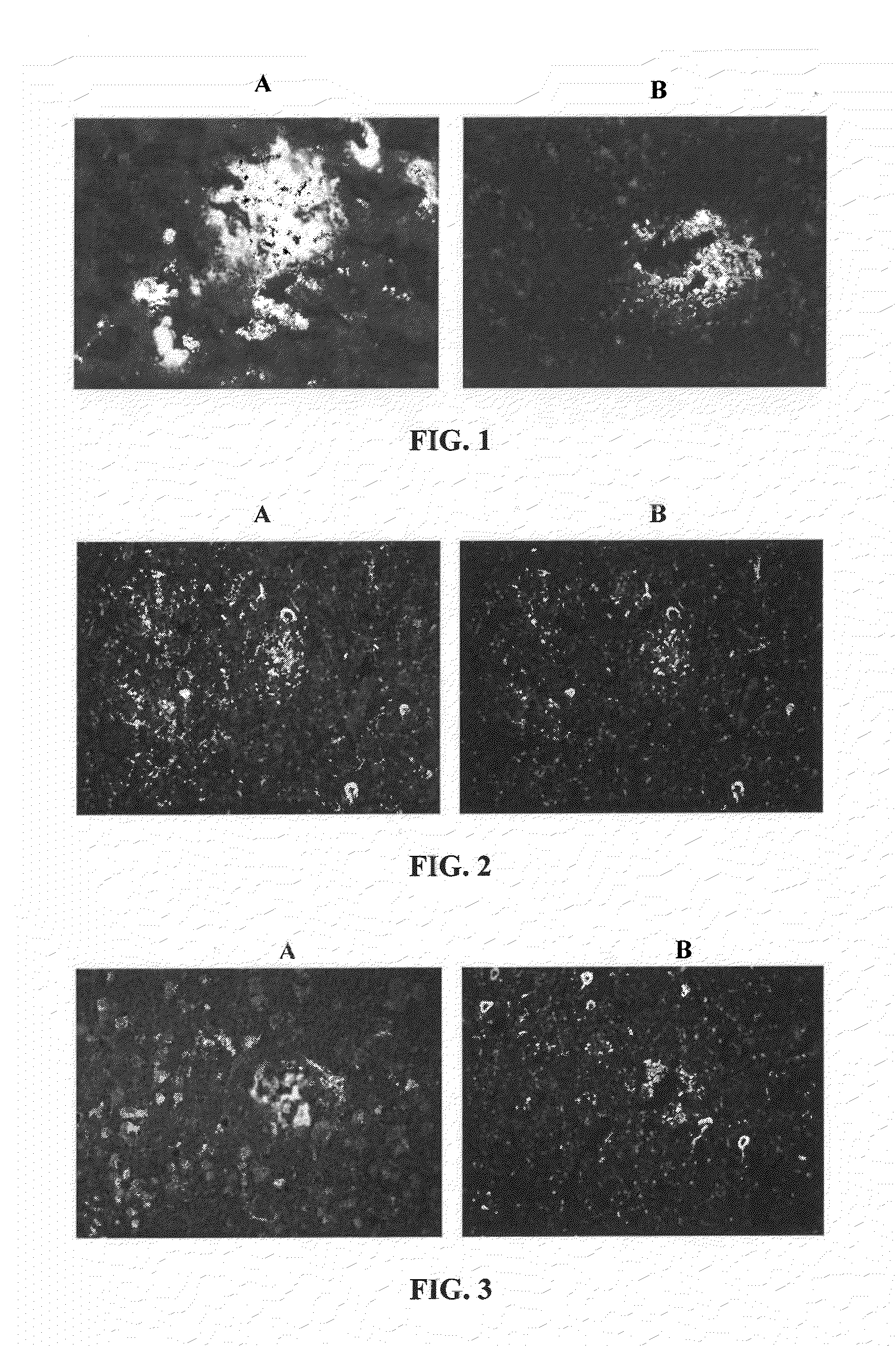
[0320]Antibodies from phenotypically healthy subjects, or clinically unusually stable patients with Alzheimer's disease were tested by immunohistochemistry on brain sections obtained from patients with pathologically confirmed Alzheimer's disease. FIG. 1A demonstrates the presence of antibodies in a clinically unusually stable patient that bind to beta-amyloid plaques as was confirmed by co-staining with a known antibody against human beta-amyloid (antibody 4G8; FIG. 1B). The presence in a healthy human subject of antibodies to neurofibrillary tangles in a tissue section obtained from a patient with Alzheimer's disease is shown in FIG. 2A. This result was confirmed by co-staining with a known antibody against human tau (HT7). FIG. 3A reveals the presence in a healthy human subject of antibodies against dystrophic neurites in a tissue section obtained from a patient with Alzheimer's disease. Co...
