Method for measuring nucleotide sequence of disease associated nucleic acid molecules in sample to be detected
A nucleotide sequence and nucleic acid molecule technology, applied in the field of nucleotide sequence determination of disease-related nucleic acid molecules in samples to be tested, can solve problems such as inability to interpret mutation sites, high sequencing costs, and inability to simultaneously detect single-gene diseases.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
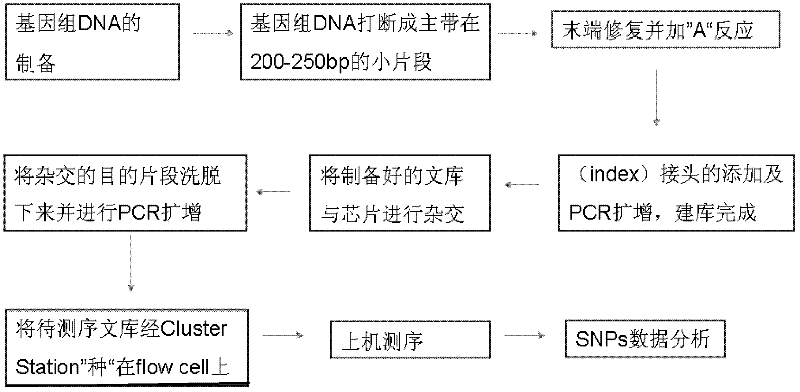
[0079] The preparation method of the library is well known to those skilled in the art, including (but not limited to) steps:
[0080] 1. A sample to be detected is provided, the sample contains an interrupted double-stranded nucleic acid fragment derived from genomic DNA, and the nucleic acid fragment has a blunt end;
[0081] 2. For the double-stranded nucleic acid fragment in the previous step, add an adapter connection sequence at the end; and through the adapter connection sequence, add an adapter at both ends of the double-stranded nucleic acid fragment, wherein the adapter has a primer binding region and a connecting complementary region, the connecting complementary region is complementary to the linking sequence of the linker; the sequences of the primer binding regions of the linkers at the 3' end and the 5' end of both sides are different.
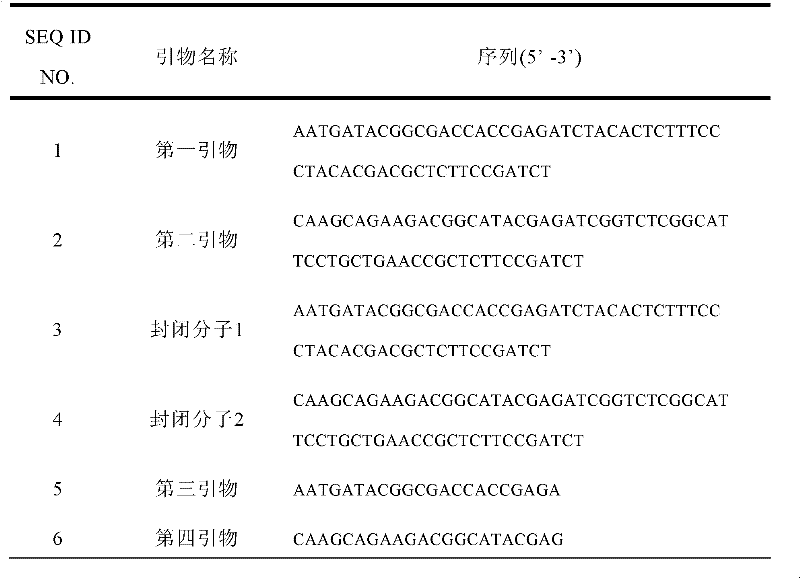
[0082] 3. Amplify the DNA double-stranded nucleic acid fragment with the adapter obtained in the previous step with the first ...
Embodiment 1
[0142] Establishment of chip hybridization platform
[0143] The probes are designed from the exon sequence and 100 bp before and after the exon of the known disease-causing gene of single gene disease, a total of more than 70,000 probes, its SEQ ID NO., chromosomal coordinates, capture position, length and the disease involved See Table 4 for the species.
[0144] Table 4
[0145]
Embodiment 2
[0147] DNA library preparation
[0148] 1. Genomic DNA acquisition
[0149] Take human peripheral blood, extract genomic DNA, and obtain 3 μg DNA.
[0150] 2. DNA Fragmentation
[0151] The extracted human genomic DNA sample is fragmented on a Covaris S2 instrument (purchased from Covaris, USA), and finally broken into a mixture of DNA double-stranded fragments with a main band of 200bp, and the fragments are purified. The purification process Adopt Ampure Beads method, carry out according to Agencourt AMPure protocol (U.S. Beckman Company).
[0152] 3. DNA fragment ligation
[0153] The DNA fragments are end-repaired to become a fragment mixture with blunt ends, and an "A" is added to the 3' end of each single strand to facilitate connection with adapters with "T". After connection, purify and purify Methods Ampure Beads were used according to the Agencourt AMPure protocol (Beckman Company, USA). After purification, excess reagents such as buffer, enzyme, ATP, etc. are r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com