example 2
Recombinant Human Antibodies Maintain Specificity to Abnormal Structure In Vivo and Recognize Conformational Epitope of Disease-Associated Beta-Amyloid Protein in Brain Amyloid Plaques but not the Physiological Precursor or Non-Pathogenic Derivative Thereof
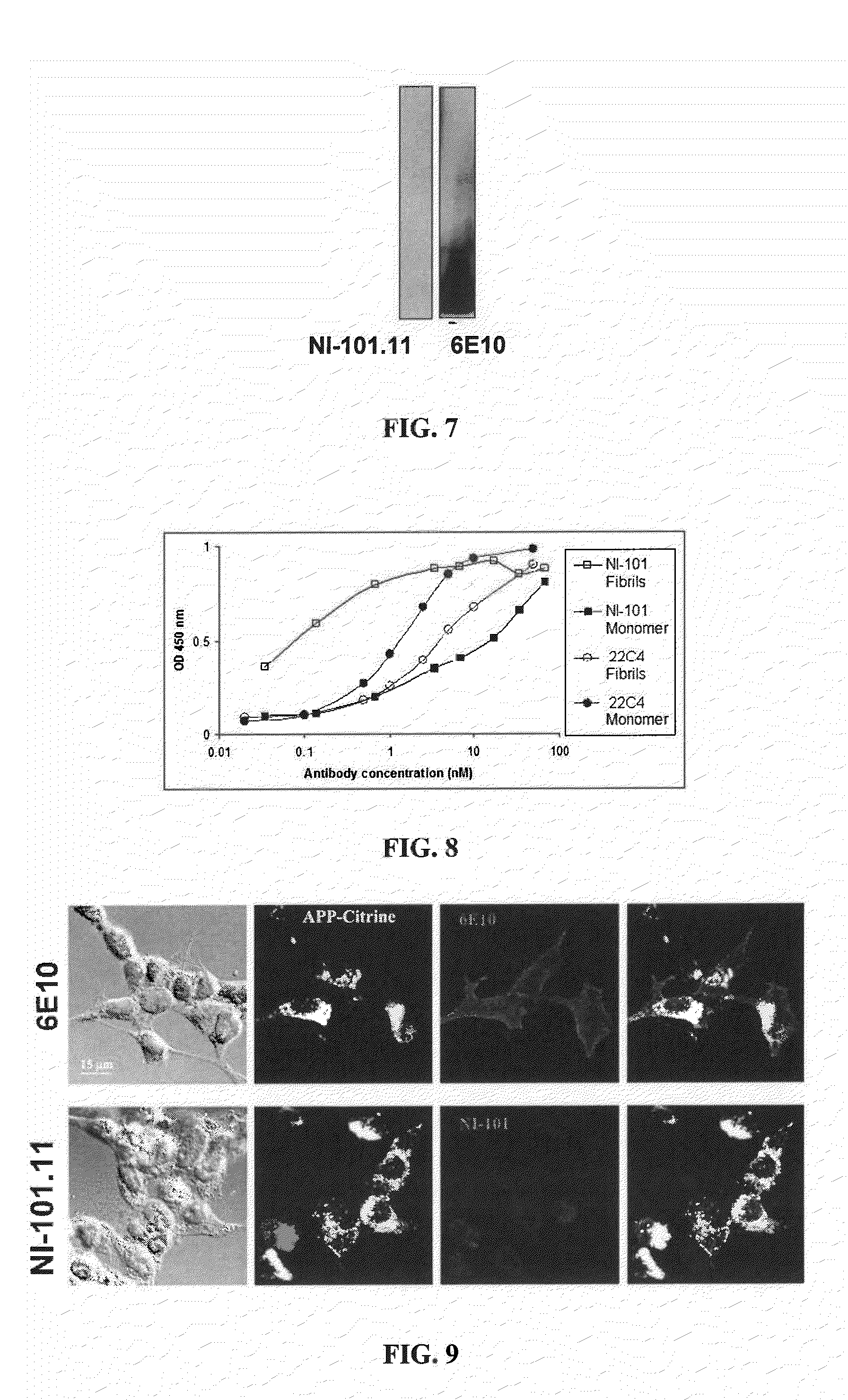
[0321]Antibodies NI-101.11, NI-101.12, NI-101.13A and NI-101.13B were obtained from clinically unusually stable Alzheimer's disease patients with a significantly reduced rate of cognitive decline. Antibody isolation and recombinant production was performed as specified in supplementary methods.
NI-101.11
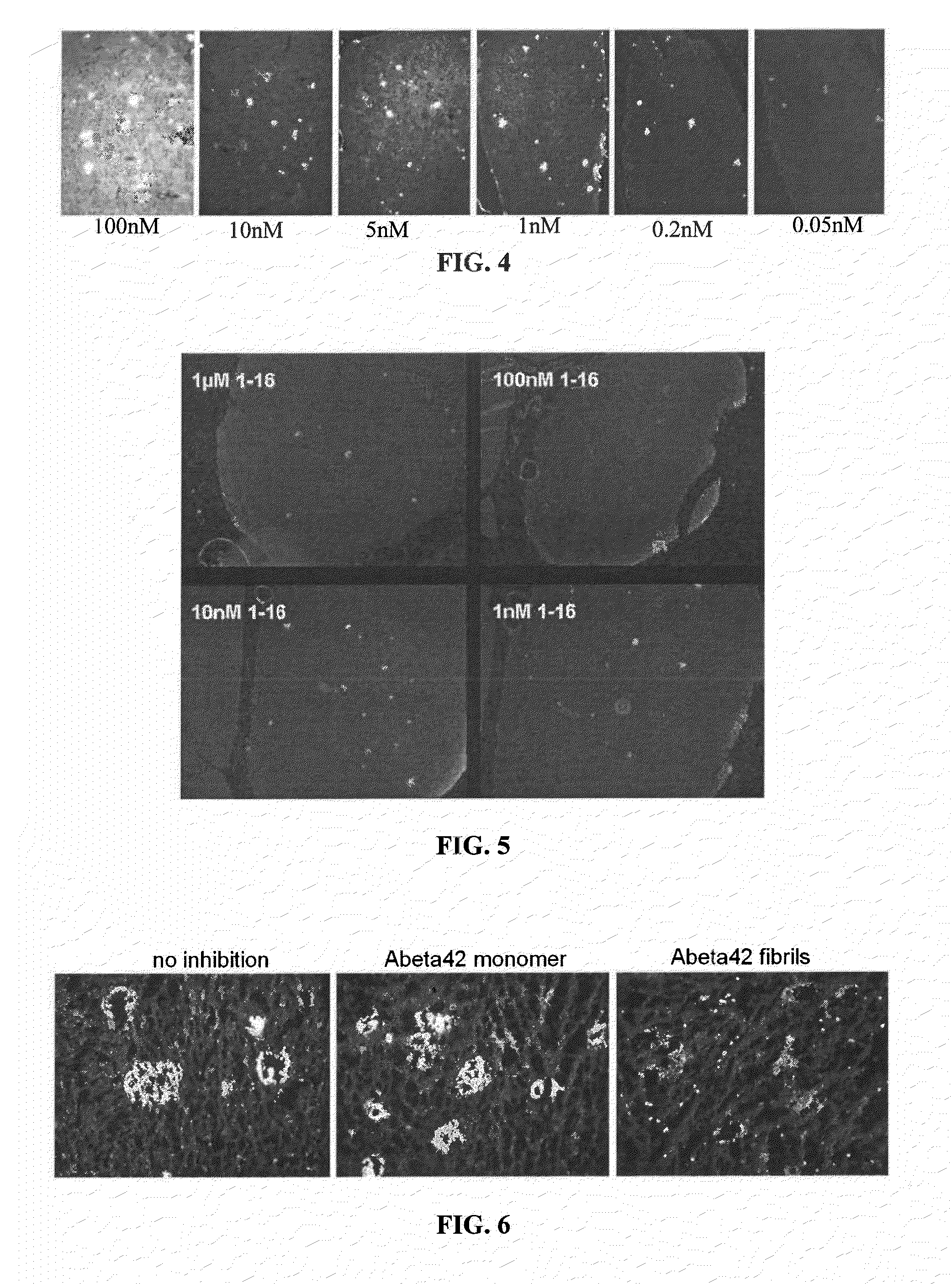
[0322]Recombinant NI-101.11 was tested for binding to brain beta-amyloid plaques (FIG. 4). Brain sections obtained from a patient with neuropathologically confirmed Alzheimer's disease were stained at the indicated concentrations. Antibody binding to beta-amyloid plaques with concentrations of 50 μM suggest high affinity binding. The binding of antibody NI-101.11 to beta-amyloid plaques at a concentration of 0.5 nM cannot be compete...
example 3
Recombinant Human Antibody Against Brain Beta-Amyloid Crosses the Blood Brain Barrier in a Transgenic Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease, and Binds to Brain Beta-Amyloid Plaques In vivo
[0331]To determine whether recombinant human NI-101.11 antibody crosses the blood brain barrier and binds to brain beta-amyloid plaques in vivo transgenic PS-1 / APPswe Alzheimer's disease model mice received two peripheral injections of 150 μg NI-101.11 at day 1 and day 3. Mice were sacrificed 24 h after the second injection and perfused with PBS. Brains were harvested and brain sections were stained with FITC-labeled antibodies against human IgG or with the mouse monoclonal Abeta antibody 6E10 followed by a FITC-labeled antibody against mouse IgG to confirm the presence of brain beta-amyloid plaques. Intense staining of amyloid plaques with anti-human IgG indicated that the recombinant human NI-101.11 antibody can cross the blood-brain barrier of transgenic mice and bind to brain beta-amyloid plaques ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| dissociation constant | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